🐘🤘 Hydra
Hydra is open source, column-oriented Postgres. You can query billions of rows instantly on Postgres without code changes. Parallelized analytics in minutes, not weeks.
🚀 Quick start
Try the Hydra Free Tier to create a column-oriented Postgres instance. Then connect to it with your preferred Postgres client (psql, dbeaver, etc).
Alternatively, you can run Hydra locally.
💪 Benchmarks - fastest Postgres aggregates on earth
Benchmarks were run on a c6a.4xlarge (16 vCPU, 32 GB RAM) with 500 GB of GP2 storage. Results in seconds, smaller is better.
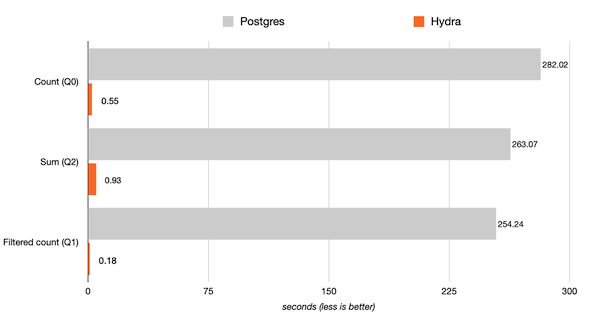
Review Clickbench for comprehensive results and the list of 42 queries tested.
This benchmark represents typical workload in the following areas: clickstream and traffic analysis, web analytics, machine-generated data, structured logs, and events data.
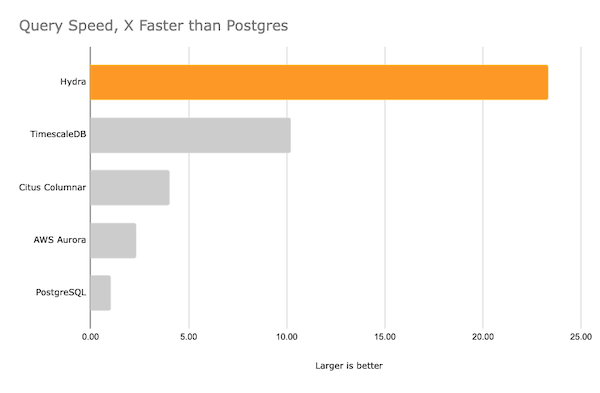
For our continuous benchmark results, see BENCHMARKS.
🙋 FAQs
View complete answers in our documentation.
Q: Why is Hydra so fast?
A: Columnar storage, query parallelization, vectorized execution, column-level caching, and tuning Postgres.
Q: How do I start using the columnar format on Postgres?
A: Data is loaded into columnar format by default. Use Postgres normally.
Q: What operations is Hydra meant for? Provide examples.
A: Aggregates (COUNT, SUM, AVG), WHERE clauses, bulk INSERTS, UPDATE, DELETE…
Q: What is columnar not meant for?
A: Frequent large updates, small transactions…
Q: What Postgres features are unsupported on columnar?
- Logical replication.
- Columnar tables don’t typically use indexes, only supporting btree and hash indexes, and their associated constraints.
Q: Is Hydra a fork?
A: Hydra is a Postgres extension, not a fork. Hydra makes use of tableam (table access method API), which was added in Postgres 12 released in 2019.
🤝 Community and Status
- [x] Alpha: Limited to select design partners
- [x] Public Alpha: available for use, but with noted frictions
- [x] Hydra 1.0 beta: Stable for non-enterprise use cases
- [x] Hydra 1.0 Release: Generally Available (GA) and ready for production use
:technologist: Developer resources
- CHANGELOG for details of recent changes
- GitHub Issues for bugs and missing features
- Discord discussion with the Community and Hydra team
- Docs for Hydra features and warehouse ops
💻 Run locally
The Hydra Docker image is a drop-in replacement for postgres Docker image.
You can try out Hydra locally using docker-compose.
git clone https://github.com/hydradatabase/hydra && cd hydra
cp .env.example .env
docker compose up
psql postgres://postgres:hydra@127.0.0.1:5432📝 License
Hydra is only possible by building on the shoulders of giants.
The code in this repo is licensed under:
- AGPL 3.0 for Hydra Columnar
- All other code is Apache 2.0
The docker image is built on the Postgres docker image, which contains a large number of open source projects, including:
- Postgres - the Postgres license
- Debian or Alpine Linux image, depending on the image used
- Hydra includes the following additional software in the image:
- multicorn - BSD license
- mysql_fdw - MIT-style license
- parquet_s3_fdw - MIT-style license
- pgsql-http - MIT license
As for any pre-built image usage, it is the image user's responsibility to ensure that any use of this image complies with any relevant licenses for all software contained within.
