With support for React v18 and React Fast Refresh
🚀 This is your boilerplate project for developing React apps inside Google Sheets, Docs, Forms and Slides projects. It's perfect for personal projects and for publishing complex add-ons in the Google Workspace Marketplace.
Apps script process deployment and versioning process
This build env deploys to sdss-gas project in the browser based apps script console under alexander.liukkonen@gmail.com
After the release version is ready and tested, it is moved over to Simulate apps script project with a simple copy-paste.
The deployments and production versioning is then handled under the separate Simulate project directory.
Updating an already live published apps script add-on
Guide from current docs: https://developers.google.com/workspace/add-ons/how-tos/update-published-add-on
Increase Node heap size
export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=8192"
📝 Table of Contents
🔎 About
Google Apps Script is Google's Javascript-based development platform for building applications and add-ons for Google Sheets, Docs, Forms and other Google Apps.
You can add custom user interfaces inside dialog windows, but the platform is designed for simple HTML pages built with templates and jQuery.
However, using this repo, it's easy to run React apps inside these dialogs, and build everything from small projects to advanced add-ons that can be published on the G Suite Marketplace.

This repo is a boilerplate project that uses React and the same development tools that you use for building traditional websites, all inside Google Apps Script projects.
See below how to get started!
🚜 Install
These instructions will get you set up with a copy of the React project code on your local machine. It will also get you logged in to clasp so you can manage script projects from the command line.
See deploy for notes on how to deploy the project and see it live in a Google Spreadsheet.
Prerequisites
-
Make sure you're running at least Node.js v14 and
npmv6. -
You'll need to enable the Google Apps Script API. You can do that by visiting script.google.com/home/usersettings.
-
To use live reload while developing, you'll need to serve your files locally using HTTPS. See local development below for how to set up your local environment.
🏁 Getting started
1. First, let's clone the repo and install the dependencies.
git clone https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script.git
cd React-Google-Apps-Script
npm install
2. Next, we'll need to log in to clasp, which lets us manage our Google Apps Script projects locally.
npm run login
3. Now let's run the setup script to create a New spreadsheet and script project from the command line.
npm run setup
Alternatively, you can use an existing Google Spreadsheet and Script file instead of creating a new one.
See instructions here for using an existing project.
You will need to update the `.clasp.json` file in the root of this project with the following three key/value pairs (see .clasp.json.SAMPLE for reference): ```json { "scriptId": "1PY037hPcy................................................", "parentId": ["1Df30......................................."], "rootDir": "./dist" } ``` - `scriptId`: Your existing script project's `scriptId`. You can find it by opening your spreadsheet, selecting **Tools > Script Editor** from the menubar, then **File > Project properties**, and it will be listed as "Script ID". - `parentId`: An array with a single string, the ID of the parent file (spreadsheet, doc, etc.) that the script project is bound to. You can get this ID from the url, where the format is usually `https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/{id}/edit`. This allows you to run `npm run open` and open your file directly from the command line. - `rootDir`: This should always be `"./dist"`, i.e. the local build folder that is used to store project files.Next, let's deploy the app so we can see it live in Google Spreadsheets.
🚀 Deploy
Run the deploy command. You may be prompted to update your manifest file. Type 'yes'.
npm run deployThe deploy command will build all necessary files using production settings, including all server code (Google Apps Script code), client code (React bundle), and config files. All bundled files will be outputted to the dist/ folder, then pushed to the Google Apps Script project.
Now open Google Sheets and navigate to your new spreadsheet (e.g. the file "My React Project"). You can also run npm run open. Make sure to refresh the page if you already had it open. You will now see a new menu item appear containing your app!

🎈 Local Development
We can develop our client-side React apps locally, and see our changes directly inside our Google Spreadsheet dialog window.

There are two steps to getting started: installing a certificate (first time only), and running the start command.
-
Generating a certificate for local development
Install the mkcert package:
# mac: brew install mkcert # windows: choco install mkcertThen run the mkcert install script:
mkcert -installCreate the certs in your repo:
npm run setup:https -
Now you're ready to start:
npm run start
The start command will create and deploy a development build, and serve your local files.

After running the start command, navigate to your spreadsheet and open one of the menu items. It should now be serving your local files. When you make and save changes to your React app, your app will reload instantly within the Google Spreadsheet, and have access to any server-side functions!

Support for Fast Refresh now means that only modified components are refreshed when files are changed, and state is not lost.
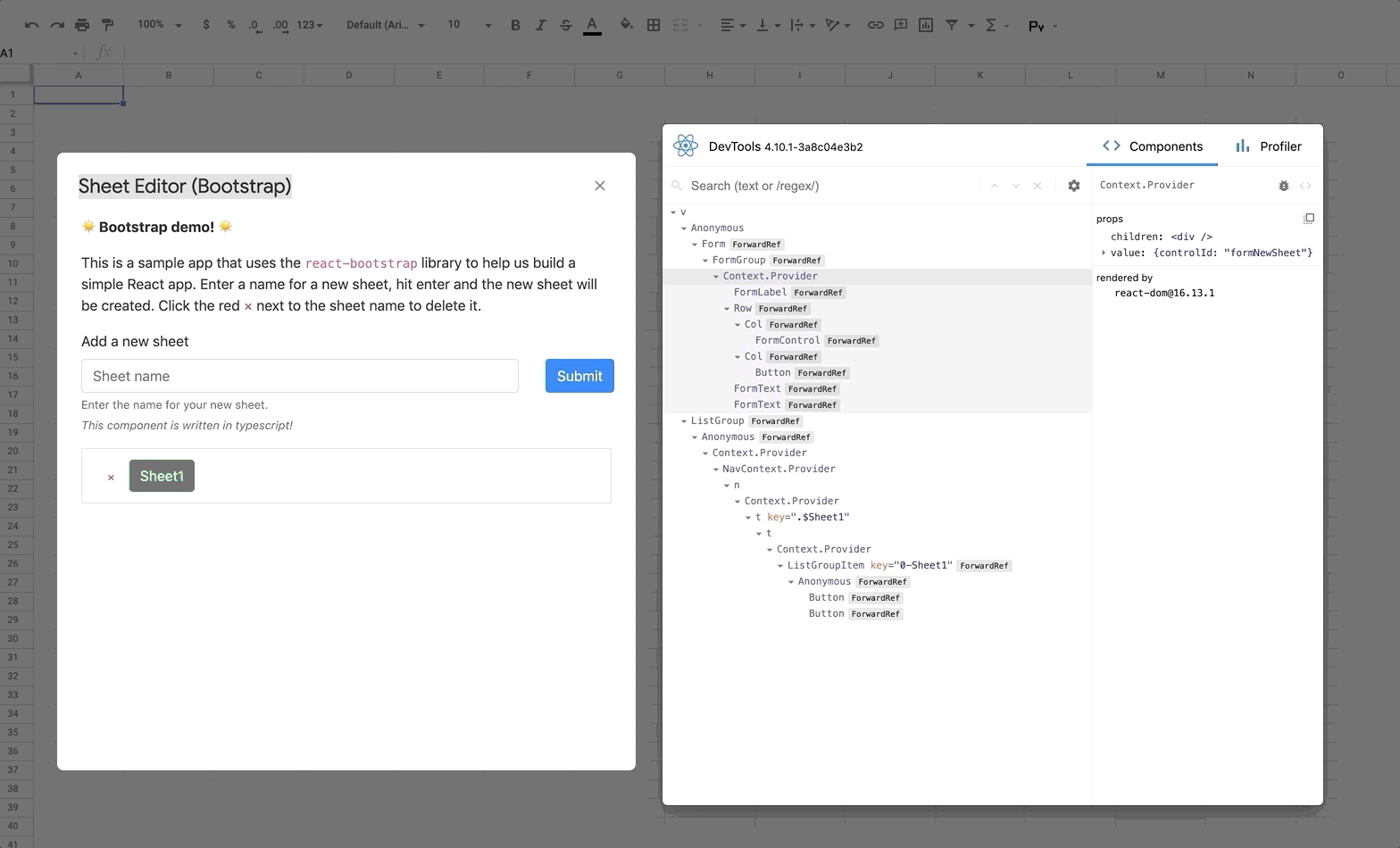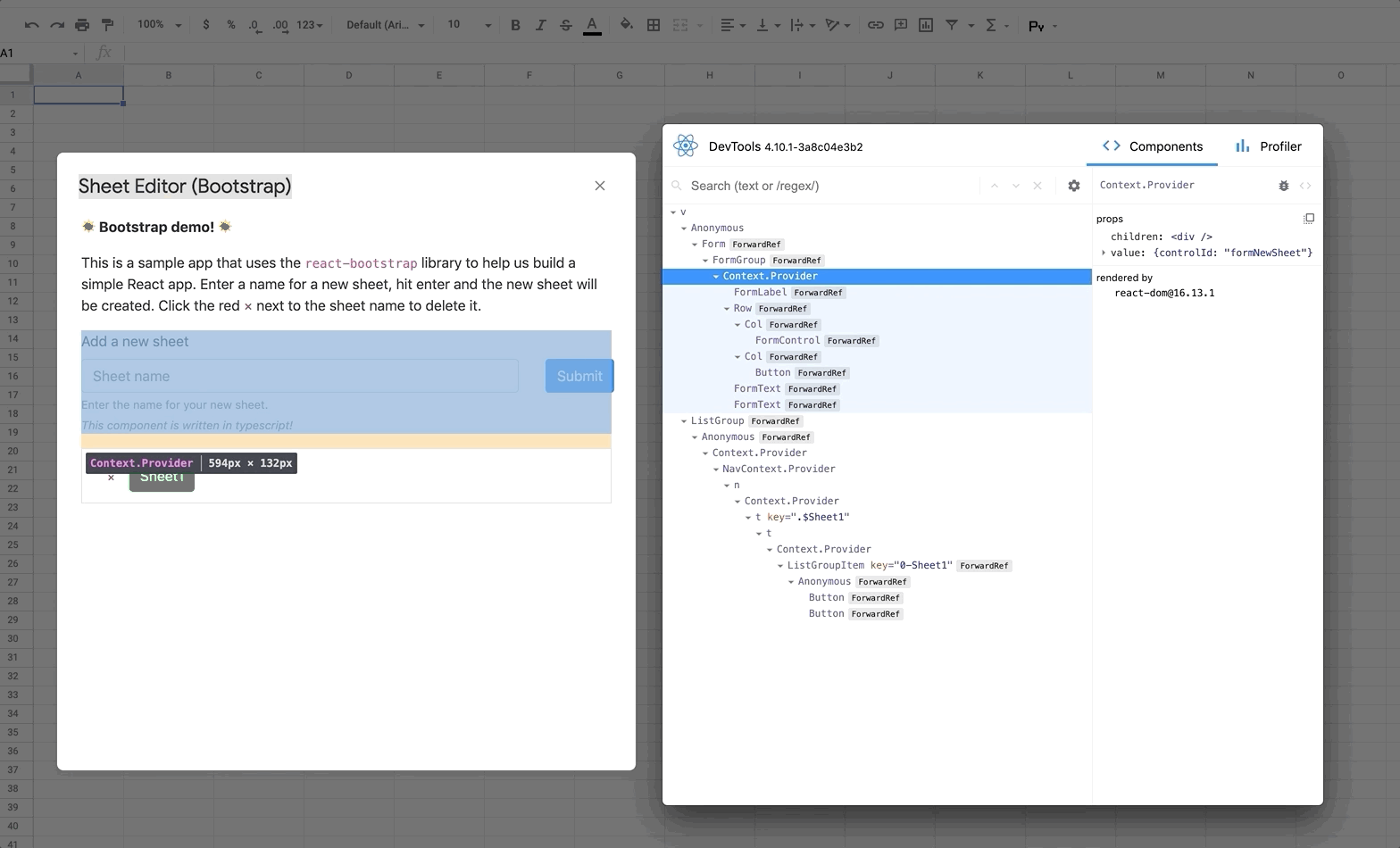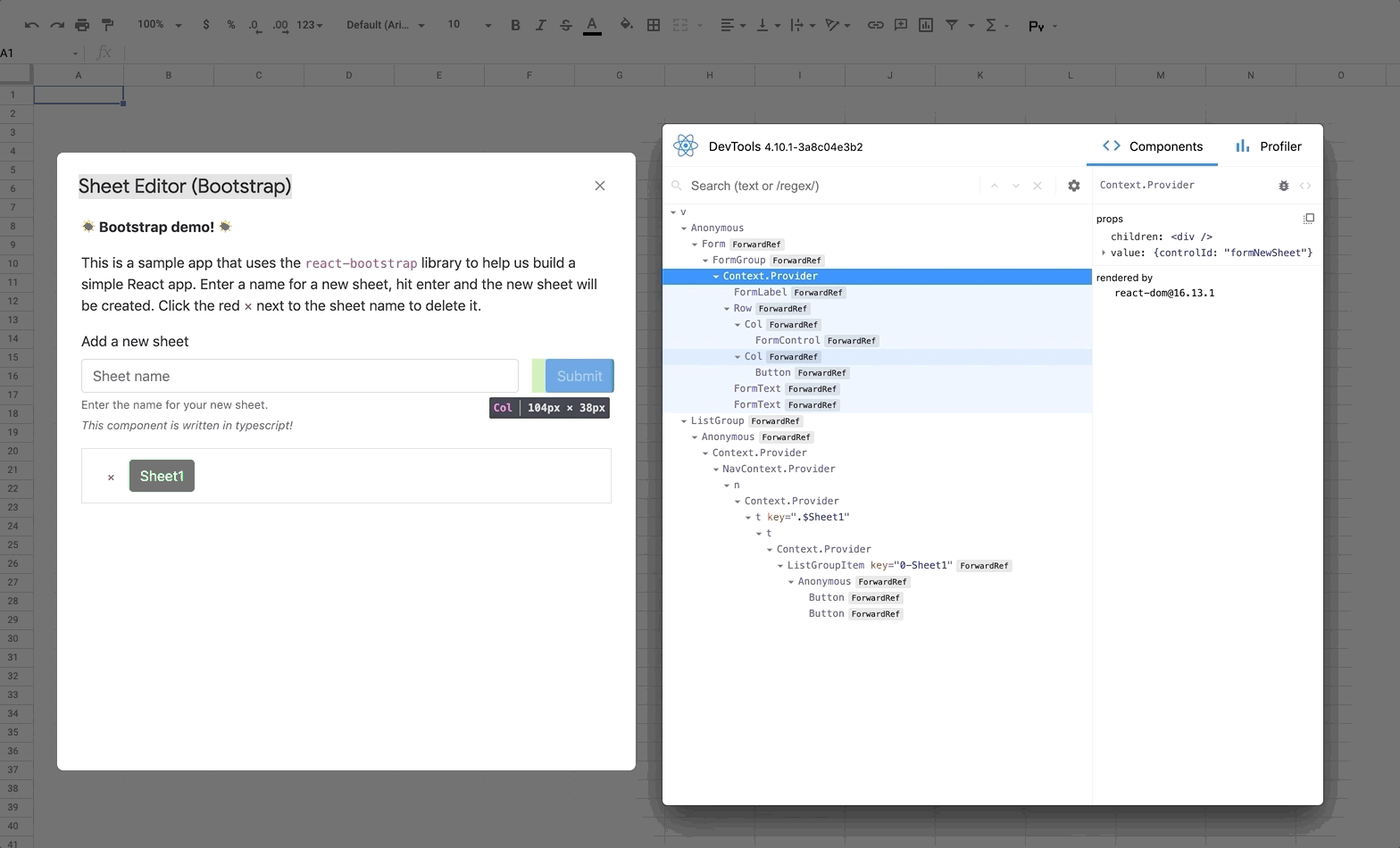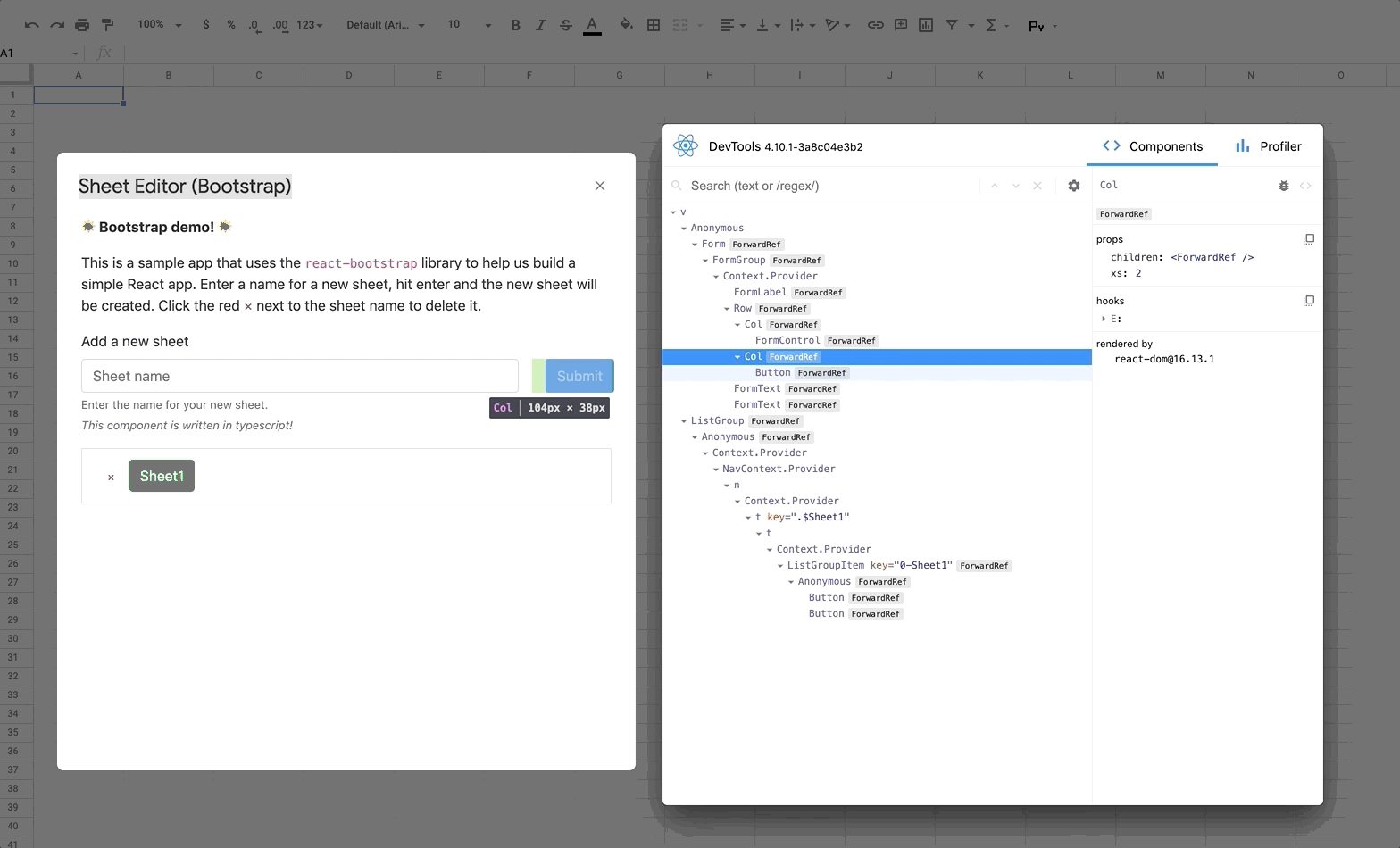
🔍 Using React DevTools
React DevTools is a tool that lets you inspect the React component hierarchies during development.
Instructions for installing React DevTools
You will need to use the "standalone" version of React DevTools since our React App is running in an iframe ([more details here](https://github.com/facebook/react/tree/master/packages/react-devtools#usage-with-react-dom)). 1. In your repo install the React DevTools package as a dev dependency: ```bash npm install -D react-devtools ``` 2. In a new terminal window run `npx react-devtools` to launch the DevTools standalone app. 3. Add `` to the top of your `` in your React app, e.g. in the [index.html](https://github.com/enuchi/React-Google-Apps-Script/blob/e73e51e56e99903885ef8dd5525986f99038d8bf/src/client/dialog-demo-bootstrap/index.html) file in the sample Bootstrap app. 4. Deploy your app (`npm run deploy:dev`) and you should see DevTools tool running and displaying your app hierarchy.
 5. Don't forget to remove the ` Githubissues.
5. Don't forget to remove the ` Githubissues.
