Grafana Shift Selector Plugin
[
The shift selector allows you to adjust the time range of your grafana dashboard to one specific shift or a range of shifts. On this page we'll show you how it works and how you can adjust the displayed shifts to a specific season or production line.

Realtime Shift Track feature (*new feature**)
With this new feature, you can enable the shift selector to track shifts automatically based on the local time. So you don't need to change shifts manually. To use this new feature, you need to enable it through the panel options.
- Enable the
"Real-time shift auto-select" - Determine a
refresh interval(these should be according to the time interval pattern of Grafana. Eg. for 5 seconds ->5s, 1 hour ->1h) - Optionally, if you have multiple groups, determine a group to auto-select from. It uses the
group_uuid
Be aware that enabling real-time will hide the date and range selectors

New panel options
- Data Mapper replaces the variables
var_query_map - Simple quick start flow (without need the need of variables)
- Icon mapper added to match the icons
- Customize day selection label. Useful if you like to localize or specify a different label.
- Display options for the shift buttons.
- With this new option you are able to show the buttons in;
- only text
- only icons
- or with icons and text, which is the default option
- Change the range
"Start-End","Start"and,"End"labels.
Quick Start (static shifts)
With this plugin you are able to choose between dynamic (from a datasource) and static.
To start quickly, set shifts (groups) in the Data Mapper panel:
- Set
Shifts from a data source to false - Copy-paste the json shown below as an example
{
"static": {
"shifts": [
{
"group": "Group 1",
"group_uuid": "group_uuid_1",
"uuid": "shift_uuid_1",
"label": "Morning Custom",
"startTime": "06:00:00",
"endTime": "14:00:00",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": "Group 2",
"group_uuid": "group_uuid_2",
"uuid": "shift_uuid_2",
"label": "Afternoon Custom",
"startTime": "14:00:00",
"endTime": "22:00:00",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": "Group 2",
"group_uuid": "group_uuid_2",
"uuid": "shift_uuid_3",
"label": "Night Custom",
"startTime": "22:00:00",
"endTime": "06:00:00",
"order": 2
}
]
}
}Now you are able to see the shifts in two groups. Group 1 and Group 2. This could for example be summer or winter time.
In order to set you shifts from a datasource please continue to read.
Shifts from datasources
Functionalities
The options you can choose are: (from left to right)
- Date selection: select a date for which you want to set a shift.
- Select which time you want to change. The dots at the end of the line shows whether you will change the start time, end time or both:
- Shift (two dots): change the time selection of the dashboard to the selected shift.
This will set both start and end time of your dashboard.
Both start and end time of the shift are displayed in the button.

- Start time (dot on left): only change the start time of the time selection to the start time of the selected shift.
The times displayed are the start times of the shifts.

- End time (dot on right): only change the end time of the time selection to the end time of the selected shift.
The times displayed are the end times of the shifts.

Multiple shift groups
The shift selector can also handle multiple shift groups, to distinguish between them, the names of these groups are added in front of the buttons.
However, if there is only one shift group available, that name will disappear, as in the example above.

Changes to time selection in Grafana
When you click a button, the selected time will change to the selected shift time. In this example we have chosen two seasonal shift groups: one for the summer and one for the winter.
| Group name | Shift name | Shift order | Start time | End time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | Morning | 1 | 8:00 | 14:00 |
| Summer | Afternoon | 2 | 14:00 | 22:00 |
| Summer | Night | 3 | 22:00 | 8:00 |
| Winter | Night | 1 | 22:30 | 10:30 |
| Winter | Day | 2 | 10:30 | 22:30 |
In this example we have selected the day May 17th 2021 which leads to the following shift times:
| Group name | Shift name | Updated start time | Updated end time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | 1. Morning | May 17th 8:00 | May 17th 14:00 |
| Summer | 2. Afternoon | May 17th 14:00 | May 17th 22:00 |
| Summer | 3. Night | May 17th 22:00 | May 18th 8:00 |
| Winter | 1. Night | May 16th 22:30 | May 17th 10:30 |
| Winter | 2. Day | May 17th 10:30 | May 17th 22:30 |
The dates in bold are the dates that belong to a shift that passes midnight. The dates are updated accordingly.
Warning: the shift selector only works well when your computer is in the right timezone. Changing the timezone in Grafana does not affect the behavior of the shift selector.
How to add it?
In order to add the shift selector, you'll have to do two things:
- Create a ShiftSelector panel
-
Create a hidden variable with the names of the shifts you want to display. To do so, go to 'dashboard settings' -> 'variables' -> 'add new variable'. Then use the following settings to create the variable:
-
Database
- Name:
var_shifts_dataModel - Type: Data source
- Hide: Variable
- Data source
- Type: Database type
- Instance name filter: Name of your data source containing the shifts data
This will result in:
- The data source will be listed in the 'Preview of values' above the submit button.
- Name:
-
Shifts data model mapper
- Name:
var_query_map - Type: Constant
- Constant options
- Value: here you can paste the mapper object. You can find an example in the
var_query_map.example.jsfile. You can remove thestaticvalues because you will be fetching them from your datasource.- Options JSON object
- project
- shift_groups: contains the
shift_groupstable fields. You can change thename,uuid,site_uuidfields according to your database scheme. - shifts: contains the
shiftstable fields. Change theuuid,start_time,end_time,order,group_uuidaccording to your databse scheme.
- shift_groups: contains the
- lookup
- shifts: the name of your shifts table
- shift_groups: the name of your shift groups table
- schema
- shifts (optional): the namespace of your shifts table database
- shift_groups (optional): the namespace of your shift groups table database
- values
- site_uuid (optional): in case you want to select a specific site
- Name:
-
Options
- Name:
var_shifts_options - Type: Query
- Hide: Variable
- Data source: {{Your Database containing the shifts and shift-groups}}
- Refresh: On Dashboard Load
- Query: a query to select the shifts associated with your factory. You can also expand the query by filtering on for instance shift group or production line (examples).
SELECT S.name AS '__text', S.uuid AS '__value' FROM shifts SThis will result in:
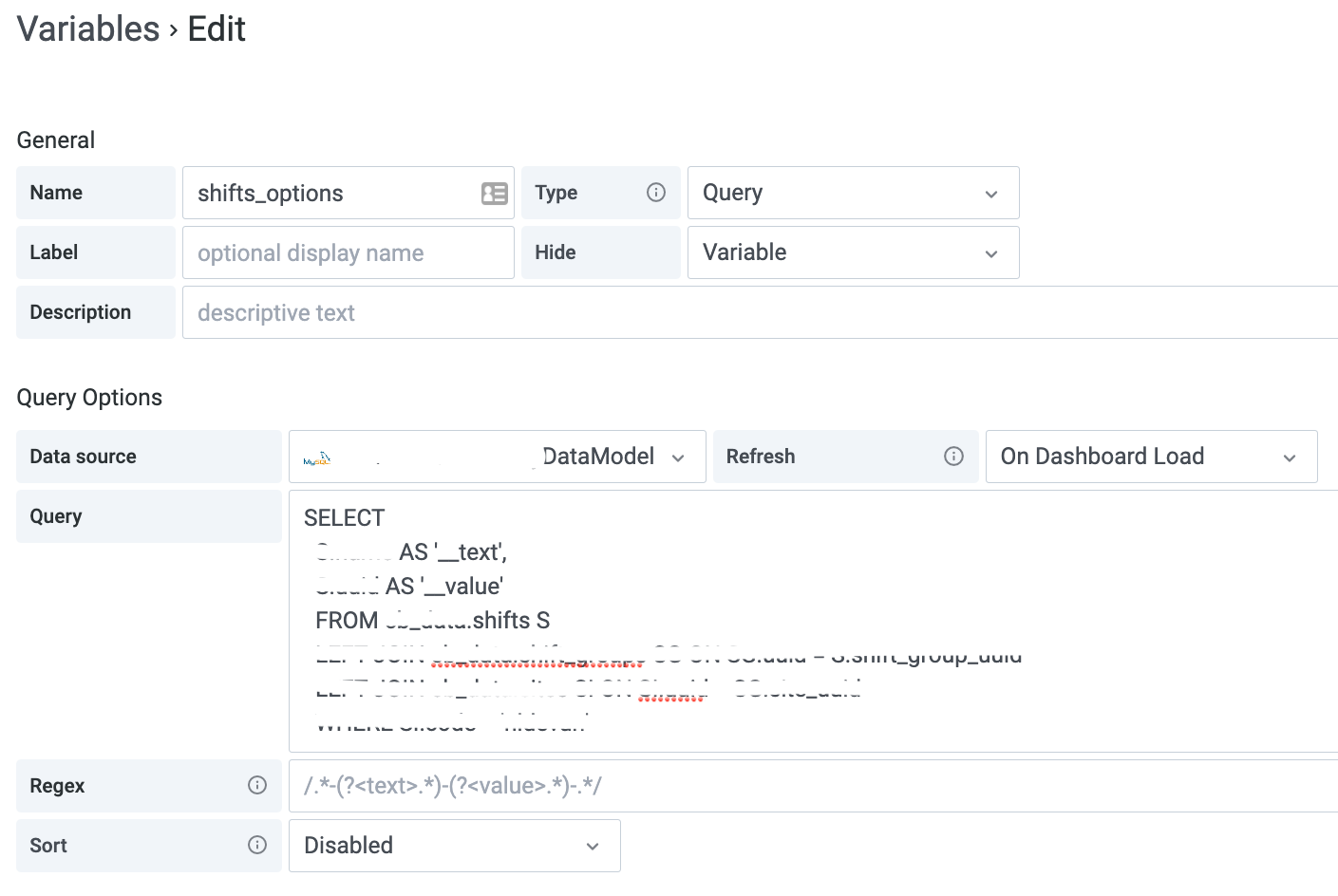
- Name:
-
*Note that when you have multiple shift groups with shifts with the same name, the names of the shifts should be unique.
If both shift groups have a shift named 'morning', it is easiest to make the name of the shift unique by adding the shift order or the shift group name to the AS '__text' in the query, two examples:
CONCAT(S.shift_order, '. ', S.name) AS '__text', -- to add the number of the order of the shift
CONCAT(SG.name, ' - ', S.name) AS '__text', -- to add the shift group nameDatabase: example
sites
CREATE TABLE `sites` (
`uuid` varchar(22) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`uuid`),
UNIQUE KEY `name_UNIQUE` (`name`),
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;shift_groups
CREATE TABLE `shift_groups` (
`uuid` varchar(22) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`site_uuid` varchar(22) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`uuid`),
UNIQUE KEY `site_uuid_name_UNIQUE` (`site_uuid`,`name`),
KEY `shift_group_site_uuid_idx` (`site_uuid`),
CONSTRAINT `shift_group_site_uuid` FOREIGN KEY (`site_uuid`) REFERENCES `sites` (`uuid`) ON DELETE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;shifts
CREATE TABLE `shifts` (
`uuid` varchar(22) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Name or description of shift',
`shift_order` int NOT NULL COMMENT 'Order of the shifts on a operational day for the shift_group_uuid as referenced by shift_group_uuid',
`start_time` time NOT NULL COMMENT 'The time that the shift starts (local timezone)',
`end_time` time NOT NULL COMMENT 'The time that the shift ends (local timezone)',
`shift_group_uuid` varchar(22) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Uuid of the shift group',
PRIMARY KEY (`uuid`),
UNIQUE KEY `name_group_uuid_UNIQUE` (`shift_group_uuid`,`name`),
UNIQUE KEY `order_group_uuid_UNIQUE` (`shift_group_uuid`,`shift_order`),
UNIQUE KEY `start_time_group_uuid_UNIQUE` (`shift_group_uuid`,`start_time`),
UNIQUE KEY `end_time_group_uuid_UNIQUE` (`shift_group_uuid`,`end_time`),
KEY `shifts_group_uuid_idx` (`shift_group_uuid`),
CONSTRAINT `shifts_shift_group_uuid_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`shift_group_uuid`) REFERENCES `shift_groups` (`uuid`) ON DELETE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;Appendix: filtering queries
If you want to filter the shifts that are displayed to for instance a certain shift group or belonging to a production line, you can add extra variables to your dashboard and implement them in the variable _shiftsoptions. Two examples are described below, of which the production line example has been implemented in a couple of global dashboards.
Filter on production line
Create a variable to select the production line (or work center):
-
Variable name: work center
-
Query: (update
example01to your factory code)SELECT WC.name AS '__text', WC.uuid AS '__value' FROM work_centers WC LEFT JOIN sites SI ON SI.uuid = WC.site_uuid WHERE SI.code = 'example01' -
Update the query for the _shiftsoptions to:
SELECT S.name AS '__text', S.uuid AS '__value' FROM shifts S LEFT JOIN shift_groups SG ON SG.uuid = S.shift_group_uuid LEFT JOIN work_center_has_shift_groups WCHSG ON WCHSG.work_center_uuid = ${work_center}
Filter on shift group
Create a variable to select the shift group:
-
Variable name: _shiftsgroup
-
Query: (update
example01to your factory site code)SELECT SG.name AS '__text', SG.uuid AS '__value' FROM shift_groups SG LEFT JOIN sites SI ON SI.uuid = SG.site_uuid WHERE SI.code = 'example01' -
Update the query for the _shiftsoptions to:
SELECT S.name AS '__text', S.uuid AS '__value' FROM shifts S LEFT JOIN shift_groups SG ON SG.uuid = S.shift_group_uuid WHERE SG.uuid = ${shift_group}