paperscraper
paperscraper is a python package for scraping publication metadata or full PDF files from
PubMed or preprint servers such as arXiv, medRxiv, bioRxiv and chemRxiv.
It provides a streamlined interface to scrape metadata, allows to retrieve citation counts
from Google Scholar, impact factors from journals and comes with simple postprocessing functions
and plotting routines for meta-analysis.
Getting started
pip install paperscraperThis is enough to query PubMed, arXiv or Google Scholar.
Download X-rxiv Dumps
However, to scrape publication data from the preprint servers biorxiv, medrxiv and chemrxiv, the setup is different. The entire dump is downloaded and stored in the server_dumps folder in a .jsonl format (one paper per line).
from paperscraper.get_dumps import biorxiv, medrxiv, chemrxiv
medrxiv() # Takes ~30min and should result in ~35 MB file
biorxiv() # Takes ~1h and should result in ~350 MB file
chemrxiv() # Takes ~45min and should result in ~20 MB fileNOTE: Once the dumps are stored, please make sure to restart the python interpreter so that the changes take effect.
NOTE: If you experience API connection issues (ConnectionError), since v0.2.12 there are automatic retries which you can even control and raise from the default of 10, as in biorxiv(max_retries=20).
Since v0.2.5 paperscraper also allows to scrape {med/bio/chem}rxiv for specific dates.
medrxiv(begin_date="2023-04-01", end_date="2023-04-08")But watch out. The resulting .jsonl file will be labelled according to the current date and all your subsequent searches will be based on this file only. If you use this option you might want to keep an eye on the source files (paperscraper/server_dumps/*jsonl) to ensure they contain the paper metadata for all papers you're interested in.
Examples
paperscraper is build on top of the packages arxiv, pymed, and scholarly.
Publication keyword search
Consider you want to perform a publication keyword search with the query:
COVID-19 AND Artificial Intelligence AND Medical Imaging.
- Scrape papers from PubMed:
from paperscraper.pubmed import get_and_dump_pubmed_papers
covid19 = ['COVID-19', 'SARS-CoV-2']
ai = ['Artificial intelligence', 'Deep learning', 'Machine learning']
mi = ['Medical imaging']
query = [covid19, ai, mi]
get_and_dump_pubmed_papers(query, output_filepath='covid19_ai_imaging.jsonl')- Scrape papers from arXiv:
from paperscraper.arxiv import get_and_dump_arxiv_papers
get_and_dump_arxiv_papers(query, output_filepath='covid19_ai_imaging.jsonl')- Scrape papers from bioRiv, medRxiv or chemRxiv:
from paperscraper.xrxiv.xrxiv_query import XRXivQuery
querier = XRXivQuery('server_dumps/chemrxiv_2020-11-10.jsonl')
querier.search_keywords(query, output_filepath='covid19_ai_imaging.jsonl')You can also use dump_queries to iterate over a bunch of queries for all available databases.
from paperscraper import dump_queries
queries = [[covid19, ai, mi], [covid19, ai], [ai]]
dump_queries(queries, '.')Or use the harmonized interface of QUERY_FN_DICT to query multiple databases of your choice:
from paperscraper.load_dumps import QUERY_FN_DICT
print(QUERY_FN_DICT.keys())
QUERY_FN_DICT['biorxiv'](query, output_filepath='biorxiv_covid_ai_imaging.jsonl')
QUERY_FN_DICT['medrxiv'](query, output_filepath='medrxiv_covid_ai_imaging.jsonl')- Scrape papers from Google Scholar:
Thanks to scholarly, there is an endpoint for Google Scholar too. It does not understand Boolean expressions like the others, but should be used just like the Google Scholar search fields.
from paperscraper.scholar import get_and_dump_scholar_papers
topic = 'Machine Learning'
get_and_dump_scholar_papers(topic)Scrape PDFs
paperscraper also allows you to download the PDF files.
from paperscraper.pdf import save_pdf
paper_data = {'doi': "10.48550/arXiv.2207.03928"}
save_pdf(paper_data, filepath='gt4sd_paper.pdf')If you want to batch download all PDFs for your previous metadata search, use the wrapper. Here we scrape the PDFs for the metadata obtained in the previous example.
from paperscraper.pdf import save_pdf_from_dump
# Save PDFs in current folder and name the files by their DOI
save_pdf_from_dump('medrxiv_covid_ai_imaging.jsonl', pdf_path='.', key_to_save='doi')NOTE: This works robustly for preprint servers, but if you use it on a PubMed dump, dont expect to obtain all PDFs. Many publishers detect and block scraping and many publications are simply behind paywalls.
Citation search
A plus of the Scholar endpoint is that the number of citations of a paper can be fetched:
from paperscraper.scholar import get_citations_from_title
title = 'Über formal unentscheidbare Sätze der Principia Mathematica und verwandter Systeme I.'
get_citations_from_title(title)NOTE: The scholar endpoint does not require authentication but since it regularly prompts with captchas, it's difficult to apply large scale.
Journal impact factor
You can also retrieve the impact factor for all journals:
>>>from paperscraper.impact import Impactor
>>>i = Impactor()
>>>i.search("Nat Comms", threshold=85, sort_by='impact')
[
{'journal': 'Nature Communications', 'factor': 17.694, 'score': 94},
{'journal': 'Natural Computing', 'factor': 1.504, 'score': 88}
]This performs a fuzzy search with a threshold of 85. threshold defaults to 100 in which case an exact search
is performed. You can also search by journal abbreviation, E-ISSN or NLM ID.
i.search("Nat Rev Earth Environ") # [{'journal': 'Nature Reviews Earth & Environment', 'factor': 37.214, 'score': 100}]
i.search("101771060") # [{'journal': 'Nature Reviews Earth & Environment', 'factor': 37.214, 'score': 100}]
i.search('2662-138X') # [{'journal': 'Nature Reviews Earth & Environment', 'factor': 37.214, 'score': 100}]
# Filter results by impact factor
i.search("Neural network", threshold=85, min_impact=1.5, max_impact=20)
# [
# {'journal': 'IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems', 'factor': 14.255, 'score': 93},
# {'journal': 'NEURAL NETWORKS', 'factor': 9.657, 'score': 91},
# {'journal': 'WORK-A Journal of Prevention Assessment & Rehabilitation', 'factor': 1.803, 'score': 86},
# {'journal': 'NETWORK-COMPUTATION IN NEURAL SYSTEMS', 'factor': 1.5, 'score': 92}
# ]
# Show all fields
i.search("quantum information", threshold=90, return_all=True)
# [
# {'factor': 10.758, 'jcr': 'Q1', 'journal_abbr': 'npj Quantum Inf', 'eissn': '2056-6387', 'journal': 'npj Quantum Information', 'nlm_id': '101722857', 'issn': '', 'score': 92},
# {'factor': 1.577, 'jcr': 'Q3', 'journal_abbr': 'Nation', 'eissn': '0027-8378', 'journal': 'NATION', 'nlm_id': '9877123', 'issn': '0027-8378', 'score': 91}
# ]Plotting
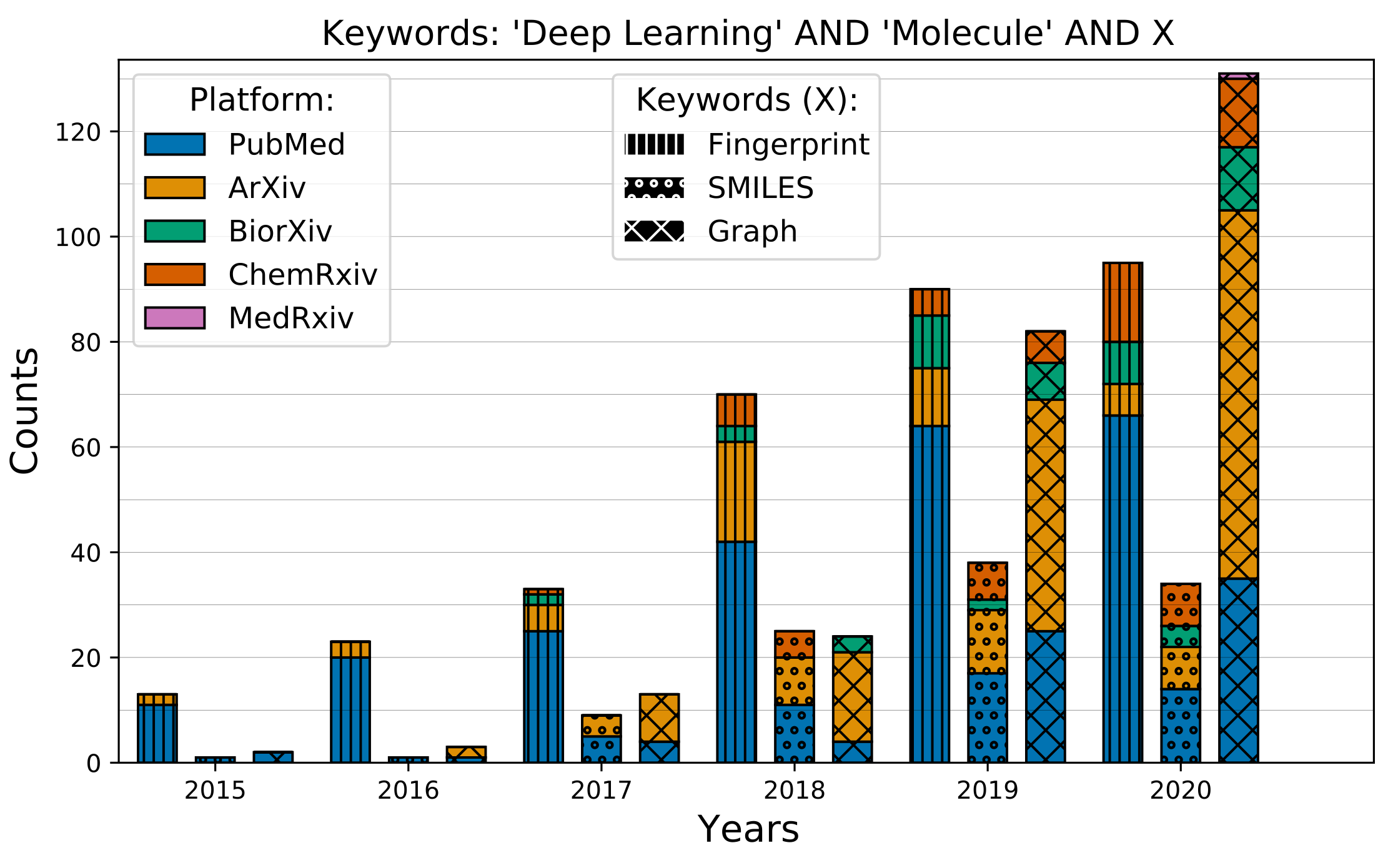
When multiple query searches are performed, two types of plots can be generated automatically: Venn diagrams and bar plots.
Barplots
Compare the temporal evolution of different queries across different servers.
from paperscraper import QUERY_FN_DICT
from paperscraper.postprocessing import aggregate_paper
from paperscraper.utils import get_filename_from_query, load_jsonl
# Define search terms and their synonyms
ml = ['Deep learning', 'Neural Network', 'Machine learning']
mol = ['molecule', 'molecular', 'drug', 'ligand', 'compound']
gnn = ['gcn', 'gnn', 'graph neural', 'graph convolutional', 'molecular graph']
smiles = ['SMILES', 'Simplified molecular']
fp = ['fingerprint', 'molecular fingerprint', 'fingerprints']
# Define queries
queries = [[ml, mol, smiles], [ml, mol, fp], [ml, mol, gnn]]
root = '../keyword_dumps'
data_dict = dict()
for query in queries:
filename = get_filename_from_query(query)
data_dict[filename] = dict()
for db,_ in QUERY_FN_DICT.items():
# Assuming the keyword search has been performed already
data = load_jsonl(os.path.join(root, db, filename))
# Unstructured matches are aggregated into 6 bins, 1 per year
# from 2015 to 2020. Sanity check is performed by having
# `filtering=True`, removing papers that don't contain all of
# the keywords in query.
data_dict[filename][db], filtered = aggregate_paper(
data, 2015, bins_per_year=1, filtering=True,
filter_keys=query, return_filtered=True
)
# Plotting is now very simple
from paperscraper.plotting import plot_comparison
data_keys = [
'deeplearning_molecule_fingerprint.jsonl',
'deeplearning_molecule_smiles.jsonl',
'deeplearning_molecule_gcn.jsonl'
]
plot_comparison(
data_dict,
data_keys,
title_text="'Deep Learning' AND 'Molecule' AND X",
keyword_text=['Fingerprint', 'SMILES', 'Graph'],
figpath='mol_representation'
)
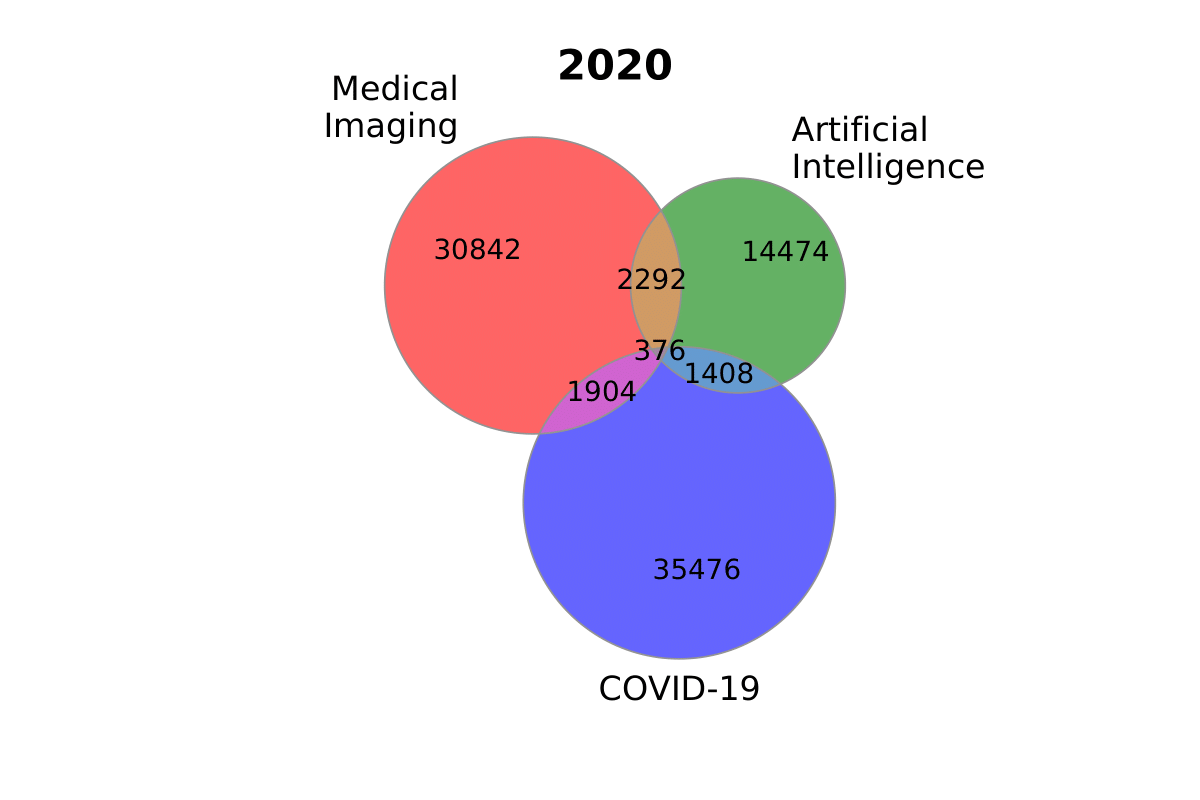
Venn Diagrams
from paperscraper.plotting import (
plot_venn_two, plot_venn_three, plot_multiple_venn
)
sizes_2020 = (30842, 14474, 2292, 35476, 1904, 1408, 376)
sizes_2019 = (55402, 11899, 2563)
labels_2020 = ('Medical\nImaging', 'Artificial\nIntelligence', 'COVID-19')
labels_2019 = ['Medical Imaging', 'Artificial\nIntelligence']
plot_venn_two(sizes_2019, labels_2019, title='2019', figname='ai_imaging')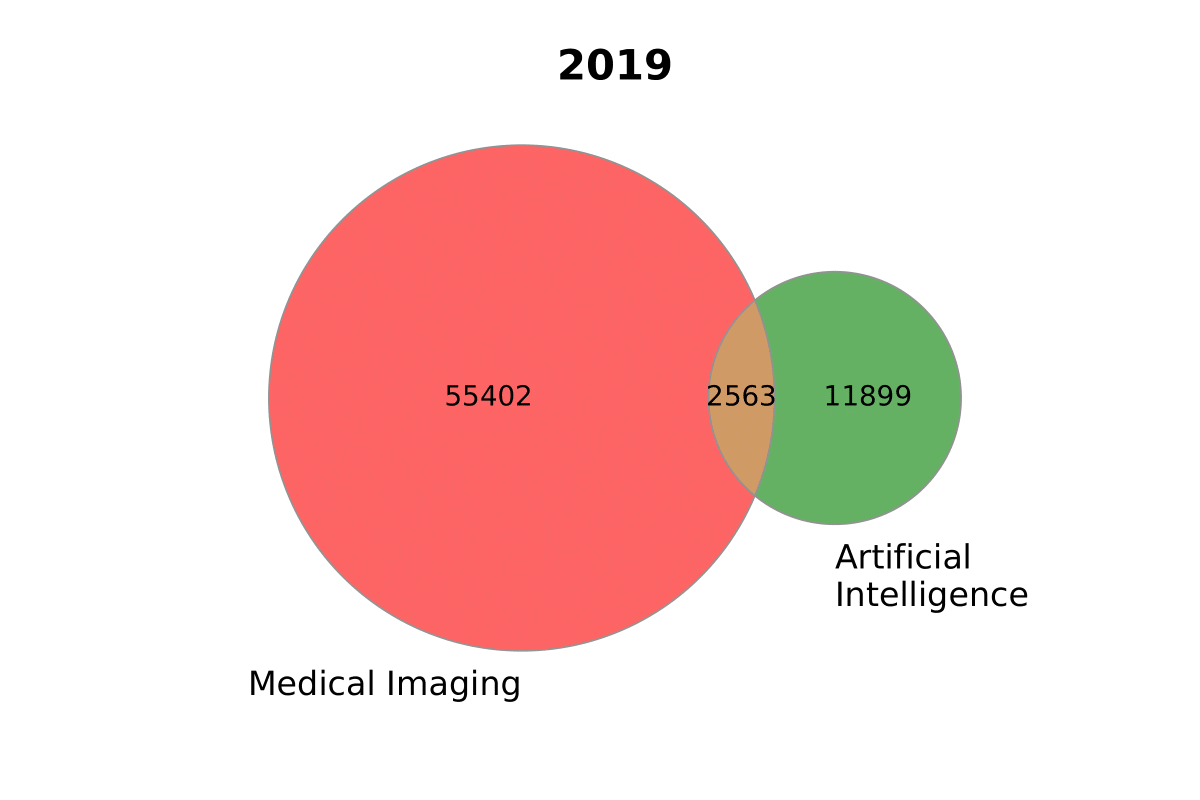
plot_venn_three(
sizes_2020, labels_2020, title='2020', figname='ai_imaging_covid'
)
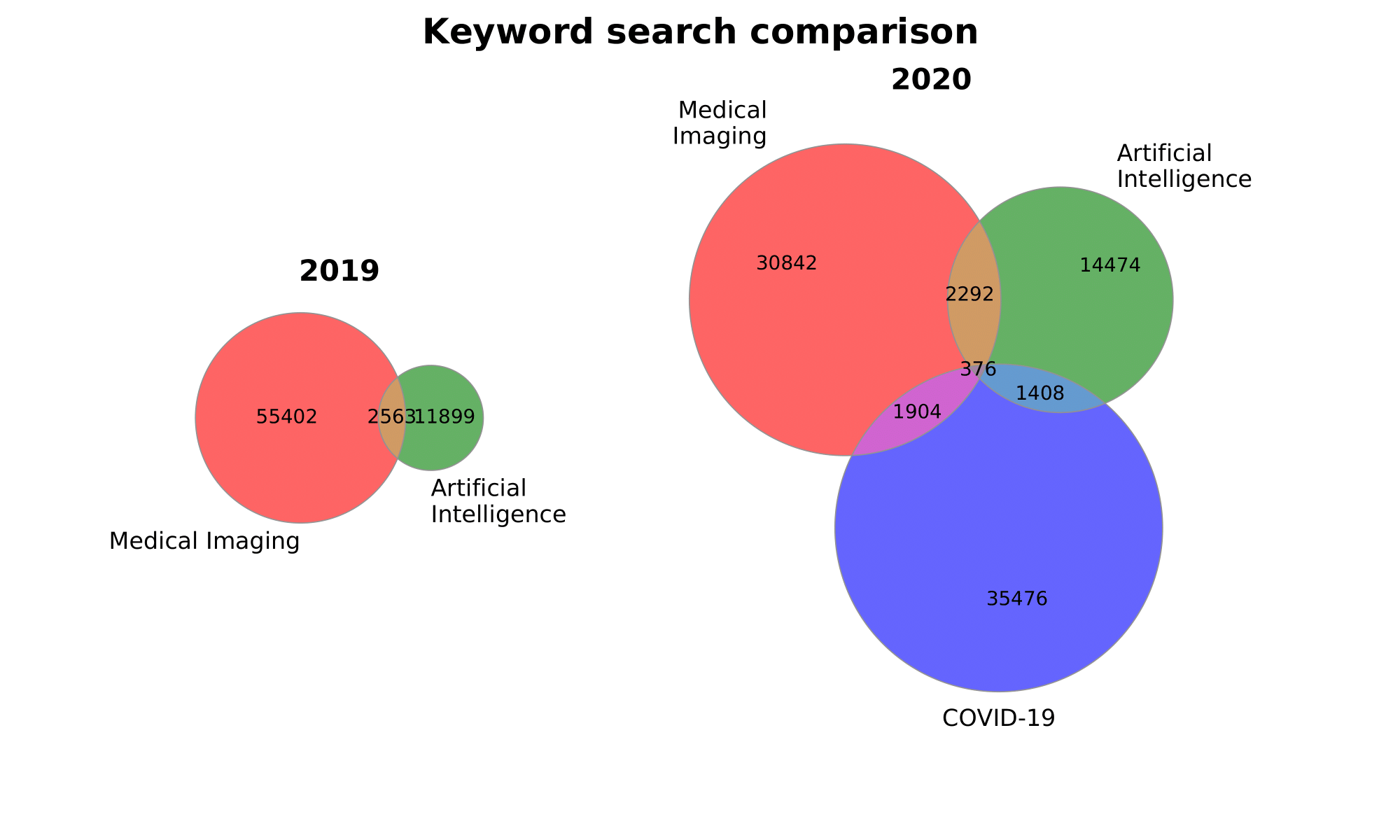
Or plot both together:
plot_multiple_venn(
[sizes_2019, sizes_2020], [labels_2019, labels_2020],
titles=['2019', '2020'], suptitle='Keyword search comparison',
gridspec_kw={'width_ratios': [1, 2]}, figsize=(10, 6),
figname='both'
)
Citation
If you use paperscraper, please cite a paper that motivated our development of this tool.
@article{born2021trends,
title={Trends in Deep Learning for Property-driven Drug Design},
author={Born, Jannis and Manica, Matteo},
journal={Current Medicinal Chemistry},
volume={28},
number={38},
pages={7862--7886},
year={2021},
publisher={Bentham Science Publishers}
}Contributions
Thanks to the following contributors:
- @memray: Since
v0.2.12there are automatic retries when downloading the {med/bio/chem}rxiv dumps. - @achouhan93: Since
v0.2.5{med/bio/chem}rxiv can be scraped for specific dates! - @daenuprobst: Since
v0.2.4PDF files can be scraped directly (paperscraper.pdf.save_pdf) - @oppih: Since
v0.2.3chemRxiv API also provides DOI and URL if available - @lukasschwab: Bumped
arxivdependency to >1.4.2in paperscraperv0.1.0. - @juliusbierk: Bugfixes



