Matft



Matft is Numpy-like library in Swift. Function name and usage is similar to Numpy.
INFO: Support Complex!!
Note: You can use Protocol version(beta version) too.
Feature & Usage
-
Many types
-
Pretty print
-
Indexing
- Positive
- Negative
- Boolean
- Fancy
- Complex
-
Slicing
- Start / To / By
- New Axis
-
View
- Assignment
-
Conversion
- Broadcast
- Transpose
- Reshape
- Astype
-
Univarsal function reduction
-
Mathematic
- Arithmetic
- Statistic
- Linear Algebra
-
Complex
-
Image Conversion
...etc.
See Function List for all functions.
Declaration
MfArray
-
The MfArray such like a numpy.ndarray
let a = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]]) let aa = Matft.arange(start: -8, to: 8, by: 1, shape: [2,2,4]) print(a) print(aa) /* mfarray = [[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4] mfarray = [[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4] */
MfType
-
You can pass MfType as MfArray's argument
mftype: .Hoge. It is similar todtype.※Note that stored data type will be Float or Double only even if you set MfType.Int. So, if you input big number to MfArray, it may be cause to overflow or strange results in any calculation (+, -, *, /,... etc.). But I believe this is not problem in practical use.
-
MfType's list is below
public enum MfType: Int{ case None // Unsupportted case Bool case UInt8 case UInt16 case UInt32 case UInt64 case UInt case Int8 case Int16 case Int32 case Int64 case Int case Float case Double case Object // Unsupported } -
Also, you can convert MfType easily using
astypelet a = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]]) print(a)//See above. if mftype is not passed, MfArray infer MfType. In this example, it's MfType.Int let a = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], mftype: .Float) print(a) /* mfarray = [[[ -8.0, -7.0, -6.0, -5.0], [ -4.0, -3.0, -2.0, -1.0]], [[ 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [ 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0]]], type=Float, shape=[2, 2, 4] */ let aa = MfArray([[[ -8, -7, -6, -5], [ -4, -3, -2, -1]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], mftype: .UInt) print(aa) /* mfarray = [[[ 4294967288, 4294967289, 4294967290, 4294967291], [ 4294967292, 4294967293, 4294967294, 4294967295]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], type=UInt, shape=[2, 2, 4] */ //Above output is same as numpy! /* >>> np.arange(-8, 8, dtype=np.uint32).reshape(2,2,4) array([[[4294967288, 4294967289, 4294967290, 4294967291], [4294967292, 4294967293, 4294967294, 4294967295]], [[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7]]], dtype=uint32) */ print(aa.astype(.Float)) /* mfarray = [[[ -8.0, -7.0, -6.0, -5.0], [ -4.0, -3.0, -2.0, -1.0]], [[ 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0], [ 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0]]], type=Float, shape=[2, 2, 4] */
Subscription
MfSlice
- You can access specific data using subscript.
You can set MfSlice (see below's list) to subscript.
-
MfSlice(start: Int? = nil, to: Int? = nil, by: Int = 1) -
Matft.newaxis -
~< //this is prefix, postfix and infix operator. same as python's slice, ":" -
Matft.all // same as python's slice :, matft's 0~< -
Matft.reverse // same as python's slice ::-1, matft's ~<<-1
(Positive) Indexing
-
Normal indexing
let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 27, by: 1, shape: [3,3,3]) print(a) /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]], [[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]], [[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]]], type=Int, shape=[3, 3, 3] */ print(a[2,1,0]) // 21Caution
MfArray conforms to Collection protocol, so 1D MfArray returns MfArray! Use
itemas workaround instead of subscription such likelet a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 27, by: 1, shape: [27]) print(a[0]) /* 0 // a[0] is MfArray!! Nevertheless, The scalar is printed (I don't know why...) */ print(a[0] + 4) /* mfarray = [ 4], type=Int, shape=[1] */ // Workaround print(a.item(index: 0, type: Int.self)) /* 0 */ print(a.item(index: 0, type: Int.self) + 4) /* 4 */Slicing
-
If you replace
:with~<, you can get sliced mfarray. Note that usea[0~<]instead ofa[:]to get all elements along axis.print(a[~<1]) //same as a[:1] for numpy /* mfarray = [[[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]]], type=Int, shape=[1, 3, 3] */ print(a[1~<3]) //same as a[1:3] for numpy /* mfarray = [[[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]], [[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 3, 3] */ print(a[~<~<2]) //same as a[::2] for numpy //print(a[~<<2]) //alias /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]], [[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 3, 3] */ print(a[Matft.all, 0]) //same as a[:, 0] for numpy /* mfarray = [[ 0, 1, 2], [ 9, 10, 11], [18, 19, 20]], type=Int, shape=[3, 3] */
Negative Indexing
-
Negative indexing is also available That's implementation was hardest for me...
print(a[~<-1]) /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]], [[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 3, 3] */ print(a[-1~<-3]) /* mfarray = [], type=Int, shape=[0, 3, 3] */ print(a[Matft.reverse]) //print(a[~<~<-1]) //alias //print(a[~<<-1]) //alias /* mfarray = [[[ 18, 19, 20], [ 21, 22, 23], [ 24, 25, 26]], [[ 9, 10, 11], [ 12, 13, 14], [ 15, 16, 17]], [[ 0, 1, 2], [ 3, 4, 5], [ 6, 7, 8]]], type=Int, shape=[3, 3, 3]*/
Boolean Indexing
-
You can use boolean indexing.
Caution! I don't check performance, so this boolean indexing may be slowUnfortunately, Matft is too slower than numpy...
(numpy is 1ms, Matft is 7ms...)
let img = MfArray([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], mftype: .UInt8) img[img > 3] = MfArray([10], mftype: .UInt8) print(img) /* mfarray = [[ 1, 2, 3], [ 10, 10, 10], [ 10, 10, 10]], type=UInt8, shape=[3, 3] */
Fancy Indexing
-
You can use fancy indexing!!!
let a = MfArray([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]) a[MfArray([0, 1, 2]), MfArray([0, -1, 0])] = MfArray([999,888,777]) print(a) /* mfarray = [[ 999, 2], [ 3, 888], [ 777, 6]], type=Int, shape=[3, 2] */ a.T[MfArray([0, 1, -1]), MfArray([0, 1, 0])] = MfArray([-999,-888,-777]) print(a) /* mfarray = [[ -999, -777], [ 3, -888], [ 777, 6]], type=Int, shape=[3, 2] */
View
-
Note that returned subscripted mfarray will have
baseproperty (is similar toviewin Numpy). See numpy doc in detail.let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 4*4*2, by: 1, shape: [4,4,2]) let b = a[0~<, 1] b[~<<-1] = MfArray([9999]) // cannot pass Int directly such like 9999 print(a) /* mfarray = [[[ 0, 1], [ 9999, 9999], [ 4, 5], [ 6, 7]], [[ 8, 9], [ 9999, 9999], [ 12, 13], [ 14, 15]], [[ 16, 17], [ 9999, 9999], [ 20, 21], [ 22, 23]], [[ 24, 25], [ 9999, 9999], [ 28, 29], [ 30, 31]]], type=Int, shape=[4, 4, 2] */
Complex
Matft supports Complex!!
But this is beta version. so, any bug may be ocurred.
Please report me by issue! (Progres
TODO
- [x] Arithmetic Operation
- [x] Angle, Conjugate and Absolute
- [x] Math (partial:
sin,cos,tan,exp,log) - [x] Basic Subscription Getter
- [x] Basic Subscription Setter
- [x] Boolean Indexing Getter
- [ ] Boolean Indexing Setter
- [x] Fancy Indexing Getter
- [ ] Fancy Indexing Setter
let real = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 16, by: 1).reshape([2,2,4])
let imag = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: -16, by: -1).reshape([2,2,4])
let a = MfArray(real: real, imag: imag)
print(a)
/*
mfarray =
[[[ 0 +0j, 1 -1j, 2 -2j, 3 -3j],
[ 4 -4j, 5 -5j, 6 -6j, 7 -7j]],
[[ 8 -8j, 9 -9j, 10 -10j, 11 -11j],
[ 12 -12j, 13 -13j, 14 -14j, 15 -15j]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4]
*/
print(a+a)
/*
mfarray =
[[[ 0 +0j, 2 -2j, 4 -4j, 6 -6j],
[ 8 -8j, 10 -10j, 12 -12j, 14 -14j]],
[[ 16 -16j, 18 -18j, 20 -20j, 22 -22j],
[ 24 -24j, 26 -26j, 28 -28j, 30 -30j]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4]
*/
print(Matft.complex.angle(a))
/*
mfarray =
[[[ -0.0, -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982],
[ -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982]],
[[ -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982],
[ -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982, -0.7853982]]], type=Float, shape=[2, 2, 4]
*/
print(Matft.complex.conjugate(a))
/*
mfarray =
[[[ 0 +0j, 1 +1j, 2 +2j, 3 +3j],
[ 4 +4j, 5 +5j, 6 +6j, 7 +7j]],
[[ 8 +8j, 9 +9j, 10 +10j, 11 +11j],
[ 12 +12j, 13 +13j, 14 +14j, 15 +15j]]], type=Int, shape=[2, 2, 4]
*/Image
You can acheive an image processing by Matft! (Beta version) Please refer to the example here.
@IBOutlet weak var originalImageView: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var reverseImageView: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var swapImageView: UIImageView!
func reverse(){
var image = Matft.image.cgimage2mfarray(self.reverseImageView.image!.cgImage!)
// reverse
image = image[Matft.reverse] // same as image[~<<-1]
self.reverseImageView.image = UIImage(cgImage: Matft.image.mfarray2cgimage(image))
}
func swapchannel(){
var image = Matft.image.cgimage2mfarray(self.swapImageView.image!.cgImage!)
// swap channel
image = image[Matft.all, Matft.all, MfArray([1,0,2,3])] // same as image[0~<, 0~<, MfArray([1,0,2,3])]
self.swapImageView.image = UIImage(cgImage: Matft.image.mfarray2cgimage(image))
}For more complex conversion, see OpenCV code.

Function List
Below is Matft's function list. As I mentioned above, almost functions are similar to Numpy. Also, these function use Accelerate framework inside, the perfomance may keep high.
* means method function exists too. Shortly, you can use a.shallowcopy() where a is MfArray.
^ means method function only. Shortly, you can use a.tolist() not Matft.tolist where a is MfArray.
# means support complex operation
- Creation
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| *#Matft.shallowcopy | *numpy.copy |
| *#Matft.deepcopy | copy.deepcopy |
| Matft.nums | numpy.ones * N |
| Matft.nums_like | numpy.ones_like * N |
| Matft.arange | numpy.arange |
| Matft.eye | numpy.eye |
| Matft.diag | numpy.diag |
| Matft.vstack | numpy.vstack |
| Matft.hstack | numpy.hstack |
| Matft.concatenate | numpy.concatenate |
| *Matft.append | numpy.append |
| *Matft.insert | numpy.insert |
| *Matft.take | numpy.take |
| ^MfArray.item | ^numpy.ndarray.item |
- Conversion
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| *#Matft.astype | *numpy.astype |
| *#Matft.transpose | *numpy.transpose |
| *#Matft.expand_dims | *numpy.expand_dims |
| *#Matft.squeeze | *numpy.squeeze |
| *#Matft.broadcast_to | *numpy.broadcast_to |
| *#Matft.to_contiguous | *numpy.ascontiguousarray |
| *#Matft.flatten | *numpy.flatten |
| *#Matft.flip | *numpy.flip |
| *#Matft.clip | *numpy.clip |
| *#Matft.swapaxes | *numpy.swapaxes |
| *#Matft.moveaxis | *numpy.moveaxis |
| *Matft.roll | numpy.roll |
| *Matft.sort | *numpy.sort |
| *Matft.argsort | *numpy.argsort |
| ^MfArray.toArray | ^numpy.ndarray.tolist |
| ^MfArray.toFlattenArray | n/a |
| ^MfArray.toMLMultiArray | n/a |
| *Matft.orderedUnique | numpy.unique |
- File
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.file.loadtxt | numpy.loadtxt |
| Matft.file.genfromtxt | numpy.genfromtxt |
| Matft.file.savetxt | numpy.savetxt |
-
Operation
Line 2 is infix (prefix) operator.
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| #Matft.add + |
numpy.add + |
| #Matft.sub - |
numpy.sub - |
| #Matft.div / |
numpy.div . |
| #Matft.mul * |
numpy.multiply * |
| Matft.inner *+ |
numpy.inner n/a |
| Matft.cross *^ |
numpy.cross n/a |
| Matft.matmul *& |
numpy.matmul @ |
| Matft.dot | numpy.dot |
| Matft.equal === |
numpy.equal == |
| Matft.not_equal !== |
numpy.not_equal != |
| Matft.less < |
numpy.less < |
| Matft.less_equal <= |
numpy.less_equal <= |
| Matft.greater > |
numpy.greater > |
| Matft.greater_equal >= |
numpy.greater_equal >= |
| #Matft.allEqual == |
numpy.array_equal n/a |
| #Matft.neg - |
numpy.negative - |
- Universal Fucntion Reduction
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| *#Matft.ufuncReduce e.g.) Matft.ufuncReduce(a, Matft.add) |
numpy.add.reduce e.g.) numpy.add.reduce(a) |
| *#Matft.ufuncAccumulate e.g.) Matft.ufuncAccumulate(a, Matft.add) |
numpy.add.accumulate e.g.) numpy.add.accumulate(a) |
- Math function
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| #Matft.math.sin | numpy.sin |
| Matft.math.asin | numpy.asin |
| Matft.math.sinh | numpy.sinh |
| Matft.math.asinh | numpy.asinh |
| #Matft.math.cos | numpy.cos |
| Matft.math.acos | numpy.acos |
| Matft.math.cosh | numpy.cosh |
| Matft.math.acosh | numpy.acosh |
| #Matft.math.tan | numpy.tan |
| Matft.math.atan | numpy.atan |
| Matft.math.tanh | numpy.tanh |
| Matft.math.atanh | numpy.atanh |
| Matft.math.sqrt | numpy.sqrt |
| Matft.math.rsqrt | numpy.rsqrt |
| #Matft.math.exp | numpy.exp |
| #Matft.math.log | numpy.log |
| Matft.math.log2 | numpy.log2 |
| Matft.math.log10 | numpy.log10 |
| *Matft.math.ceil | numpy.ceil |
| *Matft.math.floor | numpy.floor |
| *Matft.math.trunc | numpy.trunc |
| *Matft.math.nearest | numpy.nearest |
| *Matft.math.round | numpy.round |
| #Matft.math.abs | numpy.abs |
| Matft.math.reciprocal | numpy.reciprocal |
| #Matft.math.power | numpy.power |
| Matft.math.arctan2 | numpy.arctan2 |
| Matft.math.square | numpy.square |
| Matft.math.sign | numpy.sign |
- Statistics function
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| *Matft.stats.mean | *numpy.mean |
| *Matft.stats.max | *numpy.max |
| *Matft.stats.argmax | *numpy.argmax |
| *Matft.stats.min | *numpy.min |
| *Matft.stats.argmin | *numpy.argmin |
| *Matft.stats.sum | *numpy.sum |
| Matft.stats.maximum | numpy.maximum |
| Matft.stats.minimum | numpy.minimum |
| *Matft.stats.sumsqrt | n/a |
| *Matft.stats.squaresum | n/a |
| *Matft.stats.cumsum | *numpy.cumsum |
- Random function
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.random.rand | numpy.random.rand |
| Matft.random.randint | numpy.random.randint |
- Linear algebra
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.linalg.solve | numpy.linalg.solve |
| Matft.linalg.inv | numpy.linalg.inv |
| Matft.linalg.det | numpy.linalg.det |
| Matft.linalg.eigen | numpy.linalg.eig |
| Matft.linalg.svd | numpy.linalg.svd |
| Matft.linalg.pinv | numpy.linalg.pinv |
| Matft.linalg.polar_left | scipy.linalg.polar |
| Matft.linalg.polar_right | scipy.linalg.polar |
| Matft.linalg.normlp_vec | scipy.linalg.norm |
| Matft.linalg.normfro_mat | scipy.linalg.norm |
| Matft.linalg.normnuc_mat | scipy.linalg.norm |
- Complex
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.complex.angle | numpy.angle |
| Matft.complex.conjugate | numpy.conj / numpy.conjugate |
| Matft.complex.abs | numpy.abs / numpy.absolute |
- FFT
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.fft.rfft | numpy.fft.rfft |
| Matft.fft.irfft | numpy.fft.irfft |
- Interpolation
Matft supports only natural cubic spline. I'll implement other boundary condition later.
| Matft | Scipy |
|---|---|
| Matft.interp1d.cubicSpline | scipy.interpolation.CubicSpline |
- Image
| Matft | Numpy |
|---|---|
| Matft.image.cgimage2mfarray | N/A |
| Matft.image.mfarray2cgimage | N/A |
| Matft | OpenCV |
|---|---|
| Matft.image.color | cv2.cvtColor |
| Matft.image.resize | cv2.resize |
| Matft.image.warpAffine | cv2.warpAffine |
Performance
I use Accelerate framework, so all of MfArray operation may keep high performance.
let a = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: 10*10*10*10*10*10, by: 1, shape: [10,10,10,10,10,10])
let aneg = Matft.arange(start: 0, to: -10*10*10*10*10*10, by: -1, shape: [10,10,10,10,10,10])
let aT = a.T
let b = a.transpose(axes: [0,3,4,2,1,5])
let c = a.transpose(axes: [1,2,3,4,5,0])
let posb = a > 0import numpy as np
a = np.arange(10**6).reshape((10,10,10,10,10,10))
aneg = np.arange(0, -10**6, -1).reshape((10,10,10,10,10,10))
aT = a.T
b = a.transpose((0,3,4,2,1,5))
c = a.transpose((1,2,3,4,5,0))
posb = a > 0- Arithmetic test
| Matft | time | Numpy | time |
|---|---|---|---|
let _ = a+aneg |
596μs |
a+aneg |
1.04ms |
let _ = b+aT |
4.46ms |
b+aT |
4.31ms |
let _ = c+aT |
5.31ms |
c+aT |
2.92ms |
- Math test
| Matft | time | Numpy | time |
|---|---|---|---|
let _ = Matft.math.sin(a) |
2.14ms |
np.sin(a) |
14.7ms |
let _ = Matft.math.sin(b) |
7.02ms |
np.sin(b) |
15.8ms |
let _ = Matft.math.sign(a) |
3.09ms |
np.sign(a) |
1.37ms |
let _ = Matft.math.sign(b) |
8.33ms |
np.sign(b) |
1.42ms |
- Bool test
| Matft | time | Numpy | time |
|---|---|---|---|
let _ = a > 0 |
4.63ms |
a > 0 |
855μs |
let _ = a > b |
17.8ms |
a > b |
1.83ms |
let _ = a === 0 |
4.65ms |
a == 0 |
603μs |
let _ = a === b |
19.7ms |
a == b |
1.78ms |
- Indexing test
| Matft | time | Numpy | time |
|---|---|---|---|
let _ = a[posb] |
1.21ms |
a[posb] |
1.29ms |
Matft achieved almost same performance as Numpy!!!
※Swift's performance test was conducted in release mode
However, as you can see the above table, Matft's boolean operation is toooooooo slow...(Issue #18)
So, a pull request is very welcome!!
Installation
SwiftPM
- Import
- Project > Build Setting > +
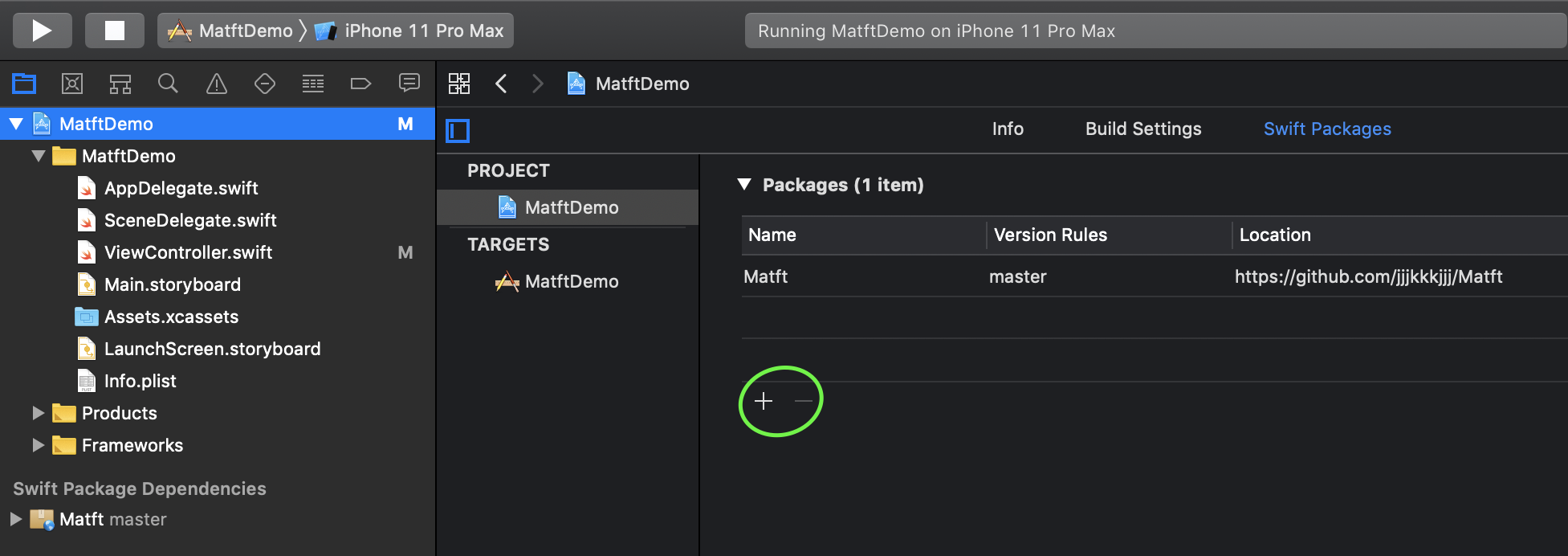
- Select Rules

- Project > Build Setting > +
- Update
- File >Swift Packages >Update to Latest Package versions
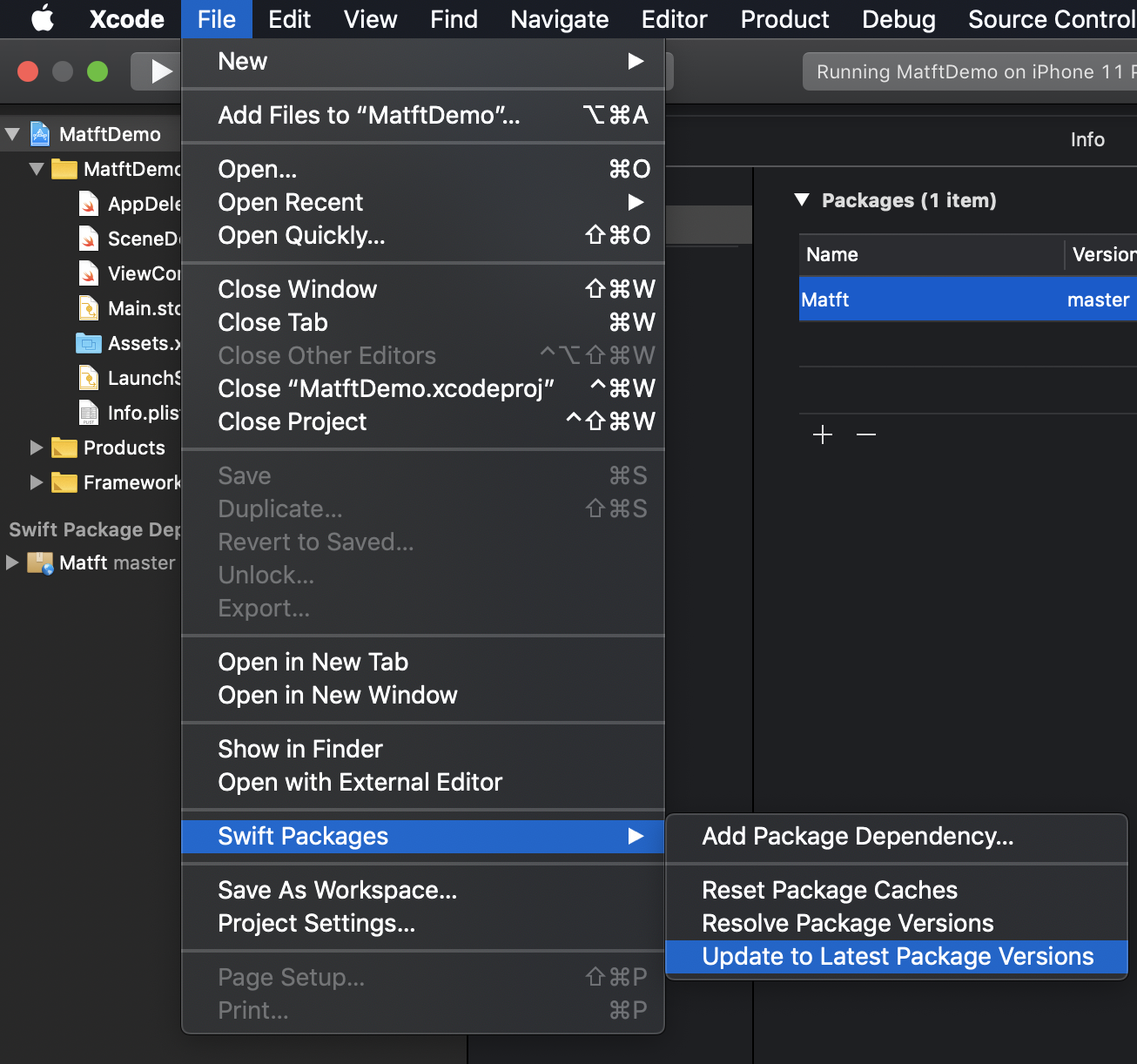
- File >Swift Packages >Update to Latest Package versions
Important!!! the below installation is outdated. Please install Matft via swiftPM!!!
Carthage
-
Set Cartfile
echo 'github "jjjkkkjjj/Matft"' > Cartfile carthage update ###or append '--platform ios' -
Import Matft.framework made by above process to your project
CocoaPods
-
Create Podfile (Skip if you have already done)
pod init -
Write
pod 'Matft'in Podfile such like belowtarget 'your project' do pod 'Matft' end -
Install Matft
pod install
Contact
Feel free to ask this project or anything via junnosuke.kado.git@gmail.com
