openpyn
A python3 script (systemd service as well) to manage OpenVPN connections. Created to easily connect to and switch between, OpenVPN servers hosted by NordVPN. Quickly Connect to the least busy servers with lowest latency from you (using current data from NordVPN’s API). Find servers in a specific country or even a city. It Tunnels DNS traffic through the VPN which normally (when using OpenVPN) goes through your ISP’s DNS (unencrypted) and compromises Privacy!
Features
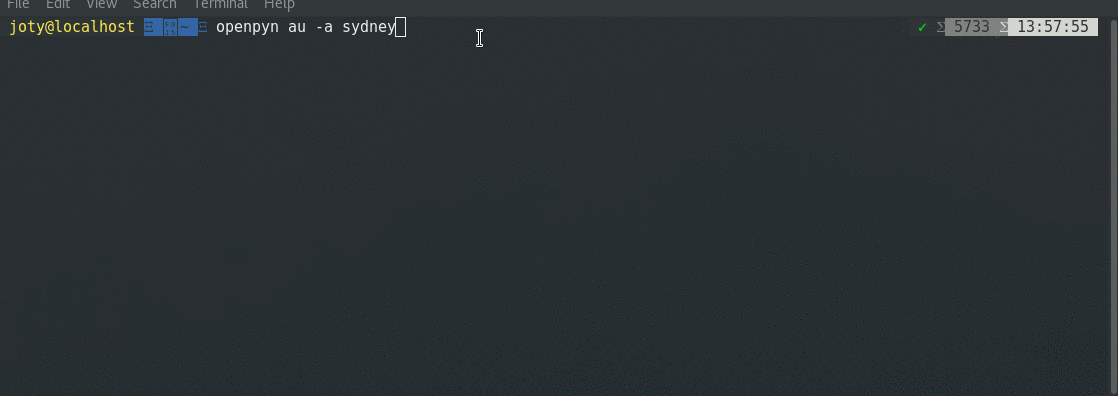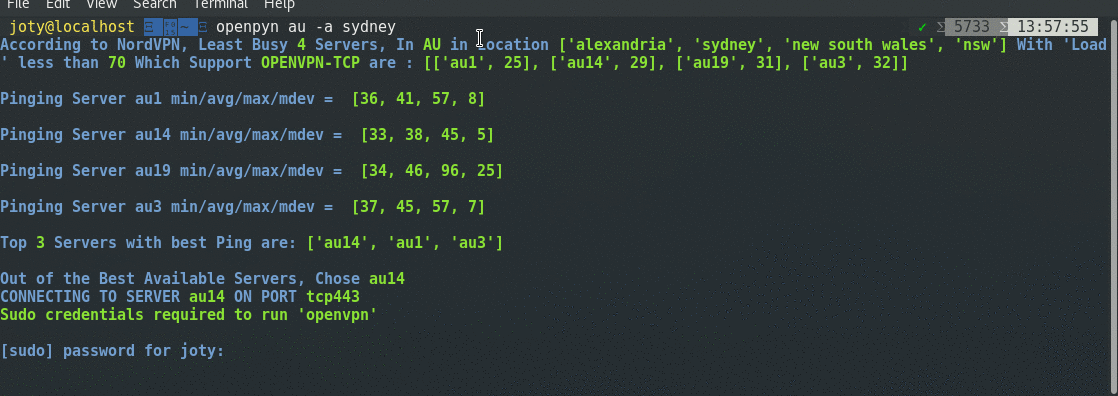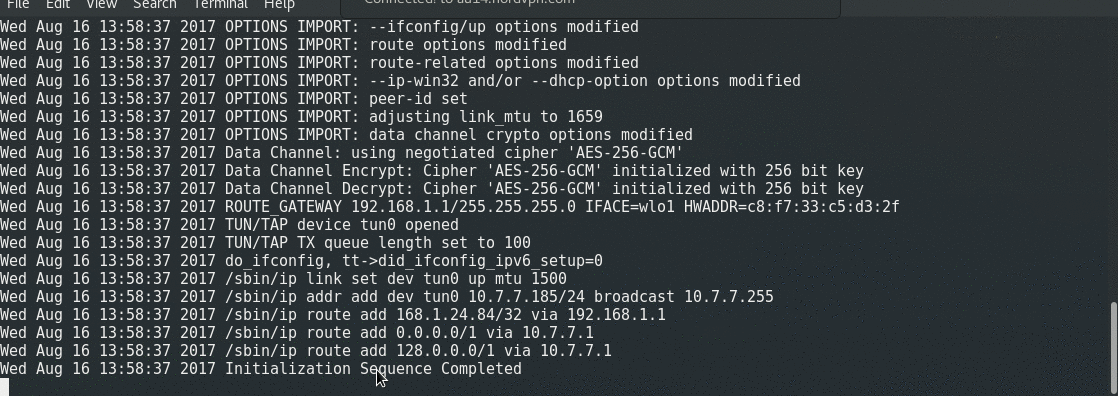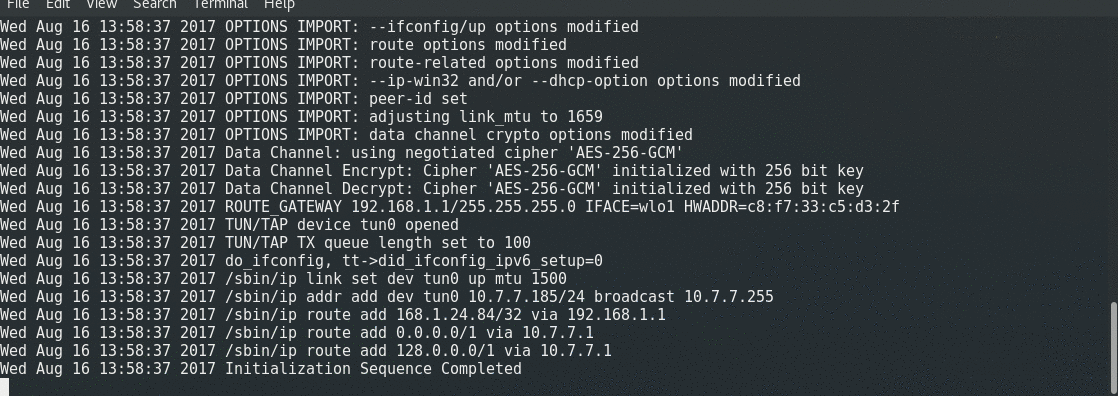
- Automatically connect to least busy, low latency servers in a given country.
- Systemd integration, easy to check VPN status, autostart at startup.
- Find and connect to servers in a specific city or state.
- Uses NordVPN’s DNS servers and tunnels DNS queries through the VPN Tunnel.
- Use Iptables rules to prevent IP leakage if tunnel breaks (Experimental), ie KILL SWITCH.
- Quickly Connect to any specific server. i.e au10 or us20.
- Downloads and Updates (modifications) the latest config files from NordVPN.
- Option to run the script in background (as a systemd service).
- Options to finetune server selection based on "Server Load" or "Ping Latency".
- Auto excludes the servers if a ping to them fails or some packets drops when pinging or if they don’t support OpenVPN (TCP or UDP depending upon which one you are trying to use).
- Finds and displays NordVPN servers (with extra info) in a given country.
- Now list and connect to servers with "Netflix" --netflix, "Peer To Peer" --p2p, "Dedicated IP" --dedicated, "Tor Over VPN" --tor, "Double VPN" --double, "Anti DDos" --anti-ddos support.
- Desktop notification are shown when VPN connects and disconnects. (needs to run without sudo)
- Auto retry if [soft,auth-failure] received, auto failover to next best server if connection dies.
- NVRAM support for Asuswrt-merlin
- Pass through OpenVPN options, e.g. openpyn uk -o '--status /var/log/status.log --log /var/log/log.log'
- Logs are stored in '/var/log/openpyn/' for information and troubleshooting.
- Temporarily disable IPv6 to prevent leakage (when using -f).
Demo
Instructions
-
Install dependencies if they are not already present.
# common dependencies sudo apt install openvpn python3-setuptools python3-pip -
The following Python dependencies are needed and will be installed when using pip.
requests colorama coloredlogs verboselogs tqdm jsonschema
Installation Methods
-
Install openpyn with pip3 (Python=>3.5) Recommended method to get the latest version and receive frequent updates. Do not install with --user switch, as OpenVPN needs to run as sudo and sudo won’t be able to locate openpyn.
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade openpyn -
Alternatively clone and install.
git clone https://github.com/jotyGill/openpyn-nordvpn.git cd openpyn-nordvpn/ sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade .For the latest in development features, try the 'test' branch instead
git clone --branch test https://github.com/jotyGill/openpyn-nordvpn.git cd openpyn-nordvpn/ sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade . -
On macOS (credit: 1951FDG)
# install Xcode command line tools xcode-select --install# install Homebrew curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh echo 'export PATH="/usr/local/sbin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile# common dependencies brew install python3 openvpn sudo brew services start openvpngit clone --branch test https://github.com/jotyGill/openpyn-nordvpn.git cd openpyn-nordvpn/ sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade . -
On Asuswrt-merlin, standard installation Entware (credit: 1951FDG)
Steps below may also work for OpenWrt
# common dependencies opkg install git git-http iputils-ping procps-ng-pgrep python3 python3-pip sudo unzip# allow admin user to run sudo sed -i 's~root ALL=(ALL) ALL~admin ALL=(ALL) ALL~g' /opt/etc/sudoerscd /tmp/share/ git clone --branch test https://github.com/jotyGill/openpyn-nordvpn.git cd openpyn-nordvpn/ python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip python3 -m pip install --upgrade .Steps below not required if only using --nvram option
# steps need to be done once after every device reboot modprobe tun iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o tun0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A POSTROUTING -t nat -o tun0 -j MASQUERADESteps below may be required if not using --nvram option
# change the DNS, either in LAN or WAN settings **DNS Server1** 103.86.96.100 **DNS Server2** 103.86.99.100
Setup
Initialise the script with "--init" (store credentials, install Systemd service, update/install VPN config files)
sudo openpyn --initNote: if you get ' openpyn: command not found' when using sudo on Fedora, create a symbolic link.
sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/openpyn /bin/openpyn
That’s it, run the script! when done with it, press "Ctr + C" to exit.
Basic Usage
- At minimum, you only need to specify the country-code, default port is UDP-1194, If you want to use TCP-443 instead, use "--tcp" switch.
openpyn us- Now, you can also specify a city or state, useful when companies (like Google) lock your account if you try to login from an IP that resides in a different physical location.
openpyn us -a ny
openpyn us --area "new york"- To enforce firewall rules to prevent DNS leakage, also from IP leakage if tunnel breaks. i.e KILL SWITCH also temporarily disables IPv6 by running "sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1"
openpyn us -f # Experimental!, Warning, clears iptables rules!
# (changes are non persistent, simply reboot if having networking issues)- When using "-f", To allow custom ports (from internal IP ranges, i.e 192.168 or 10.) through the firewall.
openpyn us -f --allow 22 80 443 # only accessible from local network-
To allow ports from other ranges use the
--allow-configor--allow-config-jsonoptions. More details can be found here -
To quickly connect to a specific server.
openpyn -s au10- To list all the Countries and their Country Codes where NordVPN hosts servers.
openpyn -l- To find detailed information about the available servers in a given country.
openpyn -l uk- To find servers with features like "peer-to-peer", "netflix", "tor over vpn", "double vpn" in all countries or a given country.
openpyn -l uk --p2p
openpyn --list uk --dedicated
openpyn -l --tor # Tor over VPN in all countries- To find the least loaded 10 NordVPN servers in US that support "peer-to-peer", sort them by the lowest latency from you, connect to the best one, if connection fails try the next one and so on.
openpyn us -t 10 --p2p- To update and run the systemd openpyn.service, use "-d" or "--daemon"
sudo openpyn us -d- To check the status of the systemd openpyn.service.
systemctl status openpyn- To kill a running OpenVPN connection.
sudo openpyn -k- To flush the iptables and kill any running OpenVPN connections.
sudo openpyn -x # optionally --allow 22 if using as SSH server- To download/update the latest VPN config files from NordVPN.
openpyn --update- To quickly connect to United States "OpenVPN Client 5" (Asuswrt-Merlin).
openpyn us --nvram 5- To kill "OpenVPN Client 5" (Asuswrt-Merlin).
openpyn -k --nvram 5Usage Options
usage: openpyn [-h] [-v] [--init] [-d] [-k] [-x] [--update] [--skip-dns-patch]
[--silent] [--test] [-n NVRAM] [--no-redirect-gateway]
[-o OPENVPN_OPTIONS] [-s SERVER] [-c COUNTRY_CODE] [--tcp]
[-a AREA] [-m MAX_LOAD] [-t TOP_SERVERS] [--p2p] [--dedicated]
[--tor] [--double] [--anti-ddos] [--netflix]
[-l [LIST_SERVERS]] [--status] [--stats] [-f] [-r]
[--allow-locally]
[--allow INTERNALLY_ALLOWED [INTERNALLY_ALLOWED ...]]
[--allow-config INTERNALLY_ALLOWED_CONFIG]
[--allow-config-json INTERNALLY_ALLOWED_CONFIG_JSON]
[country]
A python3 script/systemd service (GPLv3+) to easily connect to and switch
between, OpenVPN servers hosted by NordVPN. Quickly Connect to the least busy
servers (using current data from NordVPN website) with lowest latency from
you. Find NordVPN servers in a given country or city. Tunnels DNS traffic
through the VPN which normally (when using OpenVPN with NordVPN) goes through
your ISP’s DNS (still unencrypted, even if you use a third-party DNS servers)
positional arguments:
country Country code can also be specified without "-c,"i.e.
"openpyn au"
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version show program’s version number and exit
--init Initialise, store/change credentials, download/update
VPN config files, needs root "sudo" access.
-d, --daemon Update and start systemd service openpyn.service,
running it as a background process, to check status
"systemctl status openpyn"
-k, --kill Kill any running OpenVPN process, very useful to kill
openpyn process running in background with "-d" switch
-x, --kill-flush Kill any running OpenVPN process, and flush iptables
--update Fetch the latest config files from NordVPN’s site
--skip-dns-patch Skips DNS patching, leaves /etc/resolv.conf untouched.
(Not recommended)
--silent Do not try to send notifications. Use if "libnotify"
or "gi" are not available. Automatically used in
systemd service file
--test Simulation only, do not actually connect to the VPN
server
-n NVRAM, --nvram NVRAM
Specify client to save configuration to NVRAM
(Asuswrt-Merlin)
OpenVPN Options:
Configurable Options Being Passed Downed To OpenVPN
--no-redirect-gateway
Don’t set --redirect-gateway
-o OPENVPN_OPTIONS, --openvpn-options OPENVPN_OPTIONS
Pass through OpenVPN options, e.g. openpyn uk -o '--
status /var/log/status.log --log /var/log/log.log'
Connect Options:
Connect To A Specific Server Or Any In A Country; TCP or UDP
-s SERVER, --server SERVER
server name, i.e. ca64 or au10
-c COUNTRY_CODE, --country-code COUNTRY_CODE
Specify country code with 2 letters, i.e. au
--tcp use port TCP-443 instead of the default UDP-1194
Filter Options:
Find Specific Types Of Servers
-a AREA, --area AREA Specify area, city name or state e.g "openpyn au -a
victoria" or "openpyn au -a 'sydney'"
-m MAX_LOAD, --max-load MAX_LOAD
Specify load threshold, rejects servers with more load
than this, DEFAULT=70
-t TOP_SERVERS, --top-servers TOP_SERVERS
Specify the number of top servers to choose from the
NordVPN’s server list for the given country, these
will be pinged, DEFAULT=10
--p2p Only look for servers with "Peer To Peer" support
--dedicated Only look for servers with "Dedicated IP" support
--tor Only look for servers with "Tor Over VPN" support
--double Only look for servers with "Double VPN" support
--anti-ddos Only look for servers with "Obfuscated" support
--netflix Only look for servers that are optimised for "Netflix"
Display Options:
These Only Display Information
-l [LIST_SERVERS], --list [LIST_SERVERS]
If no argument given prints all Country Names and
Country Codes; If country code supplied ("-l us"):
Displays all servers in that given country with their
current load and OpenVPN support status. Works in
conjunction with (-a | --area, and server types
(--p2p, --tor) e.g "openpyn -l it --p2p --area milano"
--status Show last change in connection status
--stats Show OpenVPN connection stats
Firewall Options:
Firewall, KillSwitch and Route Options
-f, --force-fw-rules Enforce firewall rules to drop traffic when tunnel
breaks , force disable DNS traffic going to any other
interface
-r, --add-route Add route to default-gateway; Needed to continue
serving any service including SSH. Required on VPSs.
To ensure it doesn’t leak traffic use it with -f and
--allow
--allow-locally To be used with "-f" to allow input traffic on all
ports from locally connected / INTERNAL IP SUBNET. for
example 192.168.1.* range
--allow INTERNALLY_ALLOWED [INTERNALLY_ALLOWED ...]
To be used with "-f" to allow TCP connections to given
ports but ONLY to INTERNAL IP RANGE. for example: you
can use your PC as SSH, HTTP server for local devices
(i.e. 192.168.1.* range) by "openpyn us -f --allow 22
80"
--allow-config INTERNALLY_ALLOWED_CONFIG
To be used with "-f" to allow a complex set of allow
port rules. This option requires a path to a JSON file
that contains the relevant config
--allow-config-json INTERNALLY_ALLOWED_CONFIG_JSON
To be used with "-f" to allow a complex set of allow
port rules. This option works the same as "--allow-
config" option but accepts a JSON object as a string
insteadTodo
- [x] find servers with P2P support, Dedicated IPs, Anti DDoS, Double VPN, Onion over VPN
- [x] utilise the frequently updated api at "api.nordvpn.com/server"
- [x] clean exit, handle exceptions
- [x] store credentials from user input, if "credentials" file exists use that instead
- [x] sane command-line options following the POSIX guidelines
- [ ] ability to store profiles (sort of works as the systemd service file stores last state)
- [x] find and display server’s locations (cities)
- [x] accept full country names
- [x] colourise output
- [x] modularize
- [x] create a combined config of multiple servers (on the fly) for auto failover
- [x] uninstall.sh # sudo pip3 uninstall openpyn
- [x] view status of the connection after launching in --daemon mode
- [x] desktop notifications
- [x] initd script for Asuswrt-merlin: "/opt/etc/init.d/S23openpyn start"
