Blue Serialization
Serialize and deserialize LabVIEW classes using either JSONtext or TOML
Explore the docs »
Getting Started
This repository only houses the core for the framework. You first need to decide which type of serializer that you want to use. At the moment, the framework has the following supported serializers:
| Text Type | VIP Name | VIP dependency |
|---|---|---|
| JSON | BlueJSONTextSerializer | JSONtext |
| TOML | BlueTOMLSerializer | LV-TOML |
Installing one of these packages will pull down all of the dependencies that you need.
User Guide
How to make a serializable class
- Open/create a LabVIEW class. Inherit your class from BlueSerializable.lvclass. (You can drop something from the BlueSerializable palette down onto your code to bring the class into memory such that it can be inherited from.)
- Learn the project provider menu items, listed below:

"Create Serializable Methods"
This script will behave differently depending on whether or not it's the first time that you have run this script against your class.
- The first time that this script runs against your class, the following work will be performed:
- "SerializableData.clt" will be created and added to your class's private data
- This will be named "SerializableData" within your private data.
- Other items in your private data with this name will be forcibly renamed.
- Please, never change this filename
- GetSerializableData.vi will be created and added
- SetSerializableData.vi will be created and added
- Increment Class version major history by 1
- Initialize your BlueSerializableVersion within the class mutation history to 1
- "SerializableData.clt" will be created and added to your class's private data
- The second time that this script runs against your class, the following work will be performed:
- delete, and rescript creation of the Get/SetSerializableData.vi. (We did this in case we ever needed to update these methods and fix all the VIs out in the world.)
When this script finishes, you should see the following new files:

A few notes:
- This project provider script will fail if your class is broken-arrow. This is because the scripting is required to bring an object into memory in order to access mutation hitory. An object cannot exist in memory if the class is broken. If you forget and get an error, then fix your class and rerun this project provider script until you are able to complete it without error.
- The Get/SetSerializableData VIs are dynamic overrides. These provide access to the SerializableData in the private data. You should theoretically never have to modify these VIs. In fact, please DON'T modify these VIs unless you know what you are doing and have a good reason.
- The SerializableData.ctl provides access to the serializables for your class. This allows you to easily separate serializables from protected private data that you don't wan to be serialized/deserialized.
- Do NOT change the filename for SerializableData.ctl
"Create Mutation" (First call)
This script will allow for you to change your serializable data in a way that would normally create a backwards incompatible jump with respect to old serialized text.
When the script finishes, you should see the following new files in your project:

- GetVersionSerializableData.vi
- You theoretically never have to touch this file
- HandleVersionMutation.vi
- You theoretically never have to touch this file
- SerializableData_v1.ctl
- This is essentially a tagged version of SerializableData.ctl at the time of running the Create Mutation script.
- Do NOT change this filename.
- Do NOT change the contents of this ctl.
- Note that ALL typedefs in this file will have been disconnected. This prevents mutations in the current-generation SerializableData from affecting the old tagged version of the data
- Mutate_v1_to_v2.vi
- This is where you are required to add/write custom code. You will need to write code that defines the conversion between the old serialzable data and the current serializable data
- Note that you may need to revisit this code in the future if you update SerializableData in a way that breaks the code conversion. This is expected.
"Create Mutation" (non-First call)
When the script finishes, you should see the following new files in your project:
- SerializableData_v2.ctl
- This is a new data structure tag... just like previously discussed
- Mutate_v2_to_v2.vi
- This is a new mutation conversion VI... just like previously discussed
A few notes:
- This project provider script will fail if your class is broken-arrow. This is because the scripting is required to bring an object into memory in order to access mutation hitory. An object cannot exist in memory if the class is broken.
- In this example, the script will actually modify the Mutate_v1_to_v2.vi. We replace the SerializableData.ctl with SerializableData_v1.vi.
- You can mutate a class as many times as you'd like.
- Serialized text being converted from v1 to v3 will pass through both mutation VIs. (mutate_v1_to_v2.vi and mutate_v2_to_v3.vi). This is fine. However, it is technically allowable for users to directly modify the "HandleVersionMutation.vi" in a way that will allow you to write code that will convert v1 data directly to v3 data. I don't recommend doing this unless you know what you are doing, and have a good reason.
"View Mutation History"
This is a visualization tool and will not modify your class data or version in any manner. This menu item appears for all classes... This is not strictly a BlueSerializable.lvclass tool.
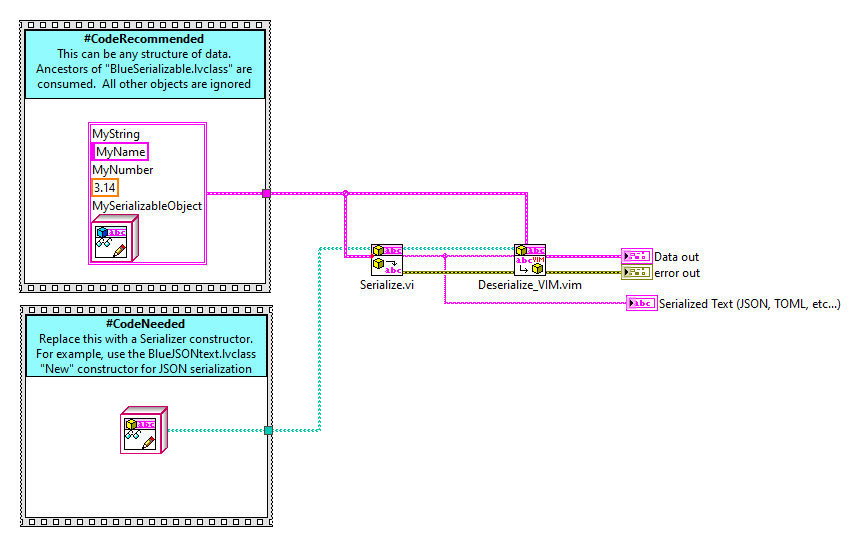
API
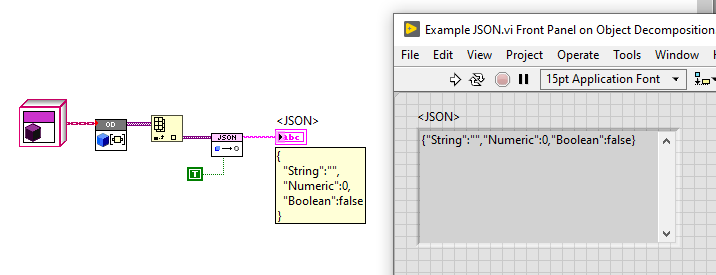
simple example:

Palette:

API - Serialize

- Input. This can be any LabVIEW data structure. This can be as complex as you'd like... nested clusters, classes, arrays, etc.
- NOTE: Don't ask me "does BlueSerialization support Map Collections, or XYZ datatypes? The answer to this question lies in whether or not the selected serializer supports this data type. For example, JSONtext does not support map collections. The BlueSerialization provides a framework for decomposing/composing LabVIEW class instances and then leveraging the selected serializer for handling all other data types.
- Output. This is serialized text. If you used a JSONtext serializer, then this will be JSON text.
| Category | Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| class slicing | slice objects per SetSerializeSliceClass.vi? | False | If True, then the wired object will be sliced to the class layer specified in the "SetSerializeSliceClass override. (No-op parent will not perform any slicing.) |
| non-Blue | serialize non-BlueSerializable objects as hex? | False | If True, then non-BlueSerializable objects will be flattened as hex data using the LabVIEW "flatten to string" node. If false, an error will be returned when a non-BlueSerializable object is discovered |
API - Deserialize

- Serialized Object String. This is your serialized text (JSON, TOML, etc.)
- Anything. This is your reference data structure that you wish to adapt the serialized text into.
- Variant. Use the "Variant to data" node to convert this variant into a LabVIEW datatype. Generally, you will use the wire-type of the "Anything" input.
| Category | Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| expansion | expand objects on type conflict? | False | If True, then the wired object is allowed to be more-specific than the serialized text. The returned object will be the more specific object. If false, then an error will be returned in this situation. |
| class slicing | slice flattened object data on error? | False | If True, then the framework will iterate upwards through a class hierarchy until it finds a load-able class instance. This means that the returned data may be less-specific than the serialized text. |
| class slicing | sliceable class names | empty str array | If a class isn't found in memory, then the framework will be allowed to slice class names in this list until finding a class in the hierarchy that is load-able. |
| non-Blue | deserialize non-BlueSerializable objects from hex? | False | If True, then the framework will unflatten non-BlueSerializable objects using the "unflatten from text" node. If False, then non-BlueSerializable objects found in the reference data will yield and error. |
| Mutation | error on inserted parent levels? | False | If False, then the framework allows for class mutation history where a parent level was added. This means that your output data will contain default-data for this added class layer. If True, then error |
| Mutation | error on obsolete parent levels? | False | If False, then the framework allows for class mutation history where a parent level was removed. This means that data for dropped class layers in your serialized text will also be unused. If True, then error. |
| Data preservation | Preserve wired non-serialized data? | Don't Preserve | "Don't Preserve": non-serialized data will not be preserved. "Preserve (error on less-specific wired types)": non-serialized data will be preserved. However, if a wired object is found to be less specific than the serialized object, then you will receive an error. "Preserve (except on less-specific wired types)": non-serialized data will be preserved except where a wired object is found to be less specific than the serialized object. (It's not possible to preserve data in this situation without class composition.) |
API - Set Serialize Slice Class

- This is used in conjunction with the serializer "Seriualize.Allow class slicing" option. (See above.)
- If class slicing is enabled on serialize, then the framework will slice to this class name
Consequence Table
If you're going to use this library, then it's important for you to understand what changes to a class will result in backwards incompatible breaks with respect to deserialization of old text. The following table documents all of this:
| Change | Backwards compatible with old serialized text? | Backwards compatible with old software builds? |
|---|---|---|
| Parent class renamed | yes | no |
| Parent class level added | yes | no |
| Parent class level removed | yes | no |
| Child or Parent class MAJOR version number incremented | yes | no |
| Child class renamed | no | no |
| class mutation history deleted | no | no |
| Changes to serializable data | maybe | maybe |
Notes:
- changes to serializable data are backwards compatible depending on the type of serializer used. Change the question to: "is this a backwards compatible change with respect to base-JSONtext?"
- Running the "Create Mutation" project provider script will increment your class's MAJOR version number.
- Don't delete class mutation history unless you have a good reason. You will break backwards compatibility with old serialized text since applications will no longer be able to use mutation history to determine the mutation path.
- You may find it helpful to manually increment your class's MAJOR version number sometime. This effectively allows you to disallow new serialized text to be loaded into old software builds.

Advanced documentation
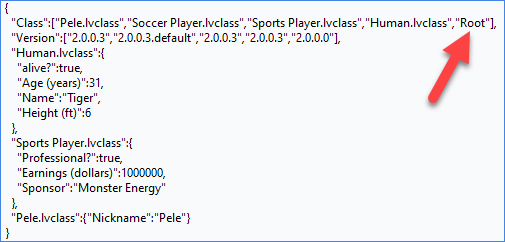
Classes with only placeholder data will result in a "default" data tag
Observe that the Soccer Player class private data is Placeholder only.

This has 2 consequences:
- Soccer Player does not have a section of data
- The version for Soccer Player has a ".default" suffix

A few notes about this behavior:
- If both the default tag and the class section data is mission, then deserialize will return an error.
- If both the default tag and the class sesion data exists, then deserialize will STILL consume the section data.
BlueSerializable appears as "Root"
A few notes about this:
- BlueSerializable does not have a section of data
- This was all done to reduce clutter in the serializable text, since we're not interested in the BlueSerialiazble class name or data
Design Decisions
Problem Statement: There is no convenient mechanism to serialize and de-serialize LabVIEW objects.
open-source libraries such as JSONtext, LV-TOML, and EasyXML have made it very easy to serialize and deserialize test to/from LabVIEW data structures. Unfortunately, none of these libraries support LabVIEW classes. As such, in order to use classes with these libraries, we used to have to be very careful not to include classes in serialized text, and then to have custom code for constructing/deconstructing objects from memory. What a pain!
Goal: Gracefully serialize and de-serialize LabVIEW objects
Subgoals:
- Support input/output of any arbitrary LabVIEW data structure
- Support nested objects
- Support arrays of objects
- Divorce serialization type from serializable data
Design Decision #1: Do NOT direct access private data through object (de)composition.
During research, we discovered 2 libraries out in the world that solve object serialization through the usage of object (de)composition:
- JSONtext branch with object support:
https://bitbucket.org/logmanoriginal/jsontext/src/lvobjectserialization/ - paid 3rd party library "JSON Object Serialization by GCraftsman":
http://sine.ni.com/nips/cds/view/p/lang/en/nid/215788
"LogMAN" from the LAVA forum even went so far as to make available his reuse library for class (de)composition: https://lavag.org/topic/21894-openg-and-object-compatibility/?do=findComment&comment=134688

This code was written with direction from the LabVIEW wiki's extremely relevant wiki page:
https://labviewwiki.org/wiki/LabVIEW_Object
There are some Pros/Cons to this approach. Pros:
- ALL classes in LabVIEW become inherently serializable
- Doesn't require data accessor VIs
- Most closely aligns with the precedent set by JSONtext and other similar serialization libraries
Cons:
- Breaks the LVOOP covenant that private data requires data accessors for access
- Pretty serious security risk. There is no way to protect private data when serializing/de-serializing
- Slow. flatten/unflatten and de(composition) is not cheap
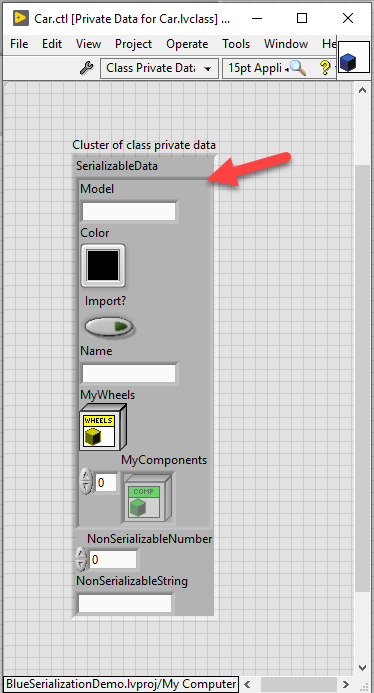
Design Decision #2: All serializable data must appear in a specific typedef'd cluster within the class private data
In the figure below, observe that there exists a "SerializableData" cluster. A few notes about this:
- Only data within this cluster is serialized and deserialized. All other data is ignored.
- This is a typedef'd cluster
- This cluster will always be named "SerializableData"
There are some Pros/Cons to this approach: Pros:
- Allows for segregation of serializable and non-serializable data
- Improves read-ability
- Allows user to protect private data from being exposed through serialization
- Allows for the creation of a single future-proof read/write data accessor for the entire "SerializableData" cluster
Cons:
- You have to create the cluster and data accessors → a non-zero amount of work
- Forces users to organize their data into this paradigm
- Will require rework of existing classes wishing to conform to this requirement
Design Decision #3: The serializer type (JSON, TOML, XML) should be divorced from the serializable data.
In the figure below, observe that we can switch between JSON and TOML serialization simply be swapping out the BlueSerializer class input:

At the moment, the following plug-in serializers are available:
| Text Type | VIP Name | VIP dependency |
|---|---|---|
| JSON | BlueJSONTextSerializer | JSONtext |
| TOML | BlueTOMLSerializer | LV-TOML |
However, the BlueSerialization core was written so that other users can easily add more serializer plug-ins to this list without modifying the core package. I hope to add XML to this list eventually.
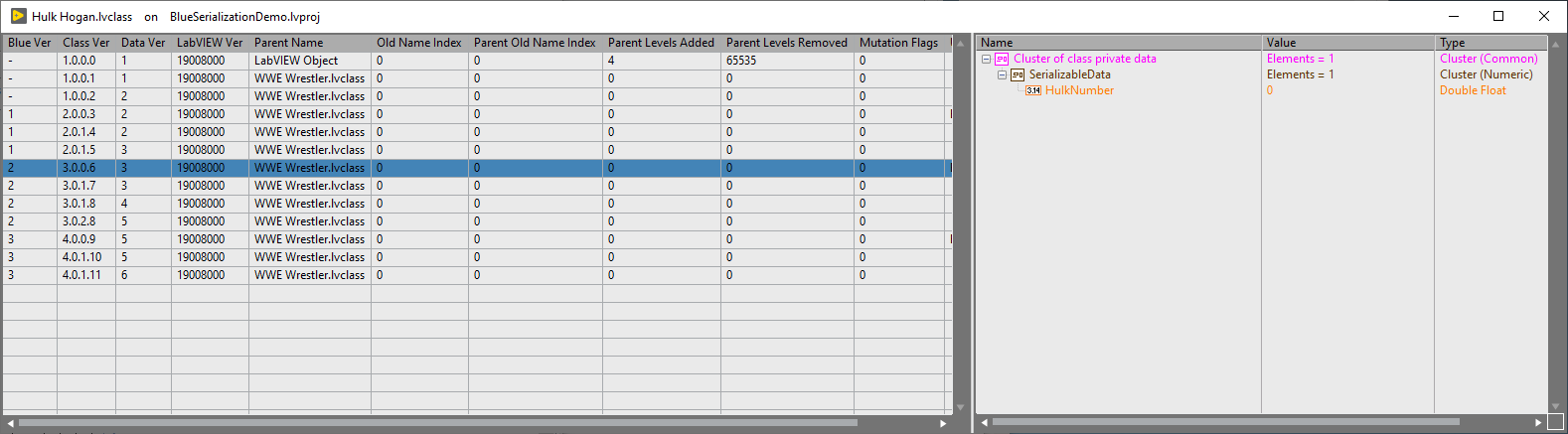
LabVIEW Class Mutation History
BlueSerialization leverages a little-known feature of LabVIEW classes called "LabVIEW class mutation history". Mutation history primarily exists within LabVIEW to support the flattening and unflattening of a LabVIEW class to/from flattened text. Since this feature isn't well known or well documented, I'll document it a bit here:
Get/Set mutation history API
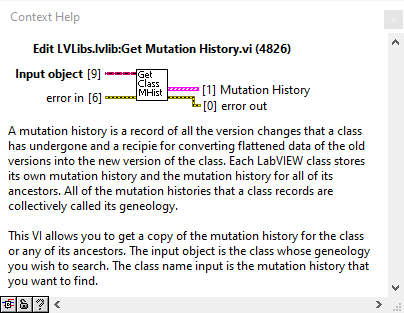

| Path |
|---|
| C:\Program Files (x86)\National Instruments\LabVIEW 2019\vi.lib\Utility\EditLVLibs\LVClass\Get Mutation History.vi |
| C:\Program Files (x86)\National Instruments\LabVIEW 2019\vi.lib\Utility\EditLVLibs\LVClass\Set Mutation History.vi |
Mutation history typedef
This typedef is, as shown below:
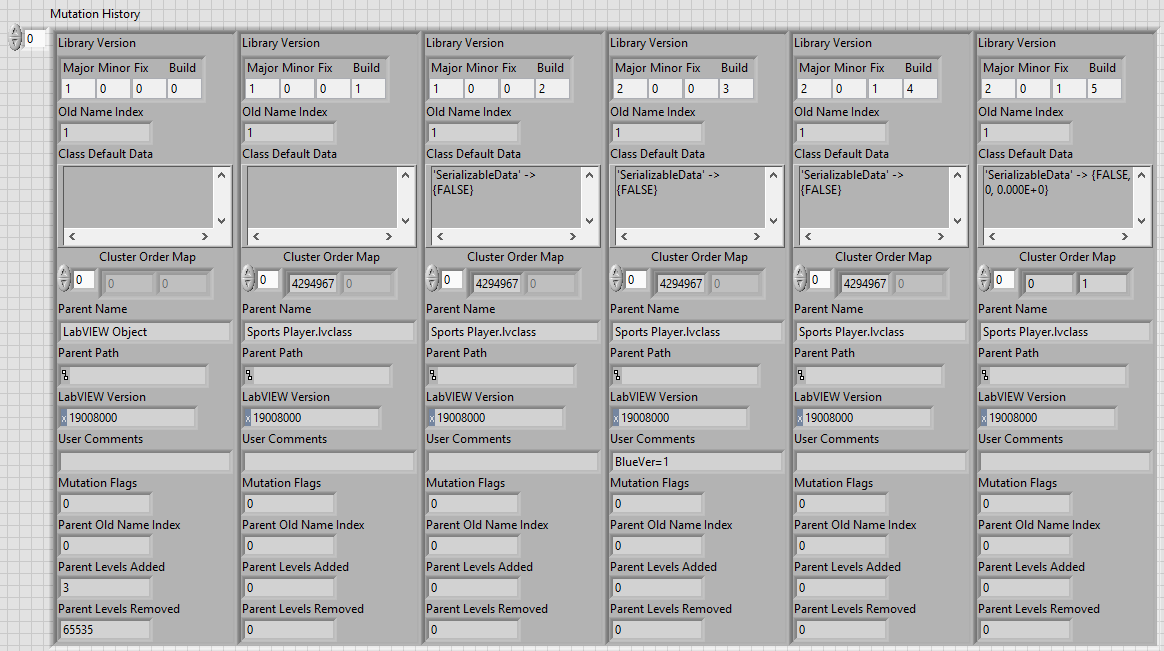
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Library Version | This matches the LVClass version type. This resets to v1.0.0.0 when the fully qualified class name changes. |
| Old Name Index | 0 == current name. This value changes each time that the fully qualified class name changes. This value, in conjunction with the Library Version, provides a unique key for finding a mutation history index. This value is directly related to the "Parent Old Name Index" value of descendant children classes. |
| Class Default Data | A new class mutation history entry is created each time that a class' private data is modified. This entry provides a "snapshot" of the private data. Note that if a class private data contains typedefs or nested objects, that updates to these items will not create a new mutation history entry |
| Cluster Order Map | This describes any reordering of elements in the private data. A value of 4294967294 indicates that order of an element has not changed. |
| Parent Name | This contains the name of the Parent classes fully qualified name |
| Parent Path | possibly unused? |
| LabVIEW Version | HEX value displays the LabVIEW version |
| User Comments | Basically a description field. BlueSerialization leverages this field for keeping track of a class's mutation version. Otherwise, to my knowledge, this field isn't used by LabVIEW internally. |
| Mutation Flags | I have no idea |
| Parent Old Name Index | This links to the "Old Name Index" of the parent class. This allows us to lookup the mutation index for a parent given the child's mutation history. |
| Parent Levels Added | This indicates the number of parent levels added. A value of 0 indicates that no parent levels were added |
| Parent Levels Removed | This indicates the number of parent levels removed. A value of 0 indicates that no parent levels were removed. A value of 65535 indicates that ALL parent levels were removed |
License
Distributed under the BSD-3 License. See LICENSE for more information.