PrtgAPI
PrtgAPI is a C#/PowerShell library for managing and maintaining PRTG Network Monitor.
PrtgAPI abstracts away the complexity of interfacing with PRTG via a collection of type safe methods and cmdlets, enabling you to develop powerful applications for managing your network.
Useful things you can do with PrtgAPI:
- Generate reports based on custom queries
- Monitor the monitoring, such as missing sensors for backup jobs or devices for new domain members!
- Create and modify sensors, devices, groups, and more! Create objects from scratch, or clone from existing!
- Generate complex sensor factory definitions
- Deploy notification triggers to individual sensors for specific clients
- Maintain standard naming/alerting/object settings across your environment
- Pause/resume items from external systems (such as pre/post event scripts and scheduled tasks)
- Batch do anything!
For information on features that are currently in the pipeline, check out the Roadmap.
Do you sometimes develop EXE/Script Advanced sensors for PRTG? Then you should also check out PrtgXml which utilizes black magic to generate the XML required by these sensors for you. Wow!
If, for some reason, you feel the need to throw money at me to show your appreciation for this project, you can do so anonymously by clicking here.
Installation
NuGet
Install-Package PrtgAPIPrtgAPI is available on both nuget.org and PowerShell Gallery. PrtgAPI provides targets for both .NET Framework and .NET Standard and is SourceLink compatible. In order to install PrtgAPI from the PowerShell Gallery you must be running PowerShell 5.1+.
If you have both the nuget.org and PowerShell Gallery package sources installed on your machine, you will need to specify the source you wish to install from, e.g.
Install-Package PrtgAPI -Source PSGalleryIf you are using Windows PowerShell, due to the PowerShell Gallery now requiring TLS 1.2 you may need to manually specify to use TLS 1.2 in order to install or update PrtgAPI
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12Manual
- Download the latest build
- Right click PrtgAPI.zip -> Properties
- On the General tab, under Security select Unblock
- Unzip the file
- Add a reference to PrtgAPI.dll to your project (fullclr: net452, coreclr: netstandard2.0), or import the PrtgAPI module into PowerShell via
Import-Module C:\path\to\PrtgAPI. Alternatively, you can run the included PrtgAPI.cmd or PrtgAPI.sh file to open a prompt and import the PrtgAPI module for you.
Compilation
For details on compiling PrtgAPI please see the wiki
Usage
For detailed usage instructions please see the wiki.
The following provides a general overview of some of the capabilities of PrtgAPI. For more info on each section, click the appropriate link to be taken to the corresponding wiki page.
Overview (C#)
Authentication
All actions in PrtgAPI revolve around a core class: PrtgClient
var client = new PrtgClient("prtg.mycoolsite.com", "username", "password");When a PrtgClient is created, it will immediately attempt to retrieve your account's passhash (an alternative to using a password) from your PRTG Server. For added security, your PassHash is then used for all future PRTG Requests made during the life of your program.
For further security, you are able to immediately pass your passhash to PrtgClient instead of using your password. Simply extract your passhash from your client object's PassHash property, then tell the PrtgClient constructor to use the passhash instead.
var client = new PrtgClient("prtg.mycoolsite.com", "username", "1234567890", AuthMode.PassHash);Objects
Many types of objects can be retrieved from PRTG.
//Get all devices present in your system
var devices = client.GetDevices();PrtgAPI defines a variety of method overloads for filtering requested objects, from simple to complex search criteria.
//List all sensors in a "down" or "down acknowledged" state.
var downSensors = client.GetSensors(Status.Down, Status.DownAcknowledged).Select(s => s.Name).ToList();//List all devices under probes whose name contains "chicago"
var chicagoProbeDevices = client.GetDevices(Property.Probe, FilterOperator.Contains, "chicago");Async is fine too
//List all sensors under the Device with Object ID 2000.
var childSensors = await client.GetSensorsAsync(Property.ParentId, 2000);You can even use IQueryable!
//Get the first three Ping sensors for devices whose name contains "dc" on the Perth Office probe.
var perthDCPingSensors = client.QuerySensors(
s => s.Type == "ping" && s.Device.Contains("dc") && s.Probe == "perth Office"
).Take(3);Object Manipulation
PrtgAPI can manipulate objects in a variety of ways, including pausing, acknowledging and resuming, reorganizing objects as well as retrieving and modifying object properties.
//Acknowledge all down sensors for 10 minutes
var sensors = client.GetSensors(Status.Down);
foreach (var sensor in sensors)
{
client.AcknowledgeSensor(sensor, 10, "Go away!");
}//Standardize all "Ping" sensors to using the name "Ping", without the whole word capitalized
var sensors = client.GetSensors(Property.Name, "ping");
foreach (var sensor in sensors)
{
client.RenameObject(sensor, "Ping");
}//Set the upper error limit on the "Total" channel of all WMI CPU Load sensors to 90%
var sensors = client.GetSensors(Property.Tags, "wmicpuloadsensor");
var channels = sensors.SelectMany(s => client.GetChannels(s, "Total"));
foreach (var channel in channels)
{
client.SetChannelProperty(channel, ChannelProperty.UpperErrorLimit, 90);
}Many operations will let you specify multiple Object IDs at once, allowing you to modify potentially thousands of objects in a single request
//Acknowledge all down sensors indefinitely via a single request.
var sensors = client.GetSensors(Status.Down);
client.AcknowledgeSensor(sensors.Select(s => s.Id).ToArray());Object Creation
You can construct an entirely new object hierarchy all within your application.
First, create a group
//Add a new group named "Servers" to the object with ID 1001
var group = client.AddGroup(1001, "Servers");Then, add a device to it
//Add a new device named "dc-1" to the "Servers" group
var device = client.AddDevice(group, "dc-1");We'll add a new sensor
//Create a brand new Ping sensor and add it to our device
var pingParams = client.GetDynamicSensorParameters(device, "ping");
var sensor = client.AddSensor(device, pingParams).Single();And since we've already defined some notification triggers elsewhere, let's copy one in!
//Get the "PagerDuty" notification trigger from the object with ID 2001
var existingTrigger = client.GetNotificationTriggers(2001).First(t => t.OnNotificationAction.Name.Contains("PagerDuty"));
//Add it to our Ping sensor
var triggerParams = new StateTriggerParameters(sensor, existingTrigger);
var newTrigger = client.AddNotificationTrigger(triggerParams);Madness!
For a comprehensive overview of the functionality of PrtgAPI and detailed usage instructions, please see the wiki
Overview (PowerShell)
To connect to your PRTG server, simply run
Connect-PrtgServer prtg.mycoolsite.comYou will then be prompted to enter your PRTG username and password. Your PassHash can also be used instead of specifying your password.
If you are scripting against PrtgAPI, you can use the included New-Credential cmdlet to bypass the authentication prompt.
Connect-PrtgServer prtg.mycoolsite.com (New-Credential prtgadmin supersecretpassword)To avoid entering your username and password every time you use PrtgAPI, you can define GoPrtg connections in your $Profile to automatically connect for you.
If Connect-PrtgServer is executed outside of a script or the PowerShell ISE, PrtgAPI will by default display advanced progress details whenever two cmdlets are chained together. This can be overridden in a variety of ways.
PrtgAPI supports a wide variety of operations, each of which taking pipeline input from each other where applicable
Add-NotificationTrigger
Add-Device
Add-Group
Add-Sensor
Acknowledge-Sensor
Approve-Probe
Backup-PrtgConfig
Clear-PrtgCache
Clone-Object
Connect-GoPrtgServer
Connect-PrtgServer
Disable-PrtgProgress
Disconnect-PrtgServer
Enable-PrtgProgress
Get-Channel
Get-Device
Get-DeviceTemplate
Get-GoPrtgServer
Get-Group
Get-ModificationHistory
Get-NotificationAction
Get-NotificationTrigger
Get-Object
Get-ObjectLog
Get-ObjectProperty
Get-Probe
Get-PrtgClient
Get-PrtgSchedule
Get-PrtgStatus
Get-PrtgTree
Get-Sensor
Get-SensorFactorySource
Get-SensorHistory
Get-SensorTarget
Get-SensorTotals
Get-SensorType
Get-SystemInfo
Install-GoPrtgServer
Load-PrtgConfigFile
Move-Object
New-Credential
New-NotificationTriggerParameters
New-SearchFilter
New-Sensor
New-SensorFactoryDefinition
New-SensorParameters
New-DeviceParameters
New-GroupParameters
New-SensorNode
New-DeviceNode
New-GroupNode
New-ProbeNode
New-TriggerNode
New-PropertyNode
Open-PrtgObject
Pause-Object
Refresh-Object
Refresh-SystemInfo
Remove-NotificationTrigger
Remove-Object
Rename-Object
Restart-Probe
Restart-PrtgCore
Resume-Object
Set-ChannelProperty
Set-GoPrtgAlias
Set-ObjectPosition
Set-ObjectProperty
Set-PrtgClient
Set-NotificationTrigger
Set-NotificationTriggerProperty
Show-PrtgTree
Simulate-ErrorStatus
Sort-PrtgObject
Start-AutoDiscovery
Uninstall-GoPrtgServer
Update-GoPrtgCredentialAll cmdlets include complete Get-Help documentation, including a cmdlet overview, parameter descriptions and example usages. For an overview of a cmdlet see Get-Help <cmdlet> or Get-Help <cmdlet> -Full for complete documentation.
Objects
Many types of objects can be retrieved from PRTG.
Get all ping sensors
C:\> Get-Sensor ping # pipe to Format-List to view all properties!
Name Id Device Group Probe Status
---- -- ------ ----- ----- ------
PING 2010 dc1 Servers Local Probe Up
Ping 2011 dc2 Servers Local Probe Down
Ping 2012 exch1 Servers Remote Probe DownAcknowledgedGet all devices whose names contain "dc"
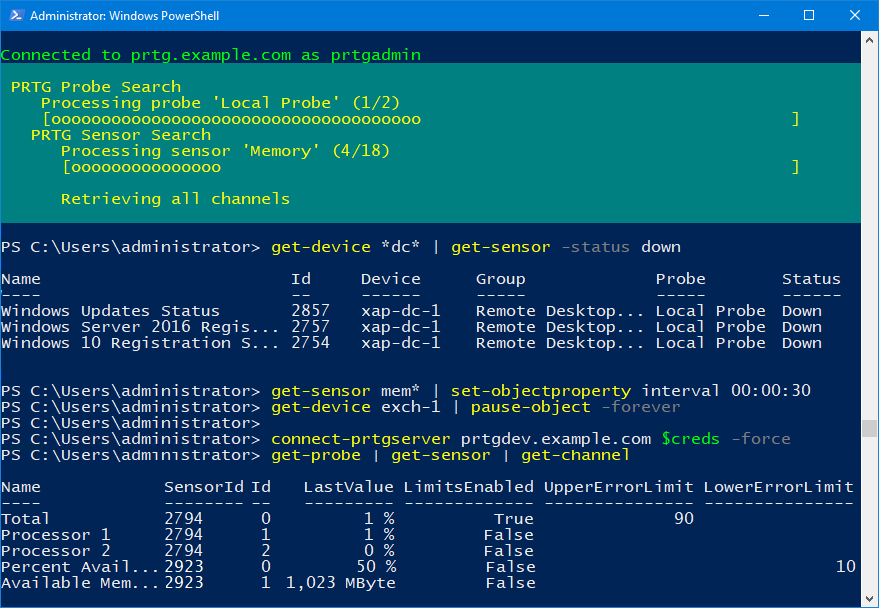
C:\> Get-Device *dc*
Name Id Status Host Group Probe
---- -- ------ ---- ----- -----
dc1 2001 Up 10.0.0.1 Servers Local Probe
dc2 2002 Down dc-2 Servers Local Probe
Get the channels of a sensor
C:\> Get-Sensor | Select -First 1 | Get-Channel
Name SensorId Id LastValue LimitsEnabled UpperErrorLimit LowerErrorLimit ErrorLimitMessage
---- -------- -- --------- ------------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
Total 3001 0 0.32 % True 95 PANIC!! PANIC!!!
Processor 1 3001 1 <1 % FalseInner objects know how to receive a variety of objects via the pipeline. As such it is not necessary to include every intermediate object type
Get-Probe | Get-SensorObject Manipulation
Delete all sensors whose device name contains "banana"
Get-Device *banana* | Get-Sensor | Remove-ObjectObjects can be opened in your web browser for viewing in the PRTG Web UI
Get-Sensor -Count 2 | Open-PrtgObjectProperties/settings of objects can be retrieved and modified via the Get-ObjectProperty and Set-ObjectProperty cmdlets respectively. Properties will automatically set the values of any properties they depend on to be activated
# Retrieve all settings of sensor with ID 1001
Get-Sensor -Id 1001 | Get-ObjectProperty# Set the scanning interval of the device with ID 2002. Will also set InheritInterval to $false
Get-Device -Id 2002 | Set-ObjectProperty Interval 00:00:30Acknowledge all down sensors
# Sensors can be paused -Forever, -Until a given date, or for a specified -Duration (in minutes) with
# an optional -Message
Get-Sensor -Status Down | Acknowledge-Sensor -Until (Get-Date).AddDays(1) -Message "Hi Mom!"Cmdlets can be chained together, in order from outer object to inner object (i.e. Probe -> Group -> Group -> Device -> Sensor -> Channel)
$sensors = Get-Probe | Select -Last 1 | Get-Group | Select -Last 2 | Get-Device | Select -First 1 | Get-Sensor
$sensors | Get-Channel perc* | Set-ChannelProperty UpperErrorLimit 100Object Creation
PowerShell makes it easy to construct complex object hierarchies
# Create a new group and a new device
$device = Get-Probe contoso | Add-Group "Servers" | Add-Device "exch-1"
# Create sensors for all of your Exchange Services
$params = $device | Get-SensorTarget WmiService *exchange* -Params
$device | Add-Sensor $paramsBy throwing your data into a CSV, you can perform arbitrarily complex configurations with minimal effort.
Other Objects
Notification triggers can be retrieved, added and modified, sensor factories can be generated, historical details can be viewed and much much more. For full usage instructions on PrtgAPI please see the wiki
Interesting Things PrtgAPI Does
- PowerShell Build Environment
- Custom Deserialization
- Cmdlet Based Event Handlers
- Inter-Cmdlet Progress
- Securely Storing Credentials
- Test Startup/Shutdown
- Test Server State Restoration
- Mock WriteProgress
- Test Logging
- PowerShell Property Binding
- Dynamic PowerShell Formats
- Hybrid IQueryable / IEnumerable requests
- Debugging Expression Trees as C#


