Opteryx
Query your data, where it lives.
A unified SQL interface to unlock insights across your diverse data sources, from blobs stores to databases - effortless cross-platform data analytics.
| Resource | Location |
|---|---|
| Source Code | https://github.com/mabel-dev/opteryx |
| Documentation | https://opteryx.dev/ |
| Download | https://pypi.org/project/opteryx/ |
Install • Examples • Get Involved
What is Opteryx?
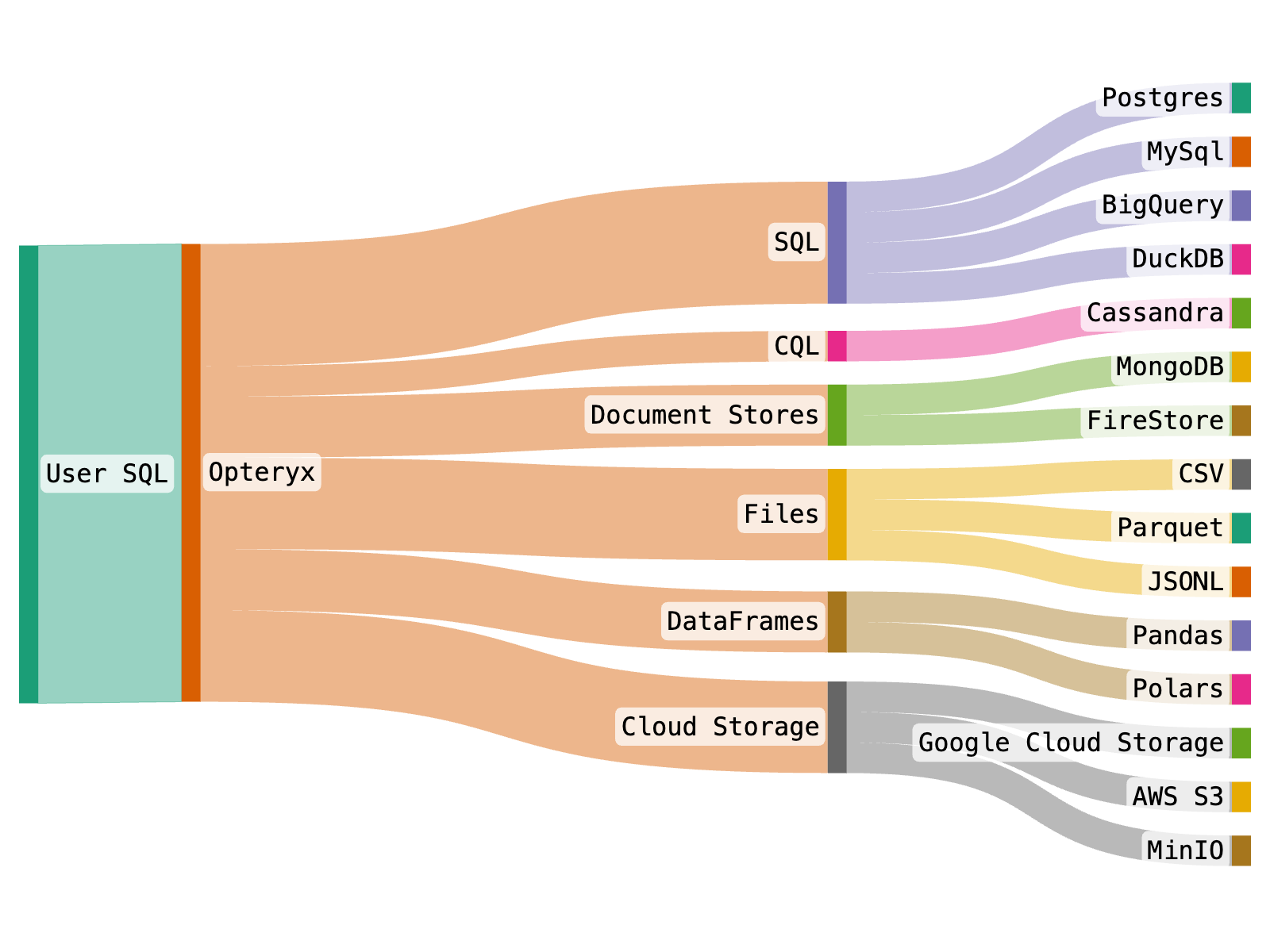
Opteryx champions the SQL-on-everything approach, streamlining cross-platform data analytics by federating SQL queries across diverse data sources, including database systems like Postgres and datalake file formats like Parquet. The goal is to enhance your data analytics process by offering a unified way to access data from across your organization.
Opteryx is a Python library that combines elements of in-process database engines like SQLite and DuckDB with federative features found in systems like Presto and Trino. The result is a versatile tool for querying data across multiple data sources in a seamless fashion.
Opteryx offers the following features:
- SQL queries on data files generated by other processes, such as logs
- A command-line tool for filtering, transforming, and combining files
- Integration with familiar tools like pandas and Polars
- Embeddable as a low-cost engine, enabling portability and allowing for hundreds of analysts to leverage ad hoc databases with ease
- Unified and federated access to data on disk, in the cloud, and in on-premises databases, not only through the same interface but in the same query
How Does it Work?
Opteryx processes queries by first determining the appropriate query language to interact with different downstream data platforms. It translates your query into SQL, CQL, or another suitable format for document stores like MongoDB, based on the data source. This enables Opteryx to efficiently retrieve the necessary data from systems such as MySQL or MongoDB to respond to your query.
Why Use Opteryx?
Familiar Interface
Opteryx supports key parts of the Python DBAPI and SQL92 standard standards which many analysts and engineers will already know how to use.
Consistent Syntax
Opteryx creates a common SQL-layer over multiple data platforms, allowing backend systems to be upgraded, migrated or consolidated without changing any Opteryx code.
Where possible, errors and warnings returned by Opteryx help the user to understand how to fix their statement to reduce time-to-success for even novice SQL users.
Consumption-Based Billing Friendly
Opteryx is well-suited for deployments to environments which are pay-as-you-use, like Google Cloud Run. Great for situations where you have low-volume usage, or multiple environments, where the costs of many traditional database deployment can quickly add up.
Python Ecosystem
Opteryx is Open Source Python, it quickly and easily integrates into Python code, including Jupyter Notebooks, so you can start querying your data within a few minutes. Opteryx integrates with many of your favorite Python data tools, you can use Opteryx to run SQL against pandas and Polars DataFrames, and even execute a JOIN on an in-memory DataFrame and a remote SQL dataset.
Time Travel
Designed for data analytics in environments where decisions need to be replayable, Opteryx allows you to query data as at a point in time in the past to replay decision algorithms against facts as they were known in the past. You can even self-join tables historic data, great for finding deltas in datasets over time. (data must be structured to enable temporal queries)
Fast
Benchmarks on M2 Pro Mac running an ad hoc GROUP BY over a 6 million row parquet file via the CLI in ~1/4th of a second from a cold start (no caching and predefined schema). (different systems will have different performance characteristics)
Instant Elasticity
Designed to run in Knative and similar environments like Google Cloud Run, Opteryx can scale down to zero, and scale up to respond to thousands of concurrent queries within seconds.
Bring your own Data

Opteryx supports multiple query engines, dataframe APIs and storage formats. You can mix-and-match sources in a single query. Opteryx can even JOIN datasets stored in different formats and different platforms in the same query, such as Parquet and MySQL.
Opteryx allows you to query your data directly in the systems where they are stored, eliminating the need to duplicate data into a common store for analytics. This saves you the cost and effort of maintaining duplicates.
Opteryx can push parts of your query to the source query engine, allowing queries to run at the speed of the backend, rather than your local computer.
And if there's not a connector in the box for your data platform; feel free to submit a pull request to add one.
Install
Installing from PyPI is recommended.
pip install opteryxTo build Opteryx from source, refer to the contribution guides.
Opteryx installs with a small set of libraries it needs for core functionality, such as Numpy, PyArrow, and orjson. Some features require additional libraries to be installed, you are notified of these libraries as they are required.
Examples
Filter a Dataset on the Command Line
In this example, we are running Opteryx from the command line to filter one of the internal example datasets and display the results on the console. ~~~bash python -m opteryx "SELECT * FROM \$astronauts WHERE 'Apollo 11' IN UNNEST(missions);" ~~~  _this example is complete and should run as-is_Execute a Simple Query in Python
In this example, we are showing the basic usage of the Python API by executing a simple query that makes no references to any datasets. ~~~python # Import the Opteryx SQL query engine library. import opteryx # Execute a SQL query to evaluate the expression 4 * 7. # The result is stored in the 'result' variable. result = opteryx.query("SELECT 4 * 7;") # Display the first row(s) of the result to verify the query executed correctly. result.head() ~~~ ID | 4 * 7 -- | ------- 1 | 28 _this example is complete and should run as-is_Execute SQL on a pandas DataFrame
In this example, we are running a SQL statement on a pandas DataFrame and returning the result as a new pandas DataFrame. ~~~python # Required imports import opteryx import pandas # Read data from the exoplanets.csv file hosted on Google Cloud Storage # The resulting DataFrame is stored in the variable `pandas_df`. pandas_df = pandas.read_csv("https://storage.googleapis.com/opteryx/exoplanets/exoplanets.csv") # Register the pandas DataFrame with Opteryx under the alias "exoplanets" # This makes the DataFrame available for SQL-like queries. opteryx.register_df("exoplanets", pandas_df) # Perform an SQL query to group the data by `koi_disposition` and count the number # of occurrences of each distinct `koi_disposition`. # The result is stored in `aggregated_df`. aggregated_df = opteryx.query("SELECT koi_disposition, COUNT(*) FROM exoplanets GROUP BY koi_disposition;").pandas() # Display the aggregated DataFrame to get a preview of the result. aggregated_df.head() ~~~ ~~~ koi_disposition COUNT(*) 0 CONFIRMED 2293 1 FALSE POSITIVE 5023 2 CANDIDATE 2248 ~~~ _this example is complete and should run as-is_Query Data on Local Disk
In this example, we are querying and filtering a file directly. This example will not run as written because the file being queried does not exist. ~~~python # Import the Opteryx query engine. import opteryx # Execute a SQL query to select the first 5 rows from the 'space_missions.parquet' table. # The result will be stored in the 'result' variable. result = opteryx.query("SELECT * FROM 'space_missions.parquet' LIMIT 5;") # Display the result. # This is useful for quick inspection of the data. result.head() ~~~ ID | Company | Location | Price | Launched_at | Rocket | Rocket_Status | Mission | Mission_Status --- | --------- | ------------------------------ | ----- | ------------------- | -------------- | ------------- | -------------- | --------------- 0 | RVSN USSR | Site 1/5, Baikonur Cosmodrome, | _null_ | 1957-10-04 19:28:00 | Sputnik 8K71PS | Retired | Sputnik-1 | Success 1 | RVSN USSR | Site 1/5, Baikonur Cosmodrome, | _null_ | 1957-11-03 02:30:00 | Sputnik 8K71PS | Retired | Sputnik-2 | Success 2 | US Navy | LC-18A, Cape Canaveral AFS, Fl | _null_ | 1957-12-06 16:44:00 | Vanguard | Retired | Vanguard TV3 | Failure 3 | AMBA | LC-26A, Cape Canaveral AFS, Fl | _null_ | 1958-02-01 03:48:00 | Juno I | Retired | Explorer 1 | Success 4 | US Navy | LC-18A, Cape Canaveral AFS, Fl | _null_ | 1958-02-05 07:33:00 | Vanguard | Retired | Vanguard TV3BU | Failure _this example requires a data file, [space_missions.parquet](https://storage.googleapis.com/opteryx/space_missions/space_missions.parquet)._Query Data in SQLite
In this example, we are querying a SQLite database via Opteryx. This example will not run as written because the file being queried does not exist. ~~~python # Import the Opteryx query engine and the SqlConnector from its connectors module. import opteryx from opteryx.connectors import SqlConnector # Register a new data store with the prefix "sql", specifying the SQL Connector to handle it. # This allows queries with the 'sql' prefix to be routed to the appropriate SQL database. opteryx.register_store( prefix="sql", # Prefix for distinguishing this particular store connector=SqlConnector, # Specify the connector to handle queries for this store remove_prefix=True, # Remove the prefix from the table name when querying SQLite connection="sqlite:///database.db" # SQLAlchemy connection string for the SQLite database ) # Execute a SQL query to select specified columns from the 'planets' table in the SQL store, # limiting the output to 5 rows. The result is stored in the 'result' variable. result = opteryx.query("SELECT name, mass, diameter, density FROM sql.planets LIMIT 5;") # Display the result. # This is useful for quickly verifying that the query executed correctly. result.head() ~~~ ID | name | mass | diameter | density -- | ------- | ------ | -------- | ------- 1 | Mercury | 0.33 | 4879 | 5427 2 | Venus | 4.87 | 12104 | 5243 3 | Earth | 5.97 | 12756 | 5514 4 | Mars | 0.642 | 6792 | 3933 5 | Jupiter | 1898.0 | 142984 | 1326 _this example requires a data file, [database.db](https://storage.googleapis.com/opteryx/planets/database.db)._Query Data on GCS
In this example, we are to querying a dataset on GCS in a public bucket called 'opteryx'. ~~~python # Import the Opteryx query engine and the GcpCloudStorageConnector from its connectors module. import opteryx from opteryx.connectors import GcpCloudStorageConnector # Register a new data store named 'opteryx', specifying the GcpCloudStorageConnector to handle it. # This allows queries for this particular store to be routed to the appropriate GCP Cloud Storage bucket. opteryx.register_store( "opteryx", # Name of the store to register GcpCloudStorageConnector # Connector to handle queries for this store ) # Execute a SQL query to select all columns from the 'space_missions' table located in the 'opteryx' store, # and limit the output to 5 rows. The result is stored in the 'result' variable. result = opteryx.query("SELECT * FROM opteryx.space_missions LIMIT 5;") # Display the result. # This is useful for quickly verifying that the query executed correctly. result.head() ~~~ ID | Company | Location | Price | Launched_at | Rocket | Rocket_Status | Mission | Mission_Status --- | --------- | ------------------------------ | ----- | ------------------- | -------------- | ------------- | -------------- | --------------- 0 | RVSN USSR | Site 1/5, Baikonur Cosmodrome, | _null_ | 1957-10-04 19:28:00 | Sputnik 8K71PS | Retired | Sputnik-1 | Success 1 | RVSN USSR | Site 1/5, Baikonur Cosmodrome, | _null_ | 1957-11-03 02:30:00 | Sputnik 8K71PS | Retired | Sputnik-2 | Success 2 | US Navy | LC-18A, Cape Canaveral AFS, Fl | _null_ | 1957-12-06 16:44:00 | Vanguard | Retired | Vanguard TV3 | Failure 3 | AMBA | LC-26A, Cape Canaveral AFS, Fl | _null_ | 1958-02-01 03:48:00 | Juno I | Retired | Explorer 1 | Success 4 | US Navy | LC-18A, Cape Canaveral AFS, Fl | _null_ | 1958-02-05 07:33:00 | Vanguard | Retired | Vanguard TV3BU | Failure _this example is complete and should run as-is_You can also try Opteryx right now using our interactive labs on Binder.
Community
Get Involved
- :star: Star this repo
- Contribute — join us in building Opteryx, through writing code, or inspiring others to use it.
- Let us know your ideas, how you are using Opteryx, or report a bug or feature request.
- See the contributor documentation for Opteryx. It's easy to get started, and we're really friendly if you need any help!
- If you're interested in contributing to the code now, check out GitHub issues. Feel free to ask questions or open a draft PR.
Security
See the project Security Policy for information about reporting vulnerabilities.
License
Opteryx is licensed under Apache 2.0 except where specific modules note otherwise.
Status
Opteryx is in beta. Beta means different things to different people, to us, being beta means:
- Core functionality has good regression test coverage to help ensure stability
- Some edge cases may have undetected bugs
- Performance tuning is incomplete
- Changes are focused on feature completion, bugs, performance, reducing debt, and security
- Code structure and APIs are not stable and may change







