Depreciated
This repository contains an early version of pyopencdms that was created before the WMO Climate Data Model Standard existed (pyopencdms-old).
This package has now been replaced by https://github.com/opencdms/pyopencdms/
This old version remains here because it is currently being used by https://github.com/climsoft/climsoft-api
OpenCDMS Python library: pyopencdms
Overview
A Climate Data Management System (CDMS) is an integrated computer-based system that facilitates the effective archival, management, analysis, delivery and utilization of a wide range of integrated climate data (WMO 2014).
pyopencdms aims to build a common Python API supporting multiple Climate Data Management Systems (CDMS) that use different underlying database engines.
The image below shows the CliDE, Climsoft, MCH, MIDAS and other CDMSs being accessed through a single common API.
In addition we will add support for the WIGOS Meta Data Representation (WMDR) and collaborate with experts to create a new "CDMS Data Model Representation" that will support addional capabilities that are beyond the scope of WMDR.
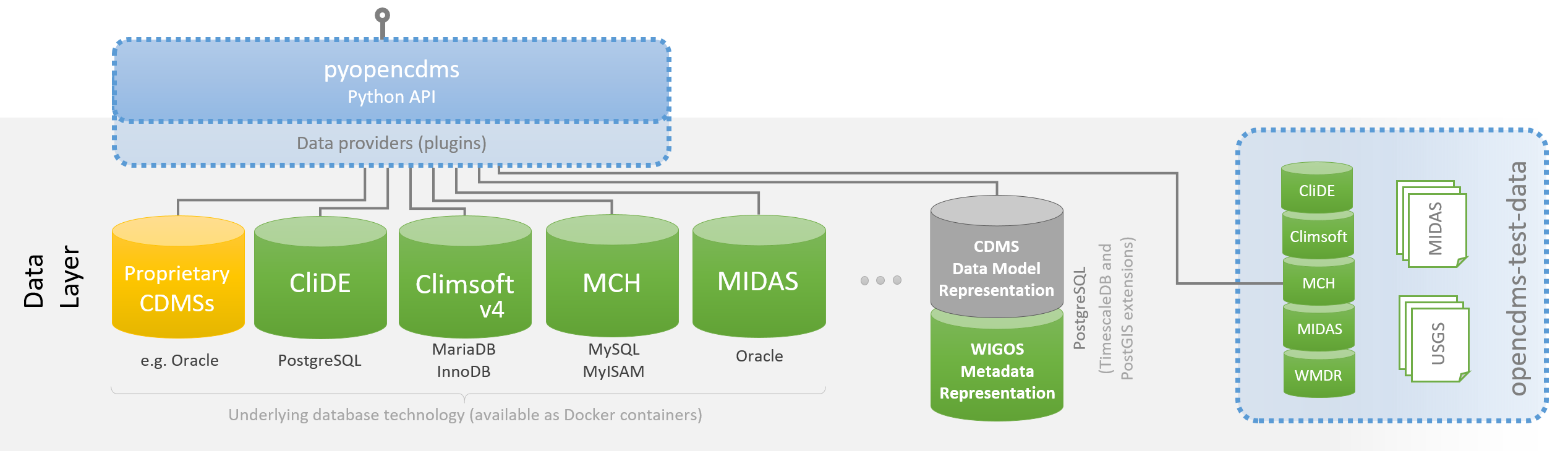
The opencdms-test-data repository will be used as a source of test data for development to ensure interoperability between systems works as intended.
Dependencies
pyopencdms officially supports Python 3.7.1 and above, 3.8, and 3.9 (in line with the Pandas package)
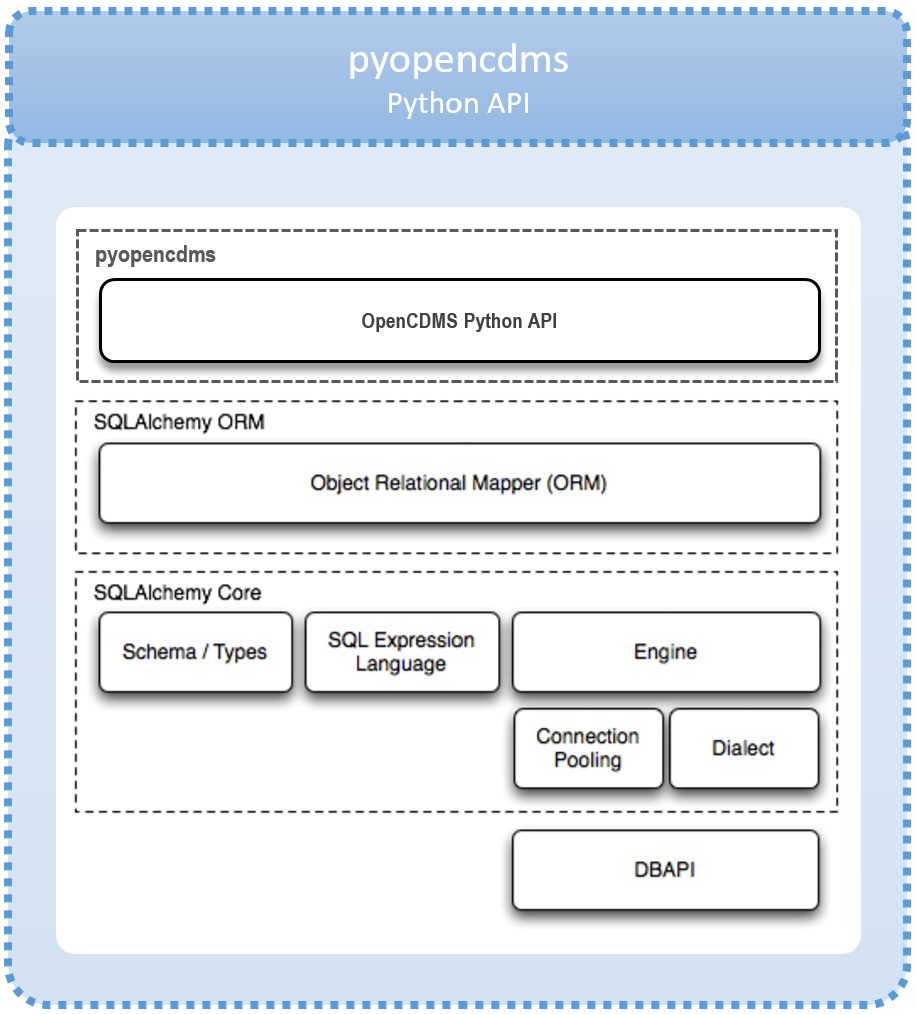
pyopencdms uses SQLAlchemy (2.0-style) to connect to multiple database technologies including PostgreSQL, MySQL/MariaDB, Oracle and SQLite.
It is expected that SQLAlchemy objects, Panda's DataFrames and JSON will be key data types for exchanging data.
Example
- Create a virtual environment for OpenCDMS development
- For Linux users,
pyopencdmsrequires that you install libmysqlclient-dev. (sudo apt install libmysqlclient-dev) - Install dependencies used by
pyopencdms - Clone a copy of the
opencdms-test-datarepository
Example python commands
NOTE: The example below is old and will be updated by the end of 2021.
import os
from pathlib import Path
from opencdms import MidasOpen
# Instead of using a database connection string, the MIDAS Open
# provider requires the root directory for the MIDAS Open data.
connection = os.path.join(Path.home(), 'opencdms-dev', 'git', 'opencdms-test-data', 'opencdms_test_data', 'data')
# All instances of CDMS Providers act as an active session
session = MidasOpen(connection)
filters = {
'src_id': 838,
'period': 'hourly',
'year': 1991,
'elements': ['wind_speed', 'wind_direction'],
}
# Get observations using filters
obs = session.obs(**filters)
# Save observations to CSV file
obs.to_csv('example_observations.csv')
Naming Convention
Data Transfer Object (DTO) naming convention
DTOs reside in opencdms.dtos.{lower_case_provider_name}.{lower_case_model_name}.py files.
Unique ID schema of any model should be in the respective schema file and named UniqueId
Create and Update schema should be in the respective schema file and named:
- Create{model_name_in_models_opencdms.models_module}
- Update{model_name_in_models_opencdms.models_module}
- For DTO used representing original row in database should be named as same as the model name in opencdms.models module.
How to use pyopencdms
After installing pyopencdms the opencdms Python package will be available to import.
Currently, opencdms package has 5 providers:
- mch
- midas_pg
- climsoft
- clide
- opencdms
mch Provider
You can manipulate opencdms.models.mch.english models using mch provider.
Here are some examples:
First set the required environment variables to point to a running instance of mch english database. Below are the default values used in the configuration:
MCH_DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
MCH_DB_PORT=3306
MCH_DB_USER=root
MCH_DB_ENGINE=mysql
MCH_DB_NAME=test
MCH_DB_DRIVER= mysqldb
MCH_DB_PASSWORD=passwordIf you are using opencdms-test-data, you need to set is the appropriate port number and database as used in the docker-compose file.
On linux you can do that by:
$ export MCH_DB_PORT=33306
$ export MCH_DB_NAME=mysql
Then:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from opencdms.utils.db import get_mch_english_connection_string
from opencdms.provider.mch import MCHProvider
db_url = get_mch_english_connection_string()
db_engine = create_engine(db_url)
station_data = dict(
station_id="TEST",
name="Test Station"
)
SessionLocal = sessionmaker(bind=db_engine)
db_session = SessionLocal()
mch_provider = MCHProvider()
# create station
station = mch_provider.create(db_session, "Station", station_data)
# get list of stations
stations = mch_provider.list(db_session, "Station")
# get a single station
station = mch_provider.get(
db_session,
"Station",
{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]}
)
# update a station
mch_provider.update(
db_session,
"Station",
{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]},
{'name': 'Updated Station Name'}
)
# delete a station
deleted = mch_provider.delete(
db_session,
"Station",
{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]}
)Similarly, we can use all other providers except opencdms provider.
Here is an example of opencdms provider
The default connection parameters are:
CLIDE_DB_HOST = 127.0.0.1
CLIDE_DB_PORT = 5432
CLIDE_DB_USER = "postgres"
CLIDE_DB_PASS = "password"
CLIDE_DB_NAME = "postgres"
CLIDE_DB_ENGINE = "postgresql"
If you are using opencdms-test-data, all you need to set is the port number. On linux you can do that by:
$ export CLIDE_DB_PORT=35433
Then:
from opencdms.provider.opencdms import OpenCDMSProvider, ProviderConfig
from tests.unit.dtos.data import station_data
# We are instantiating OpenCDMSProvider where we have enabled clide provider
provider = OpenCDMSProvider(ProviderConfig(enable_clide=True))
# first we create the dependencies StationStatu and StationTimezone Models
station_status = provider.create("StationStatu", {"status": "STATU_123", "description": "Station is active" })
station_statuses = provider.list("StationStatu")
station_tz = provider.create("StationTimezone", {"tm_zone": "GMT", "utc_diff": "0", "description": "London"})
station_tz = provider.list("StationTimezone")
# create station
station = provider.create("Station", station_data)
# get a single station
station = provider.get("Station", {"station_id": station_data["station_id"]})
# get a list of stations
stations = provider.list("Station")
# update a station
provider.update(
"Station",
{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]},
{'region': 'US' }
)
# delete a station
provider.delete(
"Station",
{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]}
)The code above will only manipulate clide models. Notice that, we have not explicitly defined db session. It will be done automatically in OpenCDMSProvider.
On climsoft, on set your database connection varibles:
export CLIMSOFT_DB_PORT=33308
export CLIMSOFT_DB_NAME=mysqlThen:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from opencdms.utils.db import get_climsoft_4_1_1_connection_string
from opencdms.models.climsoft import v4_1_1_core as climsoft
from opencdms.provider.opencdms import OpenCDMSProvider, ProviderConfig
station_data = {
"station_id": 3580,
"station_no": "1SHFY45485HH",
"name": "Test station",
"secondary_name": "Alt test station",
"latitude": 67.111,
"longitude": 128.454,
"elevation": 30,
"region": "UK",
"start_datetime": "2019-01-01",
"end_datetime": "2056-12-31",
"status_id": 1,
"timezone": "UTC",
"country": "England",
"loc_geog_area_id": "SHEL",
"rec_st_ind": 1234
}
climsoft_engine = create_engine(get_climsoft_4_1_1_connection_string())
climsoft.Base.metadata.create_all(bind=climsoft_engine)
provider = OpenCDMSProvider(
ProviderConfig(enable_climsoft=True)
)
station = provider.create("Station", station_data)
stations = provider.list("Station")
station = provider.get("Station",{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]})
station = provider.update("Station",{ "station_id": station_data["station_id"] },{"name": "New name"})
station = provider.delete("Station",{"station_id": station_data["station_id"]})
# Drop all tables
climsoft.Base.metadata.drop_all(bind=climsoft_engine)Let us look at an example where multiple provider is enables.
To run this example using the opencdms-test-data, set the required environment variables:
$ export MCH_DB_PORT=33306
$ export MCH_DB_NAME=mysql
$ export CLIDE_DB_PORT=35433
then:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from opencdms.dtos.clide import station as clide_station
from opencdms.dtos.clide import stationstatu as clide_station_status
from opencdms.dtos.clide import stationtimezone as clide_station_timezone
from opencdms.dtos.mch import station as mch_station
from opencdms.models import clide
from opencdms.models.mch import english as mch
from opencdms.provider.opencdms import OpenCDMSProvider, ProviderConfig
from opencdms.utils.db import get_clide_connection_string, \
get_mch_english_connection_string
timezone_data = dict(
tm_zone="UTC",
utc_diff=0,
description="UTC timezone"
)
station_status_data = dict(
status="ACTIVE",
description="test station status 1"
)
station_data = {
"station_id": 3450,
"station_no": "1SHFY45485HH",
"name": "Test station",
"secondary_name": "Alt test station",
"latitude": 67.111,
"longitude": 128.454,
"elevation": 30,
"region": "UK",
"start_datetime": "2019-01-01",
"end_datetime": "2056-12-31",
"status_id": 1,
"timezone": "UTC",
"country": "England",
"loc_geog_area_id": "SHEL",
"rec_st_ind": 1234
}
CLIDE_DB_URL = get_clide_connection_string()
clide_db_engine = create_engine(CLIDE_DB_URL)
MCH_DB_URL = get_mch_english_connection_string()
mch_db_engine = create_engine(MCH_DB_URL)
mch.Base.metadata.create_all(bind=mch_db_engine)
clide.Base.metadata.create_all(bind=clide_db_engine)
provider = OpenCDMSProvider(
ProviderConfig(enable_mch=True, enable_clide=True)
)
station_status = provider.create("StationStatu", station_status_data)
assert isinstance(
station_status["clide"],
clide_station_status.StationStatu
)
timezone = provider.create("StationTimezone", timezone_data)
assert isinstance(
timezone["clide"],
clide_station_timezone.StationTimezone
)
station_data["timezone"] = timezone["clide"].tm_zone
station_data["status_id"] = station_status["clide"].id
station = provider.create("Station", station_data)
assert isinstance(station["clide"], clide_station.Station)
assert isinstance(station["mch"], mch_station.Station)
station = provider.get(
"Station",
{
"station_id": station_data["station_id"]
}
)
assert isinstance(station["clide"], clide_station.Station)
assert isinstance(station["mch"], mch_station.Station)
stations = provider.list("Station")
for station in stations["clide"]:
assert isinstance(station, clide_station.Station)
for station in stations["mch"]:
assert isinstance(station, mch_station.Station)
station = provider.update(
"Station",
{
"station_id": station_data["station_id"]
},
{
'region': 'US',
"station_no": station_data["station_no"],
"timezone": station_data["timezone"],
"status_id": station_data["status_id"],
"name": "Test station",
"secondary_name": "Alt test station",
"latitude": 67.111,
"longitude": 128.454,
}
)
assert station["clide"].region == 'US'
assert station["mch"].TimeZone == 'UTC'
deleted = provider.delete(
"Station",
{
"station_id": station_data["station_id"]
}
)
assert deleted["clide"]["station_id"] == station_data['station_id']
assert deleted["mch"]["station_id"] == station_data['station_id']
Here we have declared some variables for later use. Then we migrated the database
and created an OpenCDMSProvider with mch and clide provider enabled.
Now, we want to create a station in both of mch and clide. Clide has some
constraint checks before you can create a station. So, we need a station_status_id
and timezone. So, we create those first. When we execute this line
station_status = provider.create("StationStatu", station_status_data)and then print station_status, we get,
{'clide': StationStatu(id=1, status='ACTIVE', description='test station status 1'), 'climsoft': None, 'mch': AttributeError("module 'opencdms.models.mch.english' has no attribute 'StationStatu'"), 'midas': None}Notice that, for clide station_status was created and for mch it threw an error. It's expected
because mch doesn't have station_status.
Then we go ahead and create timezone for clide station and create station.
As, station is both in mch and clide, for both of them it will be created.
station = provider.create("Station", station_data)Now, if we print station, we will see that for both of mch and clide, station was created.
print(station)
{'clide': Station(id=3450, station_no='1SHFY45485HH', status_id=1, time_zone='UTC', region='UK', latitude=None, longitude=None, start_date=None, end_date=None, ht_elev=None), 'climsoft': None, 'mch': Station(Station='3450', StationName='Test station', StationName2=None, TimeZone=None, Longitud=None, Latitud=None), 'midas': None}When we want to get a single station, we do the following:
station = provider.get(
"Station",
{
"station_id": station_data["station_id"]
}
)Here, we have passed a dict for unique_id. This dict should contain all the
attribute name and value that are required by each provider that you have enabled.
Such as, for clide only id is required and for mch only Station is required.
But in the field mapping (opencdms/dtos/clide/station.py::field_mapping and opencdms/dtos/mch/station.py::field_mapping)
for both of clide and mch, the field name is station_id. So, we only passed this
key with value.
If we passed { "station_id": station_data["station_id"], "another_ky": "random_value" }
the opencdms provider would automatically parse the necessary field and discard
everything else.
So, when we instantiate a provider and perform an operation and pass some data to use in that operation,
opencdms only takes the data that are required by each enabled provider, perform the
operation and returns a response in the form:
{
"clide": "a model or list of model/error/None",
"mch": "a model or list of model/error/None",
"midas_pg": "a model or list of model/error/None",
"climsoft": "a model or list of model/error/None"
}Running pygeoapi server
There is a pygeoapi-config.yml and a pygeoapi-openapi.yml file at the root of current directory. You are free to
modify pygeoapi-config.yml and regenerate pygeoapi-openapi.yml.
Follow these steps to regenerate pygeoapi-openapi.yml
$ export $PYGEOAPI_CONFIG='pygeoapi-config.yml'
$ export $PYGEOAPI_OPENAPI='pygeoapi-openapi.yml'
$ pygeoapi openapi generate $PYGEOAPI_CONFIG >| $PYGEOAPI_OPENAPIWhen we generate OpenAPI config file, pygeoapi provider cannot reference the proper schema definition for climsoft provider.
To fix this, we can use opendms cli tool like below
opencdms relocate-schema pygeoapi-openapi.yml climsoft # where pygeoapi-openapi.yml is location of OpenAPI config fileRun this and then to run the pygeoapi server
$ pygeoapi serve


