Chat with LLMs Everywhere
torchchat is a small codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. With torchchat, you can run LLMs using Python, within your own (C/C++) application (desktop or server) and on iOS and Android.
[!IMPORTANT] Update September 25, 2024: torchchat has multimodal support for Llama3.2 11B!!
To try it out, finish the Installation section below, then hop over to our multimodal guide to learn more.
What can you do with torchchat?
- Run models via PyTorch / Python
- Run models on desktop/server without python
- Run models on mobile
- Evaluate a model
Highlights
- [New!!] Multimodal Support for Llama 3.2 11B
- Command line interaction with popular LLMs such as Llama 3, Llama 2, Stories, Mistral and more
- PyTorch-native execution with performance
- Supports popular hardware and OS
- Linux (x86)
- Mac OS (M1/M2/M3)
- Android (Devices that support XNNPACK)
- iOS 17+ and 8+ Gb of RAM (iPhone 15 Pro+ or iPad with Apple Silicon)
- Multiple data types including: float32, float16, bfloat16
- Multiple quantization schemes
- Multiple execution modes including: Python (Eager, Compile) or Native (AOT Inductor (AOTI), ExecuTorch)
Models
The following models are supported by torchchat and have associated aliases.
| Model | Mobile Friendly | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | ✅ | Tuned for chat . Alias to llama3.2-3b. |
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.2-3B | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to llama3.2-3b-base. |
| meta-llama/Llama-Guard-3-1B | ✅ | Tuned for classification . Alias to llama3-1b-guard. |
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | ✅ | Tuned for chat . Alias to llama3.2-1b. |
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.2-1B | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to llama3.2-1b-base. |
| meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct | Multimodal (Image + Text). Tuned for chat . Alias to llama3.2-11B. |
|
| meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision | Multimodal (Image + Text). Tuned for generate . Alias to llama3.2-11B-base. |
|
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | ✅ | Tuned for chat . Alias to llama3.1. |
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to llama3.1-base. |
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct | ✅ | Tuned for chat . Alias to llama3. |
| meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to llama3-base. |
| meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf | ✅ | Tuned for chat. Alias to llama2. |
| meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf | Tuned for chat. Alias to llama2-13b-chat. |
|
| meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-chat-hf | Tuned for chat. Alias to llama2-70b-chat. |
|
| meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to llama2-base. |
| meta-llama/CodeLlama-7b-Python-hf | ✅ | Tuned for Python and generate. Alias to codellama. |
| meta-llama/CodeLlama-34b-Python-hf | ✅ | Tuned for Python and generate. Alias to codellama-34b. |
| mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1 | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to mistral-7b-v01-base. |
| mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1 | ✅ | Tuned for chat. Alias to mistral-7b-v01-instruct. |
| mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 | ✅ | Tuned for chat. Alias to mistral. |
| tinyllamas/stories15M | ✅ | Toy model for generate. Alias to stories15M. |
| tinyllamas/stories42M | ✅ | Toy model for generate. Alias to stories42M. |
| tinyllamas/stories110M | ✅ | Toy model for generate. Alias to stories110M. |
| openlm-research/open_llama_7b | ✅ | Best for generate. Alias to open-llama. |
Installation
The following steps require that you have Python 3.10 installed.
[!TIP] torchchat uses the latest changes from various PyTorch projects so it's highly recommended that you use a venv (by using the commands below) or CONDA.
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/torchchat.git
cd torchchat
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
./install/install_requirements.shCommands
The interfaces of torchchat are leveraged through Python Commands and Native Runners. While the Python Commands are enumerable in the --help menu, the latter are explored in their respective sections.
python3 torchchat.py --help# Output
usage: torchchat [-h] {chat,browser,generate,export,eval,download,list,remove,where,server} ...
positional arguments:
{chat,browser,generate,export,eval,download,list,remove,where,server}
The specific command to run
chat Chat interactively with a model via the CLI
generate Generate responses from a model given a prompt
browser Chat interactively with a model in a locally hosted browser
export Export a model artifact to AOT Inductor or ExecuTorch
download Download model artifacts
list List all supported models
remove Remove downloaded model artifacts
where Return directory containing downloaded model artifacts
server [WIP] Starts a locally hosted REST server for model interaction
eval Evaluate a model via lm-eval
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exitPython Inference (chat, generate, browser, server)
- These commands represent different flavors of performing model inference in a Python enviroment.
- Models are constructed either from CLI args or from loading exported artifacts.
Exporting (export)
- This command generates model artifacts that are consumed by Python Inference or Native Runners.
- More information is provided in the AOT Inductor and ExecuTorch sections.
Inventory Management (download, list, remove, where)
- These commands are used to manage and download models.
- More information is provided in the Download Weights section.
Evaluation (eval)
- This command test model fidelity via EleutherAI's lm_evaluation_harness.
- More information is provided in the Evaluation section.
Download Weights
Most models use Hugging Face as the distribution channel, so you will need to create a Hugging Face account.
Create a Hugging Face user access token as documented here with the write role.
Log into Hugging Face:
huggingface-cli loginTake a look at the available models:
python3 torchchat.py listThen download one for testing (this README uses llama3.1)
python3 torchchat.py download llama3.1[!NOTE] This command may prompt you to request access to Llama 3 via Hugging Face, if you do not already have access. Simply follow the prompts and re-run the command when access is granted.*
Additional Model Inventory Management Commands
### Where This subcommand shows the location of a particular model. ```bash python3 torchchat.py where llama3.1 ``` This is useful in scripts when you do not want to hard-code paths ### Remove This subcommand removes the specified model ```bash python3 torchchat.py remove llama3.1 ``` More information about these commands can be found by adding the `--help` option.Running via PyTorch / Python
The simplest way to run a model in PyTorch is via eager execution. This is the default execution mode for both PyTorch and torchchat. It performs inference without creating exporting artifacts or using a separate runner.
The model used for inference can also be configured and tailored to specific needs (compilation, quantization, etc.). See the customization guide for the options supported by torchchat.
[!TIP] For more information about these commands, please refer to the
--helpmenu.
Chat
This mode allows you to chat with an LLM in an interactive fashion.
python3 torchchat.py chat llama3.1Generate
This mode generates text based on an input prompt.
python3 torchchat.py generate llama3.1 --prompt "write me a story about a boy and his bear"Server
This mode exposes a REST API for interacting with a model. The server follows the OpenAI API specification for chat completions.
To test out the REST API, you'll need 2 terminals: one to host the server, and one to send the request. In one terminal, start the server
python3 torchchat.py server llama3.1In another terminal, query the server using curl. Depending on the model configuration, this query might take a few minutes to respond.
[!NOTE] Since this feature is under active development, not every parameter is consumed. See api/api.py for details on which request parameters are implemented. If you encounter any issues, please comment on the tracking Github issue.
Example Query
Setting `stream` to "true" in the request emits a response in chunks. If `stream` is unset or not "true", then the client will await the full response from the server. **Example Input + Output** [skip default]: begin ``` curl http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "llama3.1", "stream": "true", "max_tokens": 200, "messages": [ { "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant." }, { "role": "user", "content": "Hello!" } ] }' ``` ``` {"response":" I'm a software developer with a passion for building innovative and user-friendly applications. I have experience in developing web and mobile applications using various technologies such as Java, Python, and JavaScript. I'm always looking for new challenges and opportunities to learn and grow as a developer.\n\nIn my free time, I enjoy reading books on computer science and programming, as well as experimenting with new technologies and techniques. I'm also interested in machine learning and artificial intelligence, and I'm always looking for ways to apply these concepts to real-world problems.\n\nI'm excited to be a part of the developer community and to have the opportunity to share my knowledge and experience with others. I'm always happy to help with any questions or problems you may have, and I'm looking forward to learning from you as well.\n\nThank you for visiting my profile! I hope you find my information helpful and interesting. If you have any questions or would like to discuss any topics, please feel free to reach out to me. I"} ``` [skip default]: endBrowser
This command opens a basic browser interface for local chat by querying a local server.
First, follow the steps in the Server section above to start a local server. Then, in another terminal, launch the interface. Running the following will open a tab in your browser.
streamlit run torchchat/usages/browser.pyUse the "Max Response Tokens" slider to limit the maximum number of tokens generated by the model for each response. Click the "Reset Chat" button to remove the message history and start a fresh chat.
Desktop/Server Execution
AOTI (AOT Inductor)
AOTI compiles models before execution for faster inference. The process creates a zipped PT2 file containing all the artifacts generated by AOTInductor, and a .so file with the runnable contents that is then loaded for inference. This can be done with both Python and C++ enviroments.
The following example exports and executes the Llama3.1 8B Instruct model. The first command compiles and performs the actual export.
python3 torchchat.py export llama3.1 --output-aoti-package-path exportedModels/llama3_1_artifacts.pt2[!NOTE] If your machine has cuda add this flag for performance
--quantize torchchat/quant_config/cuda.jsonwhen exporting.
For more details on quantization and what settings to use for your use case visit our customization guide.
Run in a Python Environment
To run in a python enviroment, use the generate subcommand like before, but include the pt2 file.
python3 torchchat.py generate llama3.1 --aoti-package-path exportedModels/llama3_1_artifacts.pt2 --prompt "Hello my name is"Run using our C++ Runner
To run in a C++ enviroment, we need to build the runner binary.
torchchat/utils/scripts/build_native.sh aotiThen run the compiled executable, with the pt2.
cmake-out/aoti_run exportedModels/llama3_1_artifacts.pt2 -z `python3 torchchat.py where llama3.1`/tokenizer.model -l 3 -i "Once upon a time"Mobile Execution
ExecuTorch enables you to optimize your model for execution on a mobile or embedded device.
Set Up ExecuTorch
Before running any commands in torchchat that require ExecuTorch, you must first install ExecuTorch.
To install ExecuTorch, run the following commands. This will download the ExecuTorch repo to ./et-build/src and install various ExecuTorch libraries to ./et-build/install.
[!IMPORTANT] The following commands should be run from the torchchat root directory.
export TORCHCHAT_ROOT=${PWD}
./torchchat/utils/scripts/install_et.shExport for mobile
Similar to AOTI, to deploy onto device, we first export the PTE artifact, then we load the artifact for inference.
The following example uses the Llama3.1 8B Instruct model.
# Export
python3 torchchat.py export llama3.1 --quantize torchchat/quant_config/mobile.json --output-pte-path llama3.1.pte[!NOTE] We use
--quantize torchchat/quant_config/mobile.jsonto quantize the llama3.1 model to reduce model size and improve performance for on-device use cases.
For more details on quantization and what settings to use for your use case visit our customization guide.
Deploy and run on Desktop
While ExecuTorch does not focus on desktop inference, it is capable of doing so. This is handy for testing out PTE models without sending them to a physical device.
Specifically, there are 2 ways of doing so: Pure Python and via a Runner
Deploying via Python
``` # Execute python3 torchchat.py generate llama3.1 --pte-path llama3.1.pte --prompt "Hello my name is" ```Deploying via the c++ Runner
Build the runner ```bash torchchat/utils/scripts/build_native.sh et ``` Execute using the runner ```bash cmake-out/et_run llama3.1.pte -z `python3 torchchat.py where llama3.1`/tokenizer.model -l 3 -i "Once upon a time" ```Deploy and run on iOS
The following assumes you've completed the steps for Setting up ExecuTorch.
Deploying with Xcode
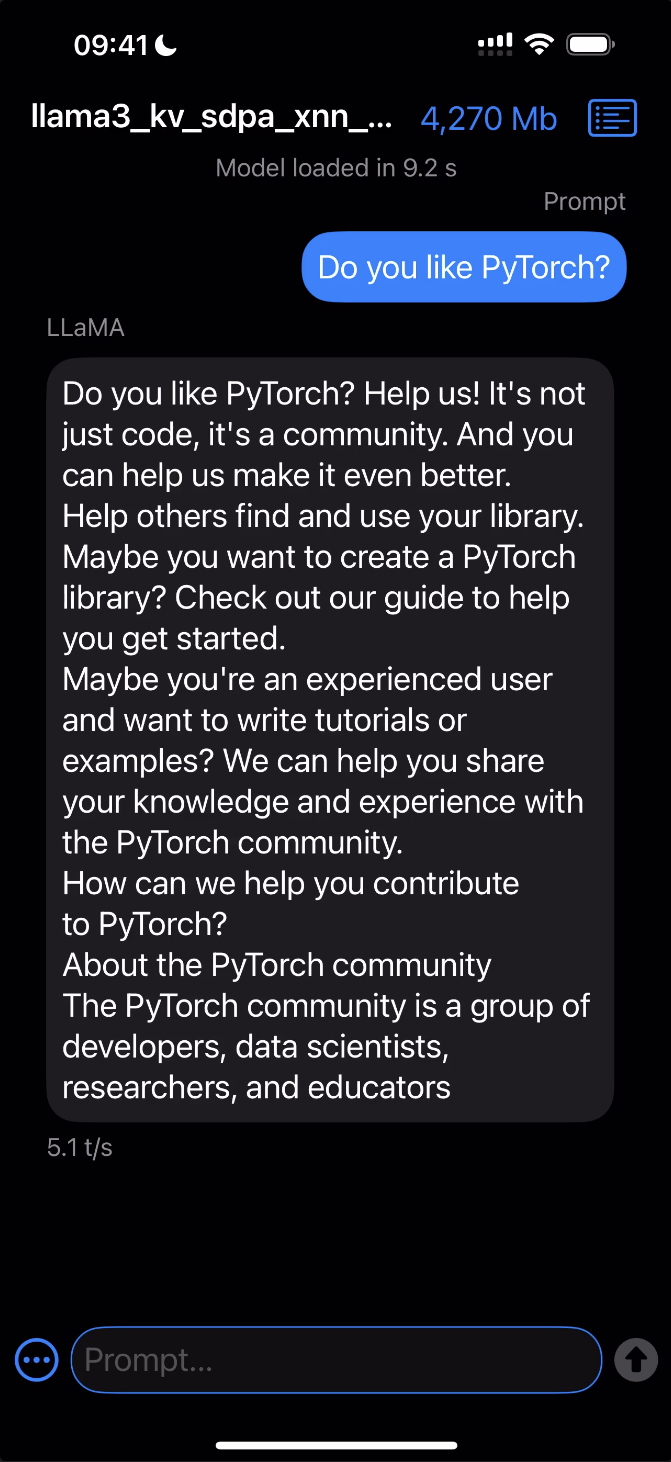
#### Requirements - [Xcode](https://apps.apple.com/us/app/xcode/id497799835?mt=12/) 15.0 or later - [Cmake](https://cmake.org/download/) 3.19 or later - Download and open the macOS `.dmg` installer and move the Cmake app to `/Applications` folder. - Install Cmake command line tools: `sudo /Applications/CMake.app/Contents/bin/cmake-gui --install` - A development provisioning profile with the [`increased-memory-limit`](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/bundleresources/entitlements/com_apple_developer_kernel_increased-memory-limit) entitlement. #### Steps 1. Open the Xcode project: ```bash open et-build/src/executorch/examples/demo-apps/apple_ios/LLaMA/LLaMA.xcodeproj ``` > Note: If you're running into any issues related to package dependencies, close Xcode, clean some of the caches and/or the build products, and open the Xcode project again: > ```bash > rm -rf \ > ~/Library/org.swift.swiftpm \ > ~/Library/Caches/org.swift.swiftpm \ > ~/Library/Caches/com.apple.dt.Xcode \ > ~/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData > ``` 2. Click the Play button to launch the app in the Simulator. 3. To run on a device, ensure you have it set up for development and a provisioning profile with the `increased-memory-limit` entitlement. Update the app's bundle identifier to match your provisioning profile with the required capability. 4. After successfully launching the app, copy the exported ExecuTorch model (`.pte`) and tokenizer (`.model`) files to the iLLaMA folder. You can find the model file called `llama3.1.pte` in the current `torchchat` directory and the tokenizer file at `$(python3 torchchat.py where llama3.1)/tokenizer.model` path. - **For the Simulator:** Drag and drop both files onto the Simulator window and save them in the `On My iPhone > iLLaMA` folder. - **For a device:** Open a separate Finder window, navigate to the Files tab, drag and drop both files into the iLLaMA folder, and wait for the copying to finish. 5. Follow the app's UI guidelines to select the model and tokenizer files from the local filesystem and issue a prompt. *Click the image below to see it in action!*Deploy and run on Android
The following assumes you've completed the steps for Setting up ExecuTorch.
Approach 1 (Recommended): Android Studio
#### Requirements - Android Studio - [Java 17](https://developer.android.com/build/jdks) - [Android SDK 34](https://developer.android.com/about/versions/14/setup-sdk) - [adb](https://developer.android.com/tools/adb) #### Steps 1. Download the AAR file, which contains the Java library and corresponding JNI library, to build and run the app. - [executorch.aar](https://ossci-android.s3.amazonaws.com/executorch/release/executorch-241002/executorch.aar) ([sha256sums](https://ossci-android.s3.amazonaws.com/executorch/release/executorch-241002/executorch.aar.sha256sums)) 2. Move the downloaded AAR file to `torchchat/edge/android/torchchat/app/libs/`. You may need to create directory `torchchat/edge/android/torchchat/app/libs/` if it does not exist. 3. Push the model and tokenizer file to your device. You can find the model file called `llama3.1.pte` in the current `torchchat` directory and the tokenizer file at `$(python3 torchchat.py where llama3.1)/tokenizer.model` path. ``` adb shell mkdir -p /data/local/tmp/llama adb push
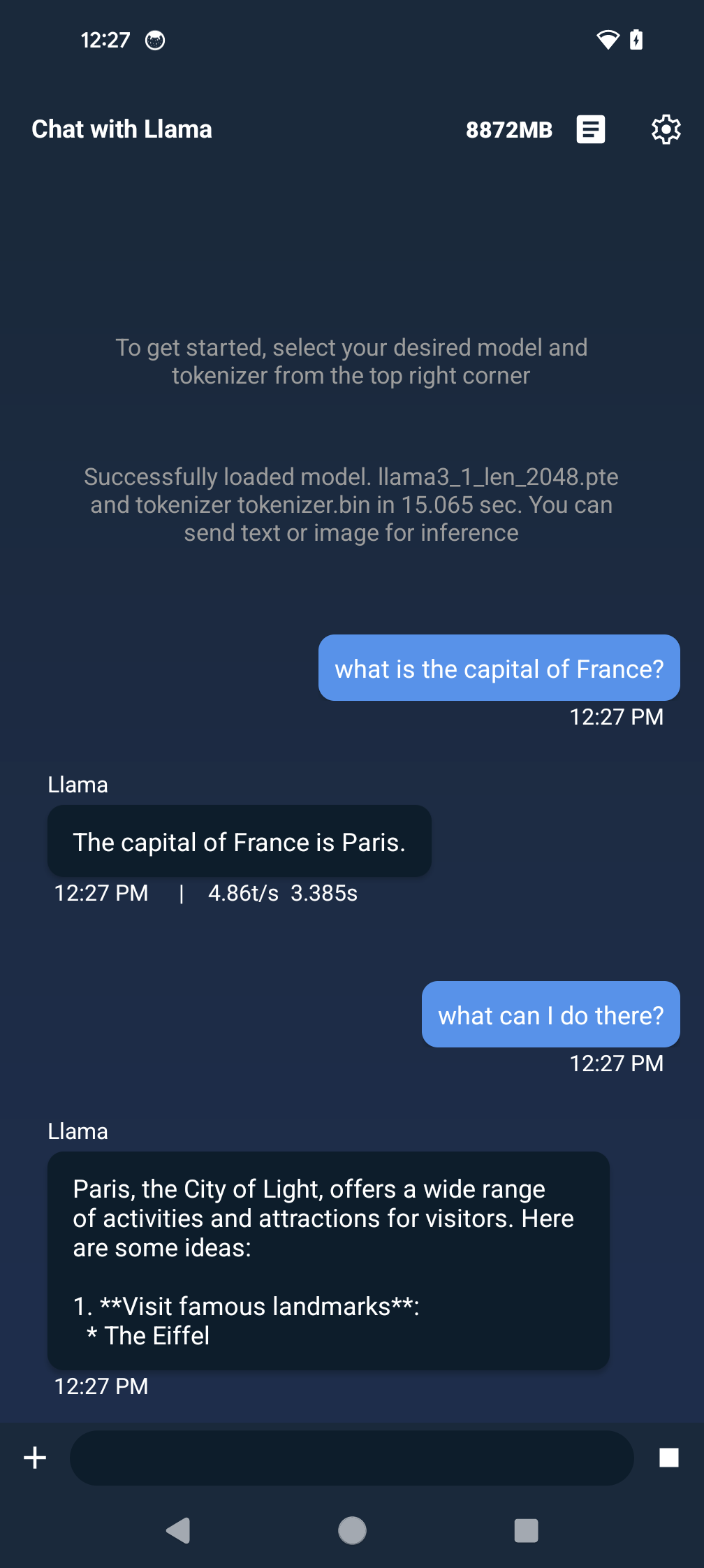
Approach 2: E2E Script
Alternatively, you can run `torchchat/utils/scripts/android_example.sh` which sets up Java, Android SDK Manager, Android SDK, Android emulator (if no physical device is found), builds the app, and launches it for you. It can be used if you don't have a GUI. ``` export TORCHCHAT_ROOT=$(pwd) sh torchchat/utils/scripts/android_example.sh ```Eval
Note: This feature is still a work in progress and not all features are working
Uses the lm_eval library to evaluate model accuracy on a variety of tasks. Defaults to wikitext and can be manually controlled using the tasks and limit args. See Evaluation
Examples
Eager mode:
python3 torchchat.py eval llama3.1 --dtype fp32 --limit 5To test the perplexity for a lowered or quantized model, pass it in the same way you would to generate:
python3 torchchat.py eval llama3.1 --pte-path llama3.1.pte --limit 5Design Principles
torchchat embodies PyTorch’s design philosophy details, especially "usability over everything else".
Native PyTorch
torchchat is a native-PyTorch library. While we provide integrations with the surrounding ecosystem (eg: Hugging Face models, etc), all of the core functionality is written in PyTorch.
Simplicity and Extensibility
torchchat is designed to be easy to understand, use and extend.
- Composition over implementation inheritance - layers of inheritance for code re-use makes the code hard to read and extend
- No training frameworks - explicitly outlining the training logic makes it easy to extend for custom use cases
- Code duplication is preferred over unnecessary abstractions
- Modular building blocks over monolithic components
Correctness
torchchat provides well-tested components with a high-bar on correctness. We provide
- Extensive unit-tests to ensure things operate as they should
Community Contributions
We really value our community and the contributions made by our wonderful users. We'll use this section to call out some of these contributions! If you'd like to help out as well, please see the CONTRIBUTING guide.
To connect with us and other community members, we invite you to join our Slack community by filling out this form. Once you've joined, you can:
- Head to the
#torchchat-generalchannel for general questions, discussion, and community support. - Join the
#torchchat-contributorschannel if you're interested in contributing directly to project development.
Looking forward to discussing with you about torchchat future!
Troubleshooting
A section of commonly encountered setup errors/exceptions. If this section doesn't contain your situation, check the GitHub issues
Model Access
Access to model is restricted and you are not in the authorized list
Some models require an additional step to access. Follow the link provided in the error to get access.
Installing ExecuTorch
Failed Building Wheel
If ./torchchat/utils/scripts/install_et.sh fails with an error like Building wheel for executorch (pyproject.toml) did not run successfully It's possible that it's linking to an older version of pytorch installed some other way like via homebrew. You can break the link by uninstalling other versions such as brew uninstall pytorch Note: You may break something that depends on this, so be aware.
CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED
Run pip install --upgrade certifi.
Filing Issues
If you encounter bugs or difficulty using torchchat, please file an GitHub issue.
Please include the exact command you ran and the output of that command.
Also, run this script and include the output saved to system_info.txt so that we can better debug your issue.
(echo "Operating System Information"; uname -a; echo ""; cat /etc/os-release; echo ""; echo "Python Version"; python --version || python3 --version; echo ""; echo "PIP Version"; pip --version || pip3 --version; echo ""; echo "Installed Packages"; pip freeze || pip3 freeze; echo ""; echo "PyTorch Version"; python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)" || python3 -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"; echo ""; echo "Collection Complete") > system_info.txtDisclaimer
The torchchat Repository Content is provided without any guarantees about performance or compatibility. In particular, torchchat makes available model architectures written in Python for PyTorch that may not perform in the same manner or meet the same standards as the original versions of those models. When using the torchchat Repository Content, including any model architectures, you are solely responsible for determining the appropriateness of using or redistributing the torchchat Repository Content and assume any risks associated with your use of the torchchat Repository Content or any models, outputs, or results, both alone and in combination with any other technologies. Additionally, you may have other legal obligations that govern your use of other content, such as the terms of service for third-party models, weights, data, or other technologies, and you are solely responsible for complying with all such obligations.
Acknowledgements
Thank you to the community for all the awesome libraries and tools you've built around local LLM inference.
-
Georgi Gerganov and his GGML project shining a spotlight on community-based enablement and inspiring so many other projects.
-
Andrej Karpathy and his llama2.c project. So many great (and simple!) ideas in llama2.c that we have directly adopted (both ideas and code) from his repo. You can never go wrong by following Andrej's work.
-
Michael Gschwind, Bert Maher, Scott Wolchok, Bin Bao, Chen Yang, Huamin Li and Mu-Chu Li who built the first version of nanogpt (
DSOGPT) with AOT Inductor proving that AOTI can be used to build efficient LLMs, and DSOs are a viable distribution format for models. nanoGPT. -
Bert Maher and his llama2.so, which built on Andrej's llama2.c and on DSOGPT to close the loop on Llama models with AOTInductor.
-
Christian Puhrsch, Horace He, Joe Isaacson and many more for their many contributions in Accelerating GenAI models in the "Anything, Fast!" pytorch.org blogs, and, in particular, Horace He for GPT, Fast!, which we have directly adopted (both ideas and code) from his repo.
License
torchchat is released under the BSD 3 license. (Additional code in this distribution is covered by the MIT and Apache Open Source licenses.) However you may have other legal obligations that govern your use of content, such as the terms of service for third-party models.