go-financial
This package is a go native port of the numpy-financial package with some additional helper
functions.
The functions in this package are a scalar version of their vectorised counterparts in
the numpy-financial library.
Currently, only some functions are ported,
which are as follows:
| numpy-financial function | go native function ported? | info |
|---|---|---|
| fv | ✅ | Computes the future value |
| ipmt | ✅ | Computes interest payment for a loan |
| pmt | ✅ | Computes the fixed periodic payment(principal + interest) made against a loan amount |
| ppmt | ✅ | Computes principal payment for a loan |
| nper | ✅ | Computes the number of periodic payments |
| pv | ✅ | Computes the present value of a payment |
| rate | ✅ | Computes the rate of interest per period |
| irr | Computes the internal rate of return | |
| npv | ✅ | Computes the net present value of a series of cash flow |
| mirr | Computes the modified internal rate of return |
Index
While the numpy-financial package contains a set of elementary financial functions, this pkg also contains some helper functions on top of it. Their usage and description can be found below:
- Amortisation(Generate Table)
- Fv(Future value)
- Pv(Present value)
- Npv(Net present value)
- Pmt(Payment)
- IPmt(Interest Payment)
- PPmt(Principal Payment)
- Nper(Number of payments)
-
Detailed documentation is available at godoc.
Amortisation(Generate Table)
To generate the schedule for a loan of 20 lakhs over 15years at 12%p.a., you can do the following:
package main
import (
"time"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
financial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/frequency"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/interesttype"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
)
func main() {
loc, err := time.LoadLocation("Asia/Kolkata")
if err != nil {
panic("location loading error")
}
currentDate := time.Date(2009, 11, 11, 4, 30, 0, 0, loc)
config := financial.Config{
// start date is inclusive
StartDate: currentDate,
// end date is inclusive.
EndDate: currentDate.AddDate(15, 0, 0).AddDate(0, 0, -1),
Frequency: frequency.ANNUALLY,
// AmountBorrowed is in paisa
AmountBorrowed: decimal.NewFromInt(200000000),
// InterestType can be flat or reducing
InterestType: interesttype.REDUCING,
// interest is in basis points
Interest: decimal.NewFromInt(1200),
// amount is paid at the end of the period
PaymentPeriod: paymentperiod.ENDING,
// all values will be rounded
EnableRounding: true,
// it will be rounded to nearest int
RoundingPlaces: 0,
// no error is tolerated
RoundingErrorTolerance: decimal.Zero,
}
amortization, err := financial.NewAmortization(&config)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
rows, err := amortization.GenerateTable()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// Generates json output of the data
financial.PrintRows(rows)
// Generates a html file with plots of the given data.
financial.PlotRows(rows, "20lakh-loan-repayment-schedule")
}
Generated plot
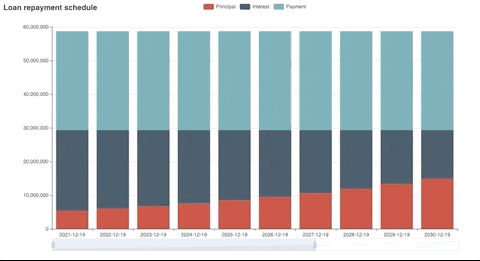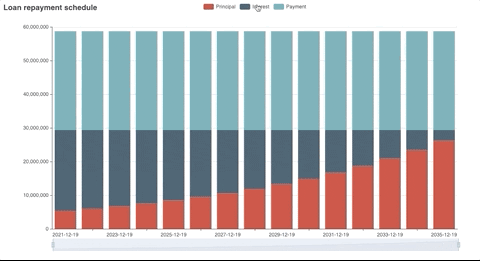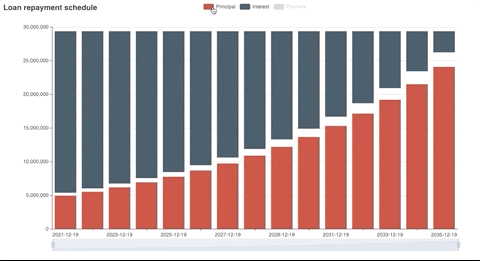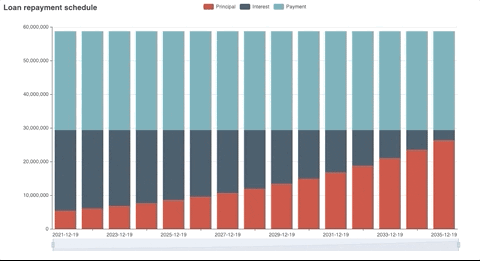
Fv
func Fv(rate decimal.Decimal, nper int64, pmt decimal.Decimal, pv decimal.Decimal, when paymentperiod.Type) decimal.Decimal Params:
pv : a present value
rate : an interest rate compounded once per period
nper : total number of periods
pmt : a (fixed) payment, paid either at the beginning (when = 1)
or the end (when = 0) of each period
when : specification of whether payment is made at the beginning (when = 1)
or the end (when = 0) of each period Fv computes future value at the end of some periods(nper).
Example(Fv)
If an investment has a 6% p.a. rate of return, compounded annually, and you are investing ₹ 10,000 at the end of each year with initial investment of ₹ 10,000, how much amount will you get at the end of 10 years ?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.06)
nper := int64(10)
payment := decimal.NewFromInt(-10000)
pv := decimal.NewFromInt(-10000)
when := paymentperiod.ENDING
fv := gofinancial.Fv(rate, nper, payment, pv, when)
fmt.Printf("fv:%v", fv.Round(0))
// Output:
// fv:149716
}Pv
func Pv(rate decimal.Decimal, nper int64, pmt decimal.Decimal, fv decimal.Decimal, when paymentperiod.Type) decimal.Decimal Params:
fv : a future value
rate : an interest rate compounded once per period
nper : total number of periods
pmt : a (fixed) payment, paid either
at the beginning (when = 1) or the end (when = 0) of each period
when : specification of whether payment is made
at the beginning (when = 1) or the end
(when = 0) of each periodPv computes present value some periods(nper) before the future value.
Example(Pv)
If an investment has a 6% p.a. rate of return, compounded annually, and you wish to possess ₹ 1,49,716 at the end of 10 peroids while providing ₹ 10,000 per period, how much should you put as your initial deposit ?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.06)
nper := int64(10)
payment := decimal.NewFromInt(-10000)
fv := decimal.NewFromInt(149716)
when := paymentperiod.ENDING
pv := gofinancial.Pv(rate, nper, payment, fv, when)
fmt.Printf("pv:%v", pv.Round(0))
// Output:
// pv:-10000
}Npv
func Npv(rate decimal.Decimal, values []decimal.Decimal) decimal.Decimal Params:
rate : a discount rate compounded once per period
values : the value of the cash flow for that time period. Values provided here must be an array of float64Npv computes net present value based on the discount rate and the values of cash flow over the course of the cash flow period
Example(Npv)
Given a rate of 0.281 per period and initial deposit of 100 followed by withdrawls of 39, 59, 55, 20. What is the net present value of the cash flow ?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.281)
values := []decimal.Decimal{decimal.NewFromInt(-100), decimal.NewFromInt(39), decimal.NewFromInt(59), decimal.NewFromInt(55), decimal.NewFromInt(20)}
npv := gofinancial.Npv(rate, values)
fmt.Printf("npv:%v", npv)
// Output:
// npv: -0.008478591638426
}Pmt
func Pmt(rate decimal.Decimal, nper int64, pv decimal.Decimal, fv decimal.Decimal, when paymentperiod.Type) decimal.DecimalParams:
rate : rate of interest compounded once per period
nper : total number of periods to be compounded for
pv : present value (e.g., an amount borrowed)
fv : future value (e.g., 0)
when : specification of whether payment is made at the
beginning (when = 1) or the end (when = 0) of each period Pmt compute the fixed payment(principal + interest) against a loan amount ( fv = 0).
It can also be used to calculate the recurring payments needed to achieve a certain future value given an initial deposit,
a fixed periodically compounded interest rate, and the total number of periods.
Example(Pmt-Loan)
If you have a loan of 1,00,000 to be paid after 2 years, with 18% p.a. compounded annually, how much total payment will you have to do each month? This example generates the total monthly payment(principal plus interest) needed for a loan of 1,00,000 over 2 years with 18% rate of interest compounded monthly
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.18 / 12)
nper := int64(12 * 2)
pv := decimal.NewFromInt(100000)
fv := decimal.NewFromInt(0)
when := paymentperiod.ENDING
pmt := gofinancial.Pmt(rate, nper, pv, fv, when)
fmt.Printf("payment:%v", pmt.Round(0))
// Output:
// payment:-4992
}Example(Pmt-Investment)
If an investment gives 6% rate of return compounded annually, how much amount should you invest each month to get 10,00,000 amount after 10 years?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.06)
nper := int64(10)
pv := decimal.NewFromInt(0)
fv := decimal.NewFromInt(1000000)
when := paymentperiod.BEGINNING
pmt := gofinancial.Pmt(rate, nper, pv, fv, when)
fmt.Printf("payment each year:%v", pmt.Round(0))
// Output:
// payment each year:-71574
}IPmt
func IPmt(rate decimal.Decimal, per int64, nper int64, pv decimal.Decimal, fv decimal.Decimal, when paymentperiod.Type) decimal.Decimal IPmt computes interest payment for a loan under a given period.
Params:
rate : rate of interest compounded once per period
per : period under consideration
nper : total number of periods to be compounded for
pv : present value (e.g., an amount borrowed)
fv : future value (e.g., 0)
when : specification of whether payment is made at the
beginning (when = 1) or the end (when = 0) of each period Example(IPmt-Loan)
If you have a loan of 1,00,000 to be paid after 2 years, with 18% p.a. compounded annually, how much of the total payment done each month will be interest ?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.18 / 12)
nper := int64(12 * 2)
pv := decimal.NewFromInt(100000)
fv := decimal.NewFromInt(0)
when := paymentperiod.ENDING
for i := int64(0); i < nper; i++ {
ipmt := gofinancial.IPmt(rate, i+1, nper, pv, fv, when)
fmt.Printf("period:%d interest:%v\n", i+1, ipmt.Round(0))
}
// Output:
// period:1 interest:-1500
// period:2 interest:-1448
// period:3 interest:-1394
// period:4 interest:-1340
// period:5 interest:-1286
// period:6 interest:-1230
// period:7 interest:-1174
// period:8 interest:-1116
// period:9 interest:-1058
// period:10 interest:-999
// period:11 interest:-939
// period:12 interest:-879
// period:13 interest:-817
// period:14 interest:-754
// period:15 interest:-691
// period:16 interest:-626
// period:17 interest:-561
// period:18 interest:-494
// period:19 interest:-427
// period:20 interest:-358
// period:21 interest:-289
// period:22 interest:-218
// period:23 interest:-146
// period:24 interest:-74
}Example(IPmt-Investment)
If an investment gives 6% rate of return compounded annually, how much interest will you earn each year against your yearly payments(71574) to get 10,00,000 amount after 10 years
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.06)
nper := int64(10)
pv := decimal.NewFromInt(0)
fv := decimal.NewFromInt(1000000)
when := paymentperiod.BEGINNING
for i := int64(1); i < nper+1; i++ {
ipmt := gofinancial.IPmt(rate, i+1, nper, pv, fv, when)
fmt.Printf("period:%d interest earned:%v\n", i, ipmt.Round(0))
}
// Output:
// period:1 interest earned:4294
// period:2 interest earned:8846
// period:3 interest earned:13672
// period:4 interest earned:18786
// period:5 interest earned:24208
// period:6 interest earned:29955
// period:7 interest earned:36047
// period:8 interest earned:42504
// period:9 interest earned:49348
// period:10 interest earned:56604
}PPmt
func PPmt(rate decimal.Decimal, per int64, nper int64, pv decimal.Decimal, fv decimal.Decimal, when paymentperiod.Type) decimal.Decimal PPmt computes principal payment for a loan under a given period.
Params:
rate : rate of interest compounded once per period
per : period under consideration
nper : total number of periods to be compounded for
pv : present value (e.g., an amount borrowed)
fv : future value (e.g., 0)
when : specification of whether payment is made at
the beginning (when = 1) or the end (when = 0) of each period Example(PPmt-Loan)
If you have a loan of 1,00,000 to be paid after 2 years, with 18% p.a. compounded annually, how much total payment done each month will be principal ?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.18 / 12)
nper := int64(12 * 2)
pv := decimal.NewFromInt(100000)
fv := decimal.NewFromInt(0)
when := paymentperiod.ENDING
for i := int64(0); i < nper; i++ {
ppmt := gofinancial.PPmt(rate, i+1, nper, pv, fv, when)
fmt.Printf("period:%d principal:%v\n", i+1, ppmt.Round(0))
}
// Output:
// period:1 principal:-3492
// period:2 principal:-3545
// period:3 principal:-3598
// period:4 principal:-3652
// period:5 principal:-3707
// period:6 principal:-3762
// period:7 principal:-3819
// period:8 principal:-3876
// period:9 principal:-3934
// period:10 principal:-3993
// period:11 principal:-4053
// period:12 principal:-4114
// period:13 principal:-4176
// period:14 principal:-4238
// period:15 principal:-4302
// period:16 principal:-4366
// period:17 principal:-4432
// period:18 principal:-4498
// period:19 principal:-4566
// period:20 principal:-4634
// period:21 principal:-4704
// period:22 principal:-4774
// period:23 principal:-4846
// period:24 principal:-4919
}Nper
func Nper(rate decimal.Decimal, pmt decimal.Decimal, pv decimal.Decimal, fv decimal.Decimal, when paymentperiod.Type) (result decimal.Decimal, err error) Params:
rate : an interest rate compounded once per period
pmt : a (fixed) payment, paid either at the beginning (when = 1)
or the end (when = 0) of each period
pv : a present value
fv : a future value
when : specification of whether payment is made at the beginning (when = 1)
or the end (when = 0) of each period Nper computes the number of periodic payments.
Example(Nper-Loan)
If a loan has a 6% annual interest, compounded monthly, and you only have \$200/month to pay towards the loan, how long would it take to pay-off the loan of \$5,000?
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
rate := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.06 / 12)
fv := decimal.NewFromFloat(0)
payment := decimal.NewFromFloat(-200)
pv := decimal.NewFromFloat(5000)
when := paymentperiod.ENDING
nper,err := gofinancial.Nper(rate, payment, pv, fv, when)
if err != nil{
fmt.Printf("error:%v\n", err)
}
fmt.Printf("nper:%v",nper.Ceil())
// Output:
// nper:27
}Rate
func Rate(pv, fv, pmt decimal.Decimal, nper int64, when paymentperiod.Type, maxIter int64, tolerance, initialGuess decimal.Decimal) (decimal.Decimal, error) Params:
pv : a present value
fv : a future value
pmt : a (fixed) payment, paid either at the beginning (when = 1)
or the end (when = 0) of each period
nper : total number of periods to be compounded for
when : specification of whether payment is made at the beginning (when = 1)
or the end (when = 0) of each period
maxIter : total number of iterations for which function should run
tolerance : tolerance threshold for acceptable result
initialGuess : an initial guess amount to start fromReturns:
rate : a value for the corresponding rate
error : returns nil if rate difference is less than the threshold (returns an error conversely)Rate computes the interest rate to ensure a balanced cashflow equation
Example(Rate-Investment)
If an investment of $2000 is done and an amount of $100 is added at the start of each period, for what periodic interest rate would the invester be able to withdraw $3000 after the end of 4 periods ? (assuming 100 iterations, 1e-6 threshold and 0.1 as initial guessing point)
package main
import (
"fmt"
gofinancial "github.com/razorpay/go-financial"
"github.com/razorpay/go-financial/enums/paymentperiod"
"github.com/shopspring/decimal"
)
func main() {
fv := decimal.NewFromFloat(-3000)
pmt := decimal.NewFromFloat(100)
pv := decimal.NewFromFloat(2000)
when := paymentperiod.BEGINNING
nper := decimal.NewFromInt(4)
maxIter := 100
tolerance := decimal.NewFromFloat(1e-6)
initialGuess := decimal.NewFromFloat(0.1),
rate, err := gofinancial.Rate(pv, fv, pmt, nper, when, maxIter, tolerance, initialGuess)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf(err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("rate: %v ", rate)
}
// Output:
// rate: 0.06106257989825202
}
