
Welcome to VerilogCreator
VerilogCreator is a QtCreator plugin. It turns QtCreator into a Verilog 2005 IDE.
The plugin is still work in progress, but it already has enough functionality to analyze existing code bases or to develop new code. The current version supports Verilog 2005 syntax checking/coloring and semantic code navigation/highlighting; there are build configurations for Icarus, Verilator, Yosys and Tcl. Projects can be configured using a file format similar to qmake.
Implemented Features
- Syntax highlighting (including ifdefed out blocks and markers)
- Context sensitive code completer, see screenshot
- Inline code warnings and errors
- Parentheses and begin/end block matching/navigation
- Hover tooltips
- Follow symbol under cursor, follow includes (multi-file support)
- Show where a symbol is used
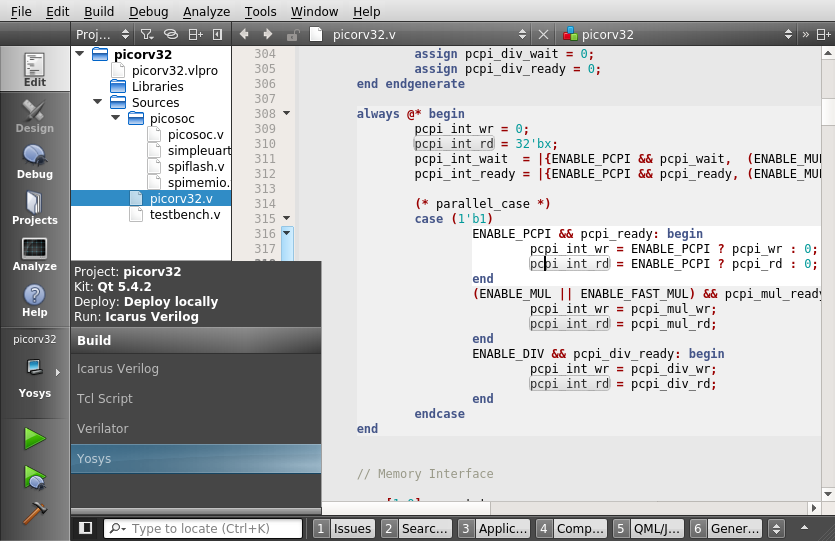
- Drop-down menu to jump to modules, module instances, functions and tasks in current file
- Outline view; see screenshot
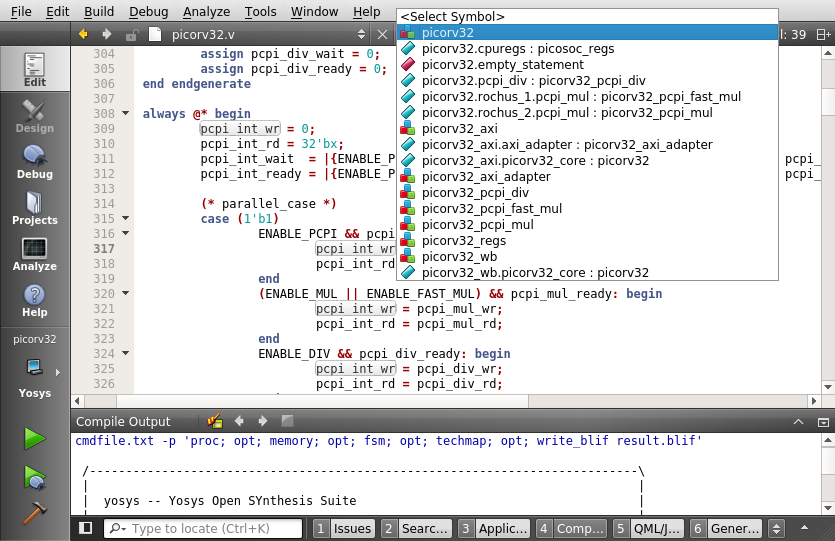
- Module locator (global) and symbol locator (current document); see screenshot 1 and screenshot 2
- Syntax based code folding and some other features supported by QtCreator, see http://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/
- Marker based code folding (MBCF); use section markers like //{ and //}, or //> and //<; see screenshot 1 and screenshot 2
- Project file to configure source files, include dirs, defines and libraries
- Icarus Verilog build and run configuration; directly run compiler and simulator from within QtCreator
- Verilator and Yosys build configurations; generate command files, optional arguments
- Build configuration based on custom Tcl scripts which can access project configuration (e.g. to run Vivado commands)
- Selected optional SystemVerilog syntax extensions such as assert, assume, cover and restrict (see here for more information)
- Supports Standard Delay Format (SDF) files with syntax highlighting, see screenshot
Project file format
VerilogCreator can either open single verilog files or project configuration files with the suffix ".vlpro".
The vlpro file can be empty; in that case all Verilog files (default suffix ".v") located in the vlpro directory including subdirectories are assumed to be the source files of the project.
Vlpro files follow the same syntax as QtCreator pro files (see http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qmake-project-files.html), but uses other variable names. The following variables are supported:
SRCFILES += /path/filename.v
SRCFILES += "/path with whitespace/filename.v"
SRCFILES += /firstpath/filename.v /secondpath/filename.v \
/thirdpath_on_new_line/filename.vSRCFILES += /directory_path1/ filename1.v filename2.v /directory_path2/ filename3.v filename4.v
The variable SRCFILES lets you add source files explicitly to your project. There are different syntax versions. You can add filenames with absolute or relative paths; if you add a directory path only then the following filenames are assumed to belong to the directory with the given path.
Note that path/filenames including whitespace have to be quoted by " ". Also note that you can add more than one element to a line separated by whitespace and that a \ lets you continue on the next line; this applies to all variables.
SRCEXT = .v .vl .verilog
The SRCEXT variable can be used to override the expected suffix of verilog files. Default is ".v".
SRCDIRS += dirpath1 dirpath2 dirpath3*
SRCDIRS += dirpath4 -filename1 -filename2 dirpath5 -filename3
With the SRCDIRS variable it is possible to add all verilog files in a given directory. All files with a suffix specified in SRCEXT are considered. There are different syntax versions. You can add directories with absolute or relative path. If you postfix the path with an "*" then also all subdirectories are implicitly added. If you want to leave out certain files add the filename to the line prefixed with "-".
LIBFILES +=
LIBDIRS +=
LIBEXT =
These variables are used the same way as their SRC counterparts. Use them to add Verilog files which are used but not modified by the present project.
INCDIRS += dirpath1 dirpath2
The variable INCDIRS specifies where the parser looks for include files (included by the Verilog include compiler directive).
DEFINES += DISABLE_SV_ASSERTION "E203_PC_SIZE 24"
This has the same effect as the Verilog include compiler directive and affects all files. Note that also the syntax corresponds to Verilog defines; since Verilog uses whitespace to separate name and values you have to use quotes in the vlpro file.
There is also a variable BUILD_UNDEFS by which defines can be deactivated in the command file generated for Icarus, Verilator and Yosys; you could for example define VERILATOR in the vlpro so VerilogCreator can see it but then use BUILD_UNDEFS = VERILATOR to avoid define warnings in Verilator.
TOPMOD = picosoc
Use TOPMOD to explicitly set the top-level module; this is useful in case there is more than one top-level module in the code base. VerilogCreator does not use this information but hands it over to Icarus, Verilator and Yosys.
SVEXT =
This variable is used to tell the parser which files should be considered SystemVerilog files; default is ".sv"; the parser will enable the SV extension for these files in any case, regardless of the UseSvExtension option.
CONFIG += UseSvExtension
Use this option to enable the SystemVerilog extension for the whole project. Without this option, all files are assumed to be in Verilog 05 format besides the files whose suffix corresponds to one in SVEXT. With the option enabled all files are assumed to be in the supported SystemVerilog 2012 subset.
OTHER_FILES +=
The variable OTHER_FILES lets you add other than source or library files (e.g. SDF files) to your project. The syntax and semantics are the same as with SRCFILES.
Supported SystemVerilog subset
If enabled (see the SVEXT and UseSvExtension project file options) the VerilogCreator plugin supports the following subset of SystemVerilog as specified in IEEE 1800-2012:
- assert_property_statement, simple_immediate_assert_statement and deferred_immediate_assert_statement
- assume_property_statement, simple_immediate_assume_statement and deferred_immediate_assume_statement
- cover_sequence_statement, cover_property_statement, simple_immediate_cover_statement and deferred_immediate_cover_statement
- restrict_property_statement
- deferred_immediate_assertion_item
- concurrent_assertion_item
- property_spec, without property_instance, checker_instantiation
- sequence_expr, without sequence_abbrev, sequence_match_item, first_match
Download Binaries
Pre-compiled versions of the VerilogCreator plugin can be downloaded for Windows, Linux and Macintosh as part of the QtcVerilog application.
See here to learn more: https://github.com/rochus-keller/QtcVerilog/blob/master/README.md
Build Steps
Follow these steps if you want to build VerilogCreator yourself:
- Make sure that QtCreator and the Qt base development package are installed on your system. VerilogCreator was developed and tested with QtCreator 3.4 and Qt 5.4 on Linux. It also compiles with QtCreator 3.6 and Qt 5.7, but not (yet) with QtCreator 4.x (see below). Instead of using QtCreator, you can also use QtcVerilog (see https://github.com/rochus-keller/QtcVerilog).
- Create a build directory; let's call it BUILD_DIR
- Download the VerilogCreator source code from https://github.com/rochus-keller/VerilogCreator/archive/master.zip and unpack it to the BUILD_DIR; rename the subdirectory to "VerilogCreator".
- Download the Verilog parser source code from https://github.com/rochus-keller/Verilog/archive/master.zip and unpack it to the BUILD_DIR; rename "Verilog-Master" to "Verilog".
- Download the Sdf parser source code from https://github.com/rochus-keller/Sdf/archive/master.zip and unpack it to the BUILD_DIR; rename "Sdf-Master" to "Sdf".
- Download the appropriate version of the QtCreator source code from https://download.qt.io/official_releases/qtcreator/ and unpack it to the BUILD_DIR. Instead of the QtCreator source code you can also use the QtcCreator source code (see https://github.com/rochus-keller/QtcVerilog).
- In case you don't have the Tcl development package installed: download http://software.rochus-keller.ch/tcl_headers.zip and unpack it to BUILD_DIR/tcl.
- Either set the QTC_SOURCE (path to the QtCreator/QtcVerilog source code directory) and QTC_BUILD (path to the QtCreator/QtcVerilog installation directory) environment variables or directly modify the QTCREATOR_SOURCES and IDE_BUILD_TREE variables in VerilogCreator.pro.
- Goto the BUILD_DIR/VerilogCreator subdirectory and execute
QTDIR/bin/qmake VerilogCreator.pro(see the Qt documentation concerning QTDIR). - Run make; after a couple of minutes the plugin is compiled and automatically deployed to the local QtCreator plugin directory (on Linux to ~/.local/share/data/QtProject/qtcreator/plugins/x.y.z/libVerilogCreator.so) or directly to QtcVerilog.
- Start QtCreator/QtcVerilog and check in the "Help/About Plugins..." dialog (section "Other Languages") that the plugin is activated.
Instead of using qmake and make you can open VerilogCreator.pro using QtCreator and build it there.
Note that on Windows you also have to compile QtCreator/QtcVerilog itself because you also need the lib files for the plugin dll's (i.e. Core.lib, TextEditor.lib and ProjectExplorer.lib). Compiling QtCreator is not an easy task; compiling QtcVerilog is much easier.
State of Development
Even though I'm using Qt for twenty years and QtCreator for ten years this is my first noteworthy QtCreator plugin. Of course I read all available documentation and watched all available lectures. But still the available information is very sparse, of lesser quality than the Qt documentation and often outdated. So I had to invest half the development time in reverse engineering of the QtCreator 3.4 source code. I don't use QtCreator 4.x yet because I'm working on Ubuntu LTS versions which only have QtCreator 3.x packages and also because I'm fully satisfied with 3.x and the more recent versions run slower and consume more resources.
I'm aware of the Binary and Source Compatibility rules of QtCreator plugins and managed to make the source code compatible with QtCreator 3.4.x to the latest 3.6.1 using ifdefs. But in QtCreator 4.x they not only have changed some function signatures, but also the architecture to a considerable extent. According to my current state of investigation, managing compatibility with a few ifdefs is no longer feasible; instead it seems necessary to maintain different codebases in parallel to be compatible with both QtCreator 3.x and 4.x and cope with the different architectures at the same time. Thus the question arises whether using QtCreator as the basis for the Verilog IDE is an advantage or rather a disadvantage. If you know a better work-around, please send me an email.
All in all it is now clear to me why there are comparatively few plugins for QtCreator in all these years and most of them come directly from the Qt Company. Source and binary compatibility between QtCreator versions is not only complex, but a full-blown nightmare. All the more annoying that many changes to the API seem to be purely cosmetic in nature. Unfortunately, you only realize the size and consequences of this problem when you have developed a sufficiently large plugin yourself and built it for several versions of QtCreator, unless you know the source code of QtCreator very well in several versions, which might only be the case for a few people.
Since I currently consider the effort to reverse engineer each QtCreator version anew and to develop different variants of the code in parallel to be too high, I do it the other way round: instead of adapting the plugin to each major and minor QtCreator version, I offer a simple binary deployment for Linux, Windows and Mac of a lean QtCreator version including VerilogCreator and some other minimal required plugins. See here to learn more: https://github.com/rochus-keller/QtcVerilog.
To do's
- Documentation
- Semantic indenter (the current one simply adjusts to the previous line)
- Parse output of Icarus/Verilator/Yosys and post it to the Issues pane
- Implement wizzard to add or import files, generate stub modules and automatically update the vlpro file
- Improve hover text
- Implement options dialog (format settings, paths, etc.)
- Improve code completer (for hierarchical identifiers)
- Integrate wave viewer
- Extend SystemVerilog support, goal is to support everything Verilator does.
Support
If you need support or would like to post issues or feature requests please use the Github issue list at https://github.com/rochus-keller/VerilogCreator/issues or send an email to the author.