OGN-Basestation
Groundstation for Open Glider Network with ESP32
The aim of this project is to create a simple base station for the OGN network. The SoftRF project was used as the base. Thanks to Linar Yusupov for this work!
A TTGO T-Beam (SoftRF Prime Edition MkII) is used as hardware, which has Wifi, Bluetooth, U-Blox GPS and a LoraWan chip.
The TT-Beam does not need another computer (Raspberry) and sends the APRS messages directly into the Open Glider network. Only WiFi and callsign have to be configured, the position is determined via gps.
Since the T-Beam is very energy-saving, it can be operated very easily on a battery with solar panels.
There are also a few drawbacks to the traditional OGN receivers. Several protocols cannot be decoded at the same time (at the moment - second protocol has no function).
Harwdare
- LILYGO TTGO T-Beam (Lora, GPS, Bluetooth, Wifi, OLED)
- TTGO LoRa32 (Lora, Bluetooth, Wifi, OLED)
Features:
- Power consumption around 20 mA in sleep mode - 120mA on normal mode
- 40 - 60 mA without GPS
- OLED status messages
- ntp time sync - no gps needed
- Deep Sleep (only TTGO)
- Auto wakeup on RX packages
- Wakeup Timer
- No additional computer necessary - only Wifi ;
- Ideal for solar and battery supply
- low cost hardware
- Frequency hopping in legacy mode and ogn (868.2 / 868.4) - Thanks Nick
- needs GPS fix
- Relay function - send data over air to basestation (2 TTGO/TBEAM needed)
- Private mode - encrypt FANET data with you own key
- modified SoftRF needed
Planed Features
- Protocol hopping - aprs messages are sent every 5 seconds - in progress
- there should be enough time to decode a second protocol
- ADS-B decoder
- we still need some hardware - in progress
- send APRS messages over LoraWan
- new binary protocol
- send Fanet service data
- new binary protocol
- Plutonium battery for a life of 100 years
Features in TESTING
For features in testing set testmode=1 in config.json.
New binary protocol (NBP) V0.1.0-24
APRS is not a particularly good protocol for low data rates. In addition, TCP is used in the OGN network, which makes little sense. Position data from aircraft are real-time data.
For this reason I have implemented a new binary protocol based on flatbuffers. A proxy that converts the binary data into APRS messages and sends them to the OGN is in progress. For testing, take a look at tools udp_server_nbp.py.
In the future, the ground station can be controlled using this protocol. This makes it possible to send a mass configuration to several stations.
NBP can also be encrypted. V0.1.0-25
Packet validation in LEGACY mode V0.1.0-24
It is possible that a legacy packet is marked as valid by the crc check, although it is damaged. This can result in position jumps. A new validation routine was built in, which checks whether a position package can be valid based on the speed and position of the aircraft.
ESP will calculate the flight distance from last two position packets and check if its possible with time and speed. Minimum two packets must be received and validated, otherwise position data not transmitted to ogn.
Private network - V0.1.0-25
RF position packets AES128 encrypted
- needs new binary protocol
- needs modified SoftRF version
- needs proxy
- only at FANET protocol
Precise instructions and a modified SoftRF version will follow.
Relay function - V0.1.0-28
If no internet connection is available, send received data to ogn base, base will transmit packets to ogn.
- relay protocol based on fanet
- 2 devices needed - 1 Relay - 1 Basestation (Base with internet access)
- line of sight from Relay to Base
"ognrelay":{
"enable":1,
"basestation":0
},- enable
- Set to 1 for relay station
- basestation
- set to 1 for basestation (connected to ogn)
If enable set to 1, basesation will be automatically deactivated. If you want to run base, set enable to 0 and basesation to 1.
Relay will receive position data and send this every 2.5 seconds to basestation (on different frequency). Basestation will listen only on relay frequency and transmit packets via APRS to ogn. So you can create network with one basesation and many relays spread over different hills. In ogn you will only see the basesation.
The protocol for relay connection are the same as configured on relay. If you receive legacy, relay will send legacy packets to base, only on different frequency.
In relay mode gps (if set static position) and Wifi will be disabled after 5 minutes.
Known bugs / Missing features
- SNR calculation not correct
- No RAM and CPU data in APRS status messages
- no GPS signal quality data in APRS messages
- no turn rate in APRS messages (always zero)
- disable sleep mode if everyone is connected to webserver
- DEEPSLEEP_RESET gets stuck after a few resets - arduino-esp32 #796
- works only with TTGO without problems
- and a lot more...
If you find a bug...
- create an issue or send me an email.
- describe your problem in a few sentences
- create a pull request
- I will try to deal with all issues, maybe it will take a little longer sometimes, just be patient
Build Instructions
- install latest Arduino IDE
- git clone https://github.com/roema/Open-Glider-Network-Groundstation.git --recursive
- make sure the arduino ide is using the correct libraries.
- take a look ath ognbase.ino
-
define TTGO / TBEAM
-
TTGO
TBEAM
Installation
- git clone --recursive https://github.com/roema/Open-Glider-Network-Groundstation.git
- Install arduino ide
- make sure you are using the correct librarys
- Compile and upload Sketch and files (.css and .html)
- Connect to OGN Wifi AP and configure
- You can update you installation http://you-ogn-ground-ip/update
- You can upload new .html .css files http://you-ogn-ground-ip/upload
Easy Installation / Upgrade
- Download binary image and install it with web-updater
- SoftRF updater works too
- Connect to Wifi OGN-XXXXXX with password 987654321
- Type 192.168.1.1 in you browser and you will see a file-upload page (only on first startup)
- Upload index.html, update.html and style.css
- html files are not necessary. Only the config.json is required for operation.
- not all functions are available on webinterface
- new config.json is required!
- Reset and connect again
Upgrade
TTGO T-Beam supports firmware upgrades via SDCARD. Take a look on ReadMe.txt in SDCARD folder.
Configuration File - config.json
The groundstation is configured via a json file. All other text files (zabbix.txt, ogn_conf.txt) are no longer required.
{
"wifi":{
"ssid":[
"ssid",
"xxxxxxx",
"xxxxxxx",
"xxxxxxx",
"xxxxxxx"
],
"pass":[
"pass",
"xxxxxxx",
"xxxxxxx",
"xxxxxxx",
"xxxxxxx"
],
"timeout":12000
},
"coordinates":{
"lat":46.90929623063438,
"lon":6.8723000923436715,
"alt":550,
"geoidsep":55
},
"zabbix":{
"enable":true,
"server":"5.150.254.37",
"port":10051,
"key":"ogn_base"
},
"testmode":{
"enable":false
},
"remotelogs":{
"enable":true,
"server":"10.0.1.200",
"port":12014
},
"aprs":{
"callsign":"Neuenburg",
"server":"aprs.glidernet.org",
"port":14580,
"band":1,
"protocol_1":3,
"protocol_2":1,
"debug":true,
"debugport":12000,
"itrackbit":false,
"istealthbit":false,
"sleepmode":false,
"rxidle":3600,
"wakeuptimer":3600,
"range":100
},
"fanetservice":{
"enable":1
},
"newprot":{
"enable":1,
"server":"10.0.1.200",
"port":12012
},
"private":{
"enable":0
},
"oled":{
"disable":0
},
"ognrelay":{
"enable":1,
"basestation":0
},
"beers":{
"show":0
}
}Installation problems
- Bootloop - erase flash with
- esptool.py erase_flash
- ESP32 Download Tool - ERASE
- use always actual .html .css files
- upload files before install new firmware!
Build erros
- like - TinyGPS++ is not found
- Arduino ide ignores the ogn libraries. Rename the original lib folder and move the ogn basesation librarys folder to the same location.
Update / File Uploader
Firmware updater can be reached at http://you-ogn-ground-ip/update
File uploader can be reached at http://you-ogn-ground-ip/upload
During the first start-up you will be automatically directed to the file upload page.
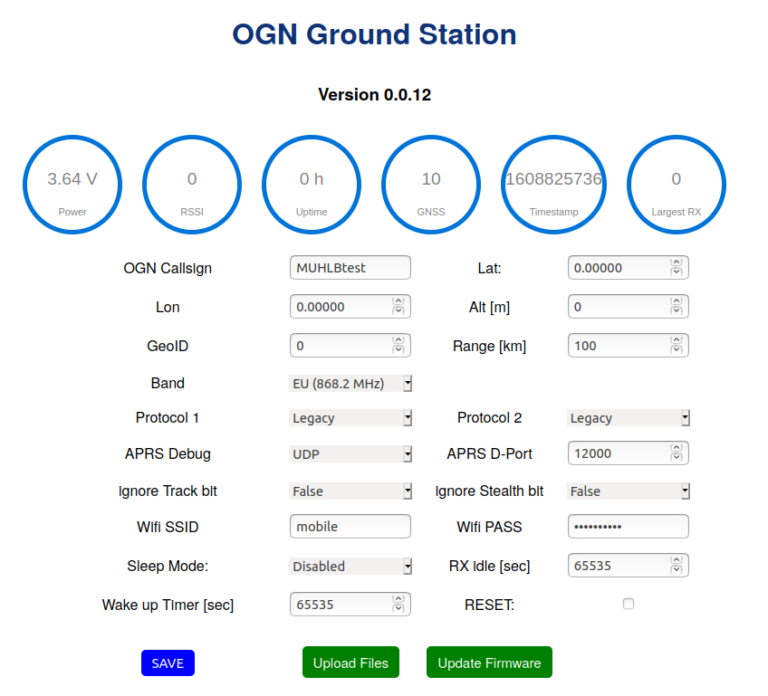
After the html and css files have been uploaded, the T-Beam can be restarted. After that, the surface should be visible like the picture.
UDP Debugging
A simple Python script is sufficient to debug the APRS messages. APRS messages are not output via the serial interface.
When the T-Beam is connected to the wifi it will send the debug messages to the ip address ending with 200.
As an an example
- 10.0.0.200
- 192.168.1.200
- 172.21.1.200
The destination port can be freely selected in the web interface. 12000 is used as the default port. Change IP and run
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
python3 udp_server.py 12000If you have several ESP32 running, they will be displayed with different colors.
Please note that no core dumps are shown here! A serial connection is necessary for this.
A new section in config.json enables remote log server.
I guarantee that no sensitive WiFi data will be transmitted!!
"remotelogs":{
"enable":false,
"server":"xxx.xxxx.xxxx.xxxx",
"port":12000
},import socket
import sys
from datetime import datetime
from termcolor import colored, cprint
colors =['blue','green','yellow','cyan','magenta','']
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
UDP_PORT_NO = int(sys.argv[1])
else:
print("usage: python3 udp_server.py <port>")
sys.exit(1)
UDP_IP_ADDRESS = "xxx.xxx.xxx.200" #change ip
serverSock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
serverSock.bind((UDP_IP_ADDRESS, UDP_PORT_NO))
stations = []
while True:
data, addr = serverSock.recvfrom(512)
if addr[0] not in stations:
stations.append(addr[0]);
now = datetime.now()
current_time = now.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
index = stations.index(addr[0])
print_c = lambda x: cprint(x, colors[index])
print_c("%s Message: %s from %s"%(current_time, data.decode("utf-8"), addr[0]))should look something like this..
17:23:49 Message: # aprsc 2.1.5-g8af3cdc 29 Dec 2020 16:23:43 GMT GLIDERN1 51.178.19.212:14580
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:09 Message: # aprsc 2.1.5-g8af3cdc 29 Dec 2020 16:24:03 GMT GLIDERN1 51.178.19.212:14580
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:09 Message: # aprsc 2.1.5-g8af3cdc 29 Dec 2020 16:24:03 GMT GLIDERN1 51.178.19.212:14580
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:29 Message: # aprsc 2.1.5-g8af3cdc 29 Dec 2020 16:24:23 GMT GLIDERN1 51.178.19.212:14580
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:29 Message: # aprsc 2.1.5-g8af3cdc 29 Dec 2020 16:24:23 GMT GLIDERN1 51.178.19.212:14580
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:47 Message: user XXXXXXX pass XXXXX vers ESP32 0.1.0-2 m/100
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:48 Message: MUHLB>APRS,TCPIP*,qAC,248280:/162447h4657.37NI00715.50E&/A=001814
from 10.0.0.30
17:24:49 Message: entering sleep mode for 43200 seconds - good night from 10.0.0.30
17:28:46 Message: good morning, startup esp32 groundstation after Deep Sleep reset digital core from 10.0.0.30OGN Debugging
If you want to debug the aprs messages in the OG network, the python aprs client is ideal.
Under Linux, the callsign can still be filtered with grep
python3 client.py | grep "callsign"from ogn.client import AprsClient
from ogn.parser import parse, ParseError
import re
pattern_table = re.compile(r'[N][ ]{1}')
def process_beacon(raw_message):
try:
beacon = parse(raw_message)
messages = re.findall(pattern_table, beacon['raw_message'])
if messages:
print(messages)
print(beacon['raw_message'])
except ParseError as e:
print('Error, {}'.format(e.message))
client = AprsClient(aprs_user='N0CALL')
client.connect()
try:
client.run(callback=process_beacon, autoreconnect=True)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('\nStop ogn gateway')
client.disconnect()Please note that pictures are not necessarily up to date!
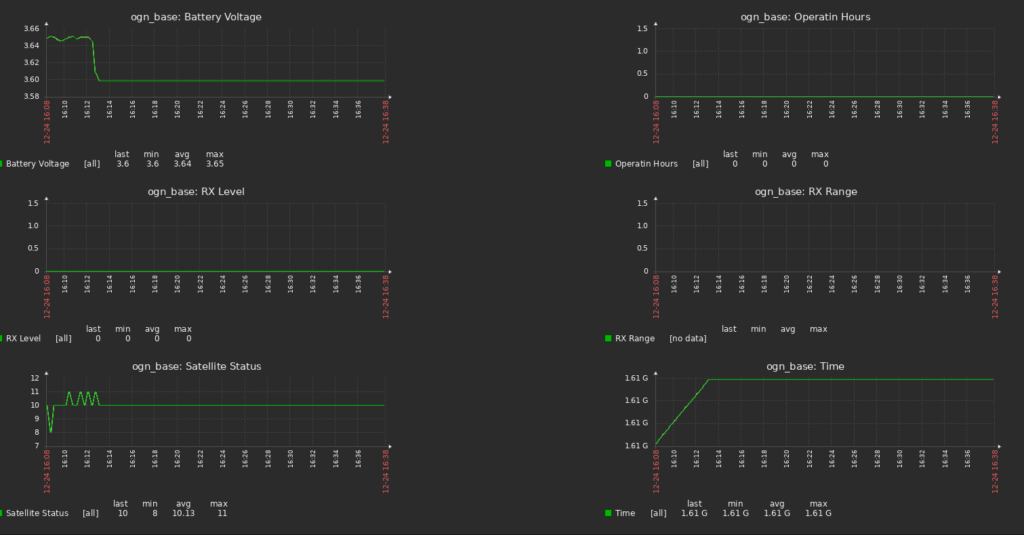
Simple monitoring with zabbix trapper
Very rudimentary. Some parameters will be added in the future.
If you have zabbix agent installed on you machine, you can test your server configuration with
zabbix_sender -z <you server ip> -p 10051 -s ogn_base -k voltage -o 5.25I am always open to wishes and suggestions, but would also like to emphasize that I do this project in my spare time. I am not responsible for any damage caused by this software.
Buy me a coffee
I first had contact with the SoftRF project at the beginning of 2020. The idea of turning it into a low cost and low power ground station came up in June. I spend a lot of my free time on this project. If you like this project, then I would be happy if you buy me a coffee [beer].
manuel.roesel@ros-it.ch
If you have any wishes or suggestions, don't hesitate to contact me!
Thanks to my testers and fermentum
- Peter A.
- Nick
- Guy
- Andreas
- Uwe
Thanks to..
Ivan Grokhotkov - Arduino core for ESP8266
Zak Kemble - nRF905 library
Stanislaw Pusep - flarm_decode
Paul Stoffregen - Arduino Time Library
Mikal Hart - TinyGPS++ and PString Libraries
Phil Burgess - Adafruit NeoPixel Library
Andy Little - Aircraft and MAVLink Libraries
Peter Knight - TrueRandom Library
Matthijs Kooijman - IBM LMIC and Semtech Basic MAC frameworks for Arduino
David Paiva - ESP8266FtpServer
Lammert Bies - Lib_crc
Pawel Jalocha - OGN library
Timur Sinitsyn, Tobias Simon, Ferry Huberts - NMEA library
yangbinbin (yangbinbin_ytu@163.com) - ADS-B encoder C++ library
Hristo Gochkov - Arduino core for ESP32
Evandro Copercini - ESP32 BT SPP library
Limor Fried and Ladyada - Adafruit BMP085 library
Kevin Townsend - Adafruit BMP280 library
Limor Fried and Kevin Townsend - Adafruit MPL3115A2 library
Oliver Kraus - U8g2 LCD, OLED and eInk library
Michael Miller - NeoPixelBus library
Shenzhen Xin Yuan (LilyGO) ET company - TTGO T-Beam and T-Watch
JS Foundation - jQuery library
XCSoar team - EGM96 data
Mike McCauley - BCM2835 C library
Dario Longobardi - SimpleNetwork library
Benoit Blanchon - ArduinoJson library
flashrom.org project - Flashrom library
Robert Wessels and Tony Cave - EasyLink library
Oliver Jowett - Dump978 library
Phil Karn - FEC library
Lewis He - AXP20X library
Bodmer - TFT library
Michael Kuyper - Basic MAC library
Erriez - ErriezCRC32 library
IntelliTrend GmbH - zabbix-iot library
Marian Craciunescu - ESP32PING library
