Desktop Notifier
desktop-notifier is a Python library for cross-platform desktop notifications.
Currently supported platforms are:
- Linux via the dbus service org.freedesktop.Notifications
- macOS and iOS via the Notification Center framework
- Windows via the WinRT / Python bridge
Features
Where supported by the native platform APIs, desktop-notifier allows for:
- Clickable notifications with callbacks on user interaction
- Multiple action buttons
- A single reply field (e.g., for chat notifications)
- Notification sounds
- Notification threads (grouping notifications by topic)
- Limiting the maximum number of notifications shown in the notification center
An example of how some of this looks like on macOS:
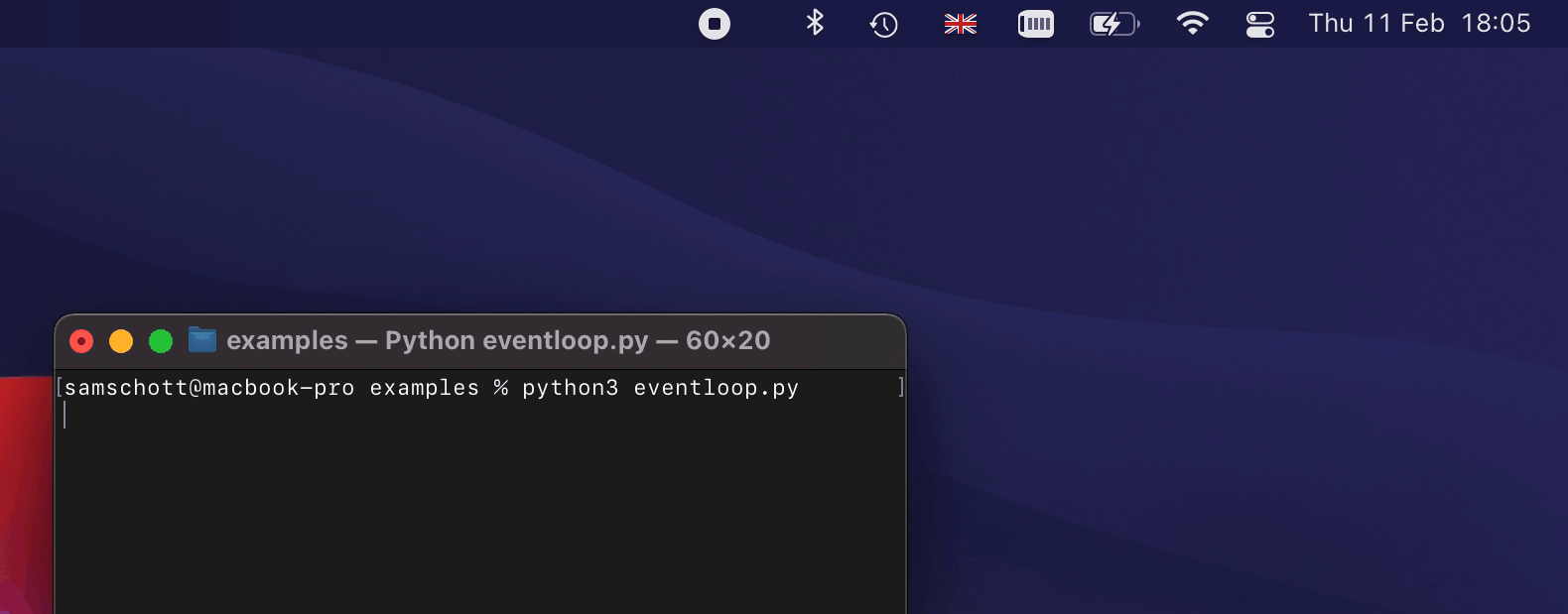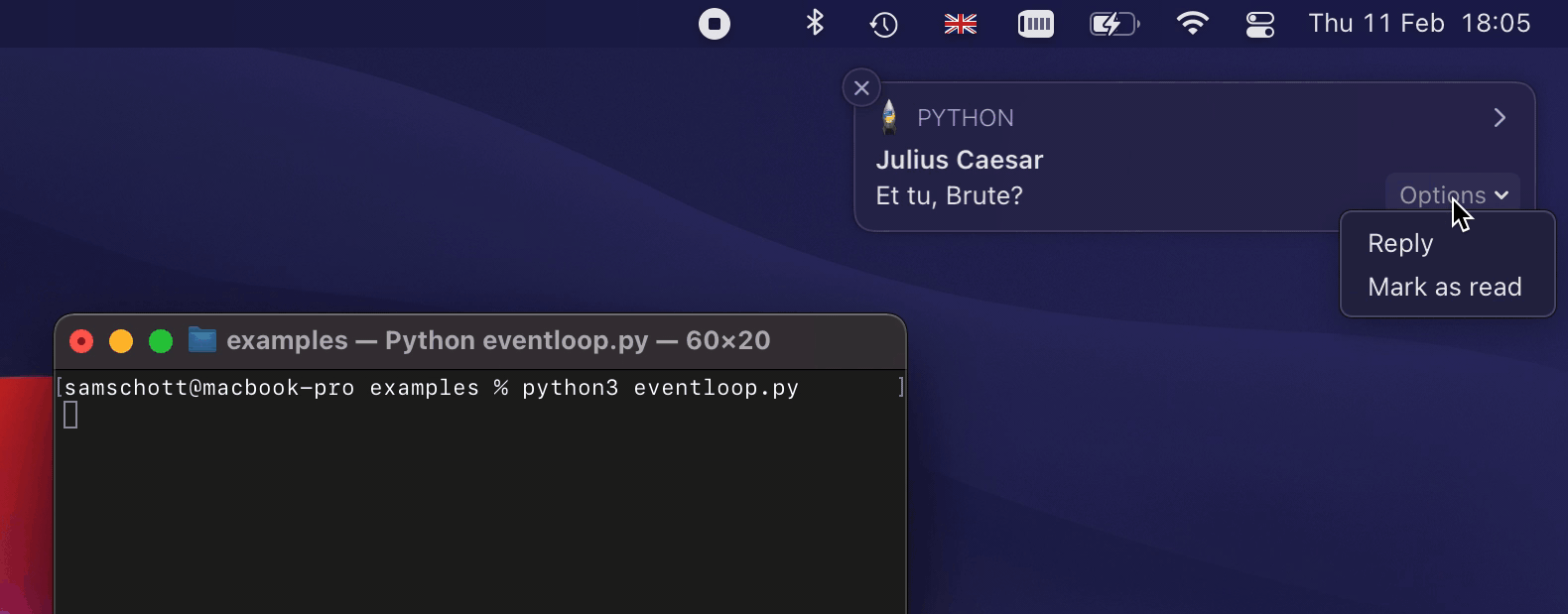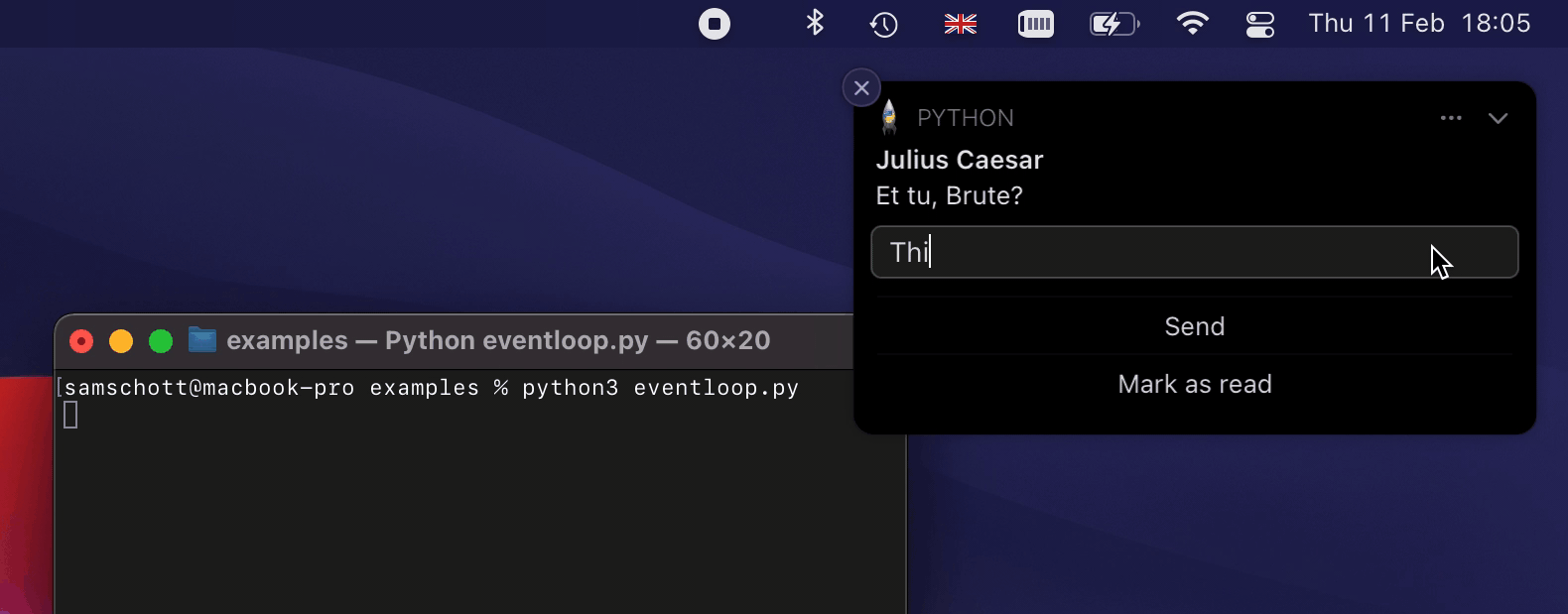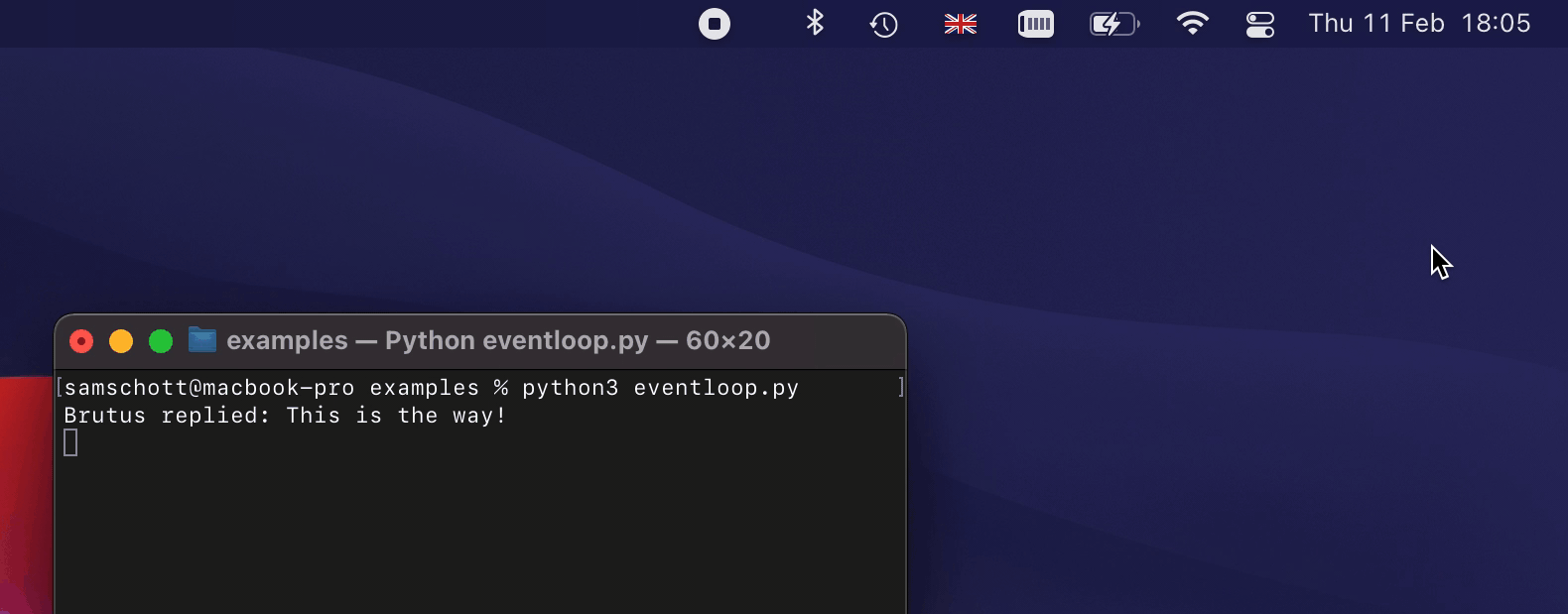
An exhaustive list of features and their platform support is provided in the
documentation.
In addition, you can query supported features at runtime with
DesktopNotifier.get_capabilities().
Any options or configurations which are not supported by the platform will be silently ignored.
Installation
From PyPI:
pip3 install -U desktop-notifierUsage
The main API consists of asynchronous methods which need to be awaited. Basic usage only requires the user to specify a notification title and message. For example:
import asyncio
from desktop_notifier import DesktopNotifier
notifier = DesktopNotifier()
async def main():
await notifier.send(title="Hello world!", message="Sent from Python")
asyncio.run(main())By default, "Python" will be used as the app name for all notifications, but you can
manually specify an app name and icon in the DesktopNotifier constructor. Advanced
usage also allows setting different notification options such as urgency, buttons,
callbacks, etc. For example, for the gif displayed above:
import asyncio
import signal
from desktop_notifier import DesktopNotifier, Urgency, Button, ReplyField, DEFAULT_SOUND
async def main() -> None:
notifier = DesktopNotifier(
app_name="Sample App",
notification_limit=10,
)
await notifier.send(
title="Julius Caesar",
message="Et tu, Brute?",
urgency=Urgency.Critical,
buttons=[
Button(
title="Mark as read",
on_pressed=lambda: print("Marked as read"),
)
],
reply_field=ReplyField(
on_replied=lambda text: print("Brutus replied:", text),
),
on_clicked=lambda: print("Notification clicked"),
on_dismissed=lambda: print("Notification dismissed"),
sound=DEFAULT_SOUND,
)
# Run the event loop forever to respond to user interactions with the notification.
stop_event = asyncio.Event()
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
loop.add_signal_handler(signal.SIGINT, stop_event.set)
loop.add_signal_handler(signal.SIGTERM, stop_event.set)
await stop_event.wait()
asyncio.run(main())Event loop integration
Using the asynchronous API is highly recommended to prevent multiple milliseconds of blocking IO from DBus or Cocoa APIs. In addition, execution of callbacks requires a running event loop. On Linux, an asyncio event loop will be sufficient but macOS requires a running CFRunLoop.
You can use rubicon-objc to integrate a Core Foundation CFRunLoop with asyncio:
import asyncio
from rubicon.objc.eventloop import EventLoopPolicy
# Install the event loop policy
asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(EventLoopPolicy())Desktop-notifier itself uses Rubicon Objective-C to interface with Cocoa APIs. A full example integrating with the CFRunLoop is given in examples/eventloop.py. Please refer to the Rubicon Objective-C docs for more information.
Likewise, you can integrate the asyncio event loop with a Gtk main loop on Gnome using gbulb. This is not required for full functionality but may be convenient when developing a Gtk app.
Notes on macOS
On macOS 10.14 and higher, the implementation uses the UNUserNotificationCenter
instead of the deprecated NSUserNotificationCenter. UNUserNotificationCenter
only allows signed executables to send desktop notifications. This means that
notifications will only work if the Python executable or bundled app has been signed.
Note that the installer from python.org provides a properly signed
Python framework but homebrew does not (manually signing the executable installed
by homebrew should work as well).
If you freeze your code with PyInstaller or a similar packaging solution, you must sign the resulting app bundle for notifications to work. An ad-hoc signature will be sufficient but signing with an Apple developer certificate is recommended for distribution and may be required on future releases of macOS.
Design choices
This package is opinionated in a few ways:
- It does not try to work around platform restrictions, such as changing the app icon on macOS. Workarounds would be hacky and likely be rejected by an App Store review.
- The main API consists of async methods and a running event loop is required to respond to user interactions with a notification. This simplifies integration with GUI apps.
- Dependencies are pure Python packages without extension modules. This simplifies app bundling and distribution. We make an exception for Windows because interoperability with the Windows Runtime is difficult to achieve without extension modules.
- If a certain feature is not supported by a platform, using it will not raise an exception. This allows clients to use a wide feature set where available without worrying about exception handling.
- If a notification cannot be scheduled, this is logged as a warning and does not raise an exception. Most platforms allow the user to control if and how notifications are delivered and notification delivery therefore cannot be taken as guaranteed.
Dependencies
- dbus-next on Linux
- rubicon-objc on macOS
- pywinrt on Windows

