Jupyter Reverse Proxy Service (HTTPS)
For full instructions on how to run notebooks on SDSC HPC systems, see:
https://hpc-training.sdsc.edu/notebooks-101/notebook-101.html
- Connection to Notebook over HTTPS using the Reverse Proxy Service (very secure)
Notice: the start_notebook script and its corresponding batch folder will be deprecated by December 31, 2020.
Overview

The SDSC Jupyter Reverse Proxy Service is a prototype system that will allow users to launch standard, secure (HTTPS) Jupyter Services on on any Comet compute node using a reverse proxy server using a simple bash script called start-jupyter. The notebooks will be hosted on the internal cluster network as an HTTP service using standard jupyter commands. The service will then be made available to the user outside of the cluster firewall as an HTTPS connection between the external users web browser and the reverse proxy server. The goal is to minimize software changes for our users while improving the security of user notebooks running on our HPC systems. The RPS service is capable of running on any HPC system capable of supporting the RP server (needs Apache).
Using the JRPS is both simple and encrypted without requiring ssh tunneling. To use RPS, SSH to connect to comet, and make sure that you have the software environment installed on the login node. Verify that you have installed the required software:
condafor installing software packages (https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.shminincondafor running the notebook environment https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh)Jupyter(notebooks, lab), and other Python packages needed for you application. See the Software Preqrequisites of the Notebooks 101 tutorial.
Note: You must have jupyter installed to run the start-jupyter command successfully.
Clone the JRPS repository
Clone this repository directly into your comet login node.
git clone https://github.com/sdsc-hpc-training-org/reverse-proxy.gitLaunching the Notebook
The start-jupyter script performs the following tasks:
- Sends a request to the Jupyter reverse proxy server (JRPS) to get a one-time token and a port number
- Launches the Jupyter notebook command using the token and port number.
- Prints a secure URL containing the token to the terminal, so that the user can copy/paste the URL into a local browser:
Your notebook is here: https://aversion-runaround-spearman.comet-user-content.sdsc.edu?token=099aa825b1403d58889842ab2c758885
### Usage
`./start-jupyter [-p <cluster partition>] [-d <path to start dir>] [-A <account>] [-b <path to batch file>] [-t <time>] [-g <number of gpus (1-3)> [-i <string>] [-I]`
-p: the partition to wait for. debug or compute Default Partition is "compute"
-d: the top-level directory of your jupyter notebook Default Dir is /home/$USER
-A: the project allocation to be used for this notebook Default Allocation is your sbatch system default allocation (also called project or group)
-b: the batch script you want to submit with your notebook. Only those in the batch folder are supported.
Default batch script is ./batch/batch_notebook.sh
-t: the time to run the notebook. Your account will be charged for the time you put here so be careful. Default time is 30 minutes
-g: number of gpus to collect for your notebook. Currently only support 1-3 on gpu-shared partitions.
-i: path to a singularity image to start your jupyter notebook in. Make sure everything, including jupyter notebook and/or jupyter lab is installed in this image.
-I: get extra information about the job you submitted using the script
(If you don't know what $USER is, try this command: `echo $USER`. This is just your comet username)
### Some common examples
Start a notebook with all defaults on any system
`./start-jupyter`
This is your waiting screen. This screen occurs before your batch job is submitted.
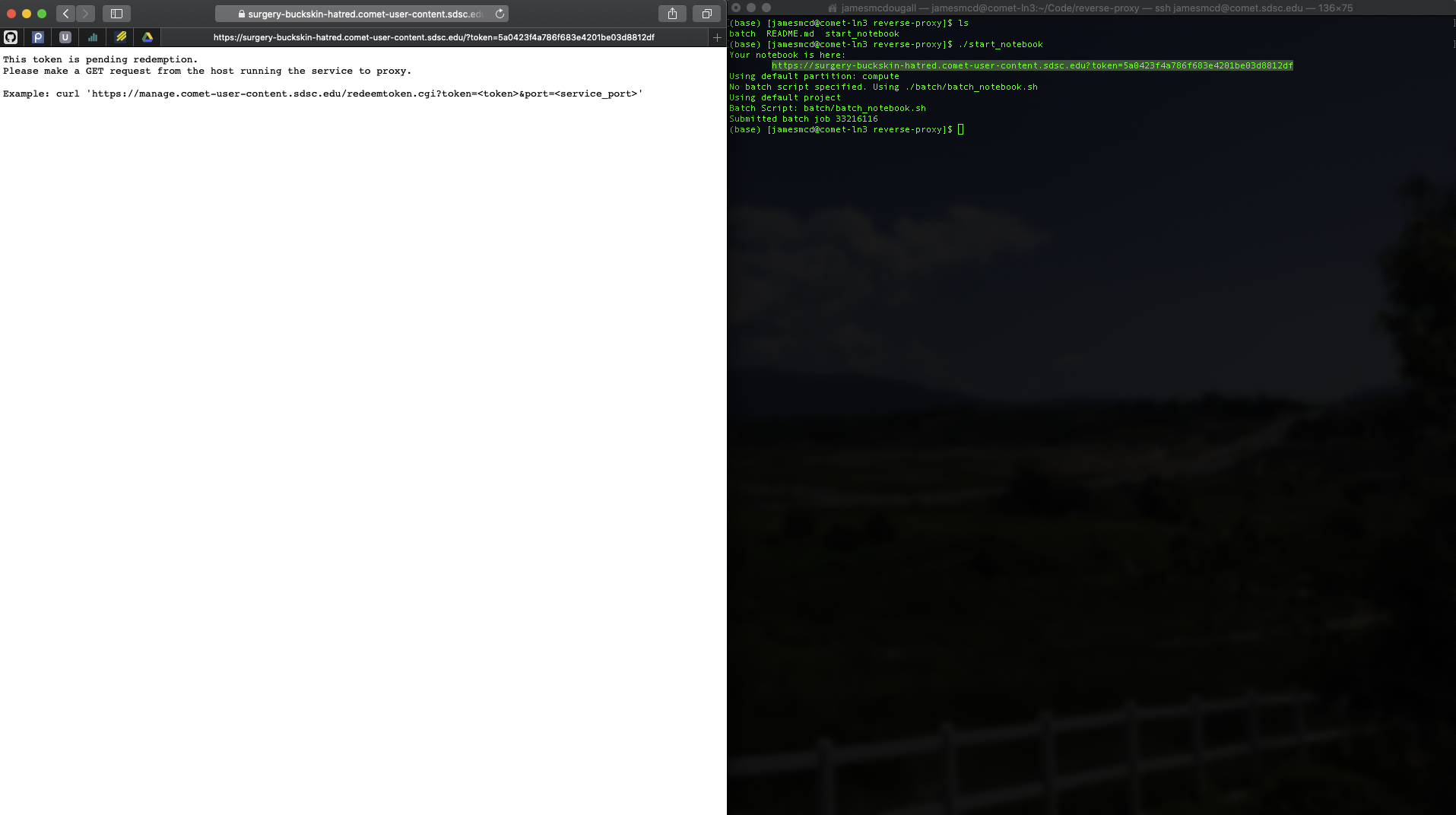
Your notebook is ready to go!

If you refresh too soon, you may see this page. This is expected and you'll just have to wait.

Note that the time positional argument must occur after all the flags. There will be an error if you put any flags after the positional argument.
### Examples:
To start a notebook using the debug queue in /share/apps/compute for 30 minutes:
`./start-jupyter -d /share/apps/compute -p debug -t 30`
To start a notebook using the compute queue in your home directory for 60 minutes:
`./start-jupyter -d ~ -p compute -t 60`
To start a jupyterlab server
`./start-jupyter -s jupyterlab`
To start a notebook server
`./start-jupyter -s notebook`
To start a notebook with a single gpu
`./start-jupyter -p gpu-shared -g 1 -d ~`
To start a notebook with a tensorflow container
`./start-jupyter -t 00:30:00 -g 1 -p gpu-shared -i /share/apps/gpu/singularity/images/tensorflow/tensorflow-v2.3.0-gpu-20200929.simg`
To start a notebook with a pytorch container
`./start-jupyter -t 00:30:00 -g 1 -p gpu-shared -i /share/apps/gpu/singularity/images/pytorch/pytorch-gpu.simg`