Transparent Proxy powered by cgroup v2
Introduction
cgproxy will transparent proxy anything running in specific cgroup. It resembles with proxychains and tsocks in default setting.
Main feature:
- supports cgroup/program level proxy control.
- supports global transparent proxy and gateway proxy.
Contents
Prerequest
-
cgroup2
Both cgroup and cgroup2 are enabled in linux by default. So you don't have to do anything about this.
systemd-cglsto see the cgroup hierarchical tree.- Why cgroup v2? Because simple, elegant and intuitive.
-
TPROXY
A process listening on port (e.g. 12345) to accept iptables TPROXY, for example v2ray's dokodemo-door in tproxy mode.
-
Iptables
Iptables version should be at least 1.6.0, run
iptables --versionto check.ubuntu 16.04, debian 9, fedora 27 and later are desired
How to build and install
distro install
-
For debian and redhat series, download from Release page
-
For archlinux series, already in archlinuxcn repo, or see archlinux AUR
-
Tested on archlinux, fedora 32, ubuntu 18.04, ubuntu 20.04, deepin 15.11, deepin v20 beta
build
- before build, install depencies: clang, nlohmann-json, libbpf, bpf(bpftool)
- then cmake standard build
# ready build dir
mkdir build
cd build
# generate
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr \
-Dbuild_execsnoop_dl=ON \
-Dbuild_static=OFF \
..
# compile
makeDefault usage
-
First enable and start service
sudo systemctl enable --now cgproxy.service -
Then prefix with cgproxy with your command, just like proxychains
cgproxy [--debug] <CMD> -
For example, test proxy
cgproxy curl -vI https://www.google.com -
To completely stop
sudo systemctl disable --now cgproxy.service
Configuration
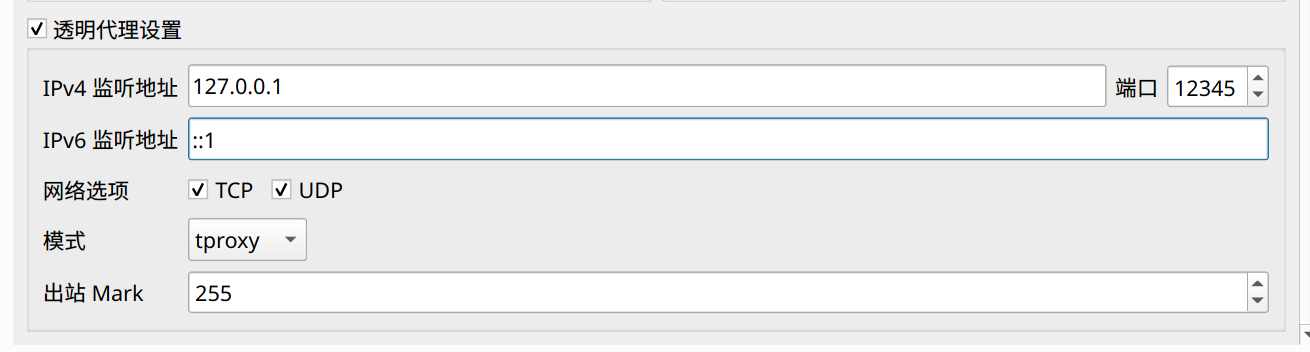
Config file: /etc/cgproxy/config.json
{
"port": 12345,
"program_noproxy": ["v2ray", "qv2ray"],
"program_proxy": [],
"cgroup_noproxy": ["/system.slice/v2ray.service"],
"cgroup_proxy": [],
"enable_gateway": false,
"enable_dns": true,
"enable_udp": true,
"enable_tcp": true,
"enable_ipv4": true,
"enable_ipv6": true,
"table": 10007,
"fwmark": 39283
}
-
port tproxy listenning port
-
program level proxy control, need execsnoop enabled:
- program_proxy program need to be proxied
- program_noproxy program that won't be proxied
-
cgroup level proxy control:
- cgroup_noproxy cgroup array that no need to proxy,
/noproxy.sliceis preserved - cgroup_proxy cgroup array that need to proxy,
/proxy.sliceis preserved
- cgroup_noproxy cgroup array that no need to proxy,
-
enable_gateway enable gateway proxy for local devices
-
enable_dns enable dns to go to proxy
-
enable_tcp
-
enable_udp
-
enable_ipv4
-
enable_ipv6
-
table, fwmark you can specify iptables and route table related parameter in case conflict.
-
options priority
program_noproxy > program_proxy > cgroup_noproxy > cgroup_proxy enable_ipv6 = enable_ipv4 > enable_dns > enable_tcp = enable_udp command cgproxy and cgnoproxy always have highest priority
Note: cgroup in configuration need to be exist, otherwise ignored
If you changed config, remember to restart service
sudo systemctl restart cgproxy.serviceGlobal transparent proxy
-
Set
"cgroup_proxy":["/"]in configuration, this will proxy all connection -
Allow your proxy program (v2ray) direct to internet to avoid loop. Two ways:
- active way, run command
example:
cgnoproxy sudo v2ray -config config_fileexample:
cgnoproxy qv2ray-
passive way, persistent config
example:
"program_noproxy":["v2ray" ,"qv2ray"]example:
"cgroup_noproxy":["/system.slice/v2ray.service"]
-
Finally, restart cgproxy service, that's all
Gateway proxy
- Set
"enable_gateway":truein configuration - And allow your proxy software (v2ray) direct to internet if necessary, described above
- Other device set this host as gateway, and set public dns if need
Other useful tools provided in this project
-
cgnoproxyrun program wihout proxy, very useful in global transparent proxycgnoproxy [--debug] <CMD> cgnoproxy [--debug] --pid <PID> -
For more detail command usage, see
man cgproxydman cgproxyman cgnoproxy
NOTES
-
v2ray TPROXY need root or special permission, use service or
sudo setcap "cap_net_admin,cap_net_bind_service=ep" /usr/lib/v2ray/v2ray -
Why not outbound mark solution, because in v2ray when
"localhost"is used, out-going DNS traffic is not controlled by V2Ray, so no mark at all, that's pity.
TIPS
systemd-cglsto see the cgroup hierarchical tree.- Check cgroup2 support
findmnt -t cgroup2 - Offer you v2ray service and full config exmaple in v2ray_config
- Offer you qv2ray config example
Licences
Known Issues
-
docker breaks cgroup v2 path match, add kernel parameter
cgroup_no_v1=net_cls,net_prioto resolve, see issue #3 for detail -
docker load
br_netfiltermodule due to hairpin nat, which is not a big deal, see commit.It enables data link layer packet to go through iptables and only once. However TPROXY do not accept this kind of packets. So to get it working, set following parameter to disable this behavior or unload br_netfilter module manualy. see issue #10 for detail.
sudo sysctl -w net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=0 sudo sysctl -w net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables=0 sudo sysctl -w net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables = 0
