Sampler. Visualization for any shell command.
Sampler is a tool for shell commands execution, visualization and alerting. Configured with a simple YAML file.
Why do I need it?
One can sample any dynamic process right from the terminal — observe changes in the database, monitor MQ in-flight messages, trigger a deployment script and get notification when it's done.
If there is a way to get a metric using a shell command, then it can be visualized with Sampler momentarily.
Installation
macOS
brew install samplersudo port install sampleror
sudo curl -Lo /usr/local/bin/sampler https://github.com/sqshq/sampler/releases/download/v1.1.0/sampler-1.1.0-darwin-amd64
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/samplerLinux
sudo wget https://github.com/sqshq/sampler/releases/download/v1.1.0/sampler-1.1.0-linux-amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/sampler
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/samplerNote: libasound2-dev system library is required to be installed for Sampler to play a trigger sound tone. Usually the library is in place, but if not - you can install it with your favorite package manager, e.g apt install libasound2-dev
Packaging status
- Fedora
sudo dnf install golang-github-sqshq-sampler(F31+) - Arch
yay -S samplerWindows (experimental)
Recommended to use with advanced console emulators, e.g. Cmder
Via Chocolatey
choco install sampleror
Docker
# Create a configuration file
vim config.yml
# Build the container image
docker build --tag sampler .
# Run a container
docker run --interactive --tty --volume $(pwd)/config.yml:/root/config.yml sampler --config /root/config.ymlUsage
You specify shell commands, Sampler executes them with a required rate. The output is used for visualization.
Using Sampler is basically a 3-step process:
- Define your shell commands in a YAML configuration file
- Run
sampler -c config.yml - Adjust components size and location on UI
But there are so many monitoring systems already
Sampler is by no means an alternative to full-scale monitoring systems, but rather an easy to setup development tool.
If spinning up and configuring Prometheus with Grafana is complete overkill for you task, Sampler might be the right solution. No servers, no databases, no deploy - you specify shell commands, and it just works.
Then it should be installed on every server I monitor?
No, you can run Sampler on local, but still gather telemetry from multiple remote machines. Any visualization might have init command, where you can ssh to a remote server. See the SSH example
Contents
Components
The following is a list of configuration examples for each component type, with macOS compatible sampling scripts.
Runchart
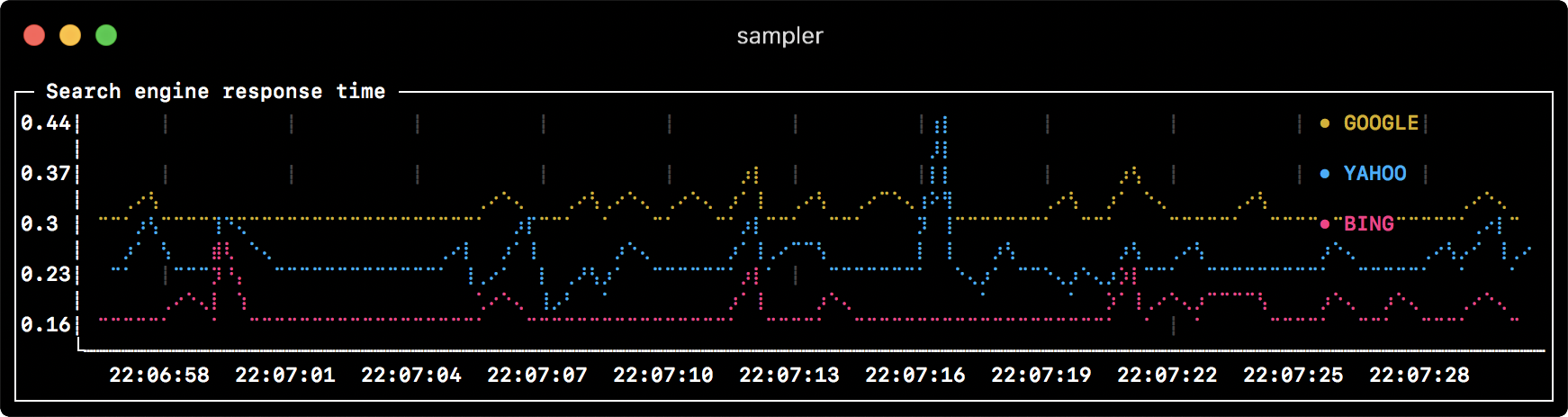
runcharts:
- title: Search engine response time
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 2 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
legend:
enabled: true # enables item labels, default = true
details: false # enables item statistics: cur/min/max/dlt values, default = true
items:
- label: GOOGLE
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.google.com
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default one is chosen from a pre-defined palette
- label: YAHOO
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://search.yahoo.com
- label: BING
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.bing.comSparkline
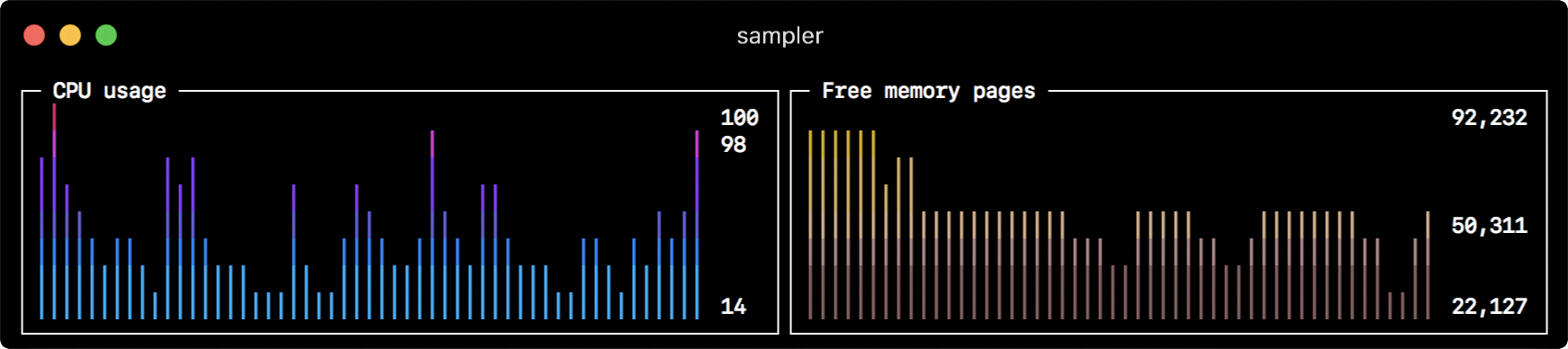
sparklines:
- title: CPU usage
rate-ms: 200
scale: 0
sample: ps -A -o %cpu | awk '{s+=$1} END {print s}'
- title: Free memory pages
rate-ms: 200
scale: 0
sample: memory_pressure | grep 'Pages free' | awk '{print $3}'Barchart
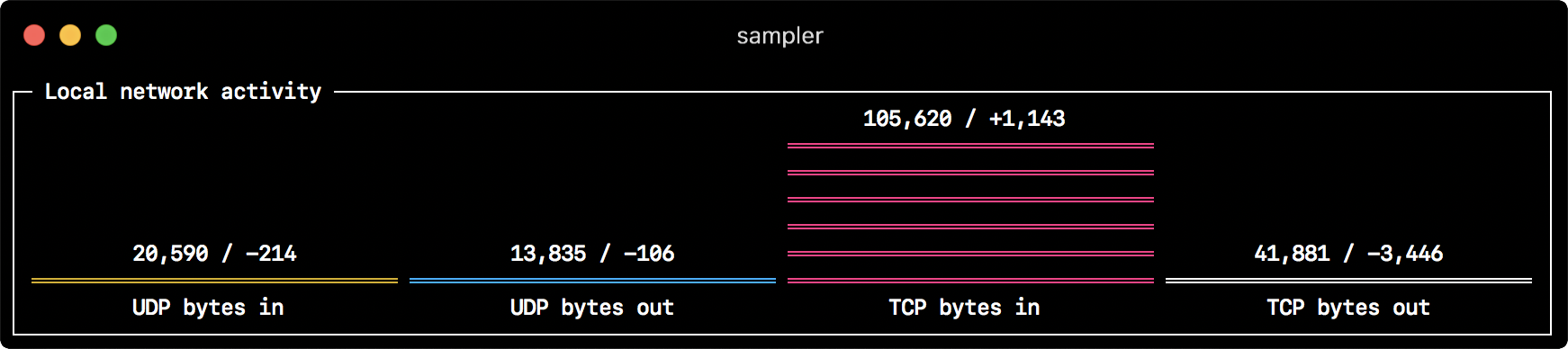
barcharts:
- title: Local network activity
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 0 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
items:
- label: UDP bytes in
sample: nettop -J bytes_in -l 1 -m udp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: UDP bytes out
sample: nettop -J bytes_out -l 1 -m udp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: TCP bytes in
sample: nettop -J bytes_in -l 1 -m tcp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: TCP bytes out
sample: nettop -J bytes_out -l 1 -m tcp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'Gauge
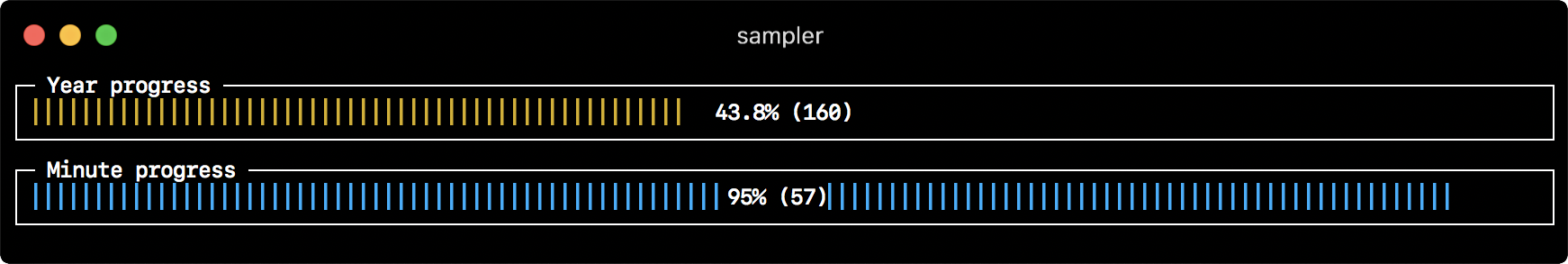
gauges:
- title: Minute progress
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 2 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
percent-only: false # toggle display of the current value, default = false
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default one is chosen from a pre-defined palette
cur:
sample: date +%S # sample script for current value
max:
sample: echo 60 # sample script for max value
min:
sample: echo 0 # sample script for min value
- title: Year progress
cur:
sample: date +%j
max:
sample: echo 365
min:
sample: echo 0Textbox
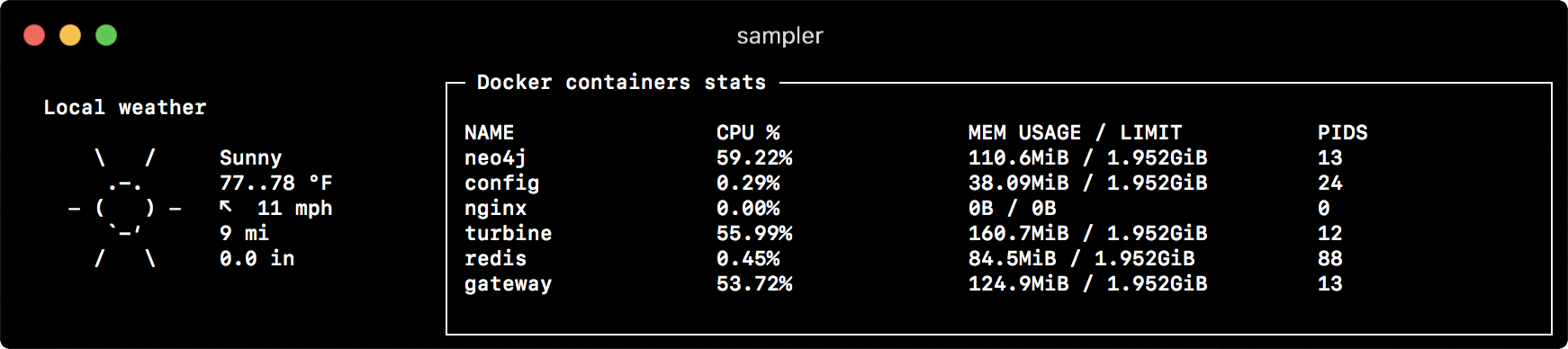
textboxes:
- title: Local weather
rate-ms: 10000 # sampling rate, default = 1000
sample: curl wttr.in?0ATQF
border: false # border around the item, default = true
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default is white
- title: Docker containers stats
rate-ms: 500
sample: docker stats --no-stream --format "table {{.Name}}\t{{.CPUPerc}}\t{{.MemUsage}}\t{{.PIDs}}"Asciibox

asciiboxes:
- title: UTC time
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
font: 3d # font type, default = 2d
border: false # border around the item, default = true
color: 43 # 8-bit color number, default is white
sample: env TZ=UTC date +%rBells and whistles
Triggers
Triggers allow to perform conditional actions, like visual/sound alerts or an arbitrary shell command. The following examples illustrate the concept.
Clock gauge, which shows minute progress and announces current time at the beginning of each minute
gauges:
- title: MINUTE PROGRESS
position: [[0, 18], [80, 0]]
cur:
sample: date +%S
max:
sample: echo 60
min:
sample: echo 0
triggers:
- title: CLOCK BELL EVERY MINUTE
condition: '[ $label == "cur" ] && [ $cur -eq 0 ] && echo 1 || echo 0' # expects "1" as TRUE indicator
actions:
terminal-bell: true # standard terminal bell, default = false
sound: true # NASA quindar tone, default = false
visual: false # notification with current value on top of the component area, default = false
script: say -v samantha `date +%I:%M%p` # an arbitrary script, which can use $cur, $prev and $label variablesSearch engine latency chart, which alerts user when latency exceeds a threshold
runcharts:
- title: SEARCH ENGINE RESPONSE TIME (sec)
rate-ms: 200
items:
- label: GOOGLE
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.google.com
- label: YAHOO
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://search.yahoo.com
triggers:
- title: Latency threshold exceeded
condition: echo "$prev < 0.3 && $cur > 0.3" |bc -l # expects "1" as TRUE indicator
actions:
terminal-bell: true # standard terminal bell, default = false
sound: true # NASA quindar tone, default = false
visual: true # visual notification on top of the component area, default = false
script: 'say alert: ${label} latency exceeded ${cur} second' # an arbitrary script, which can use $cur, $prev and $label variablesInteractive shell support
In addition to the sample command, one can specify init command (executed only once before sampling) and transform command (to post-process sample command output). That covers interactive shell use case, e.g. to establish connection to a database only once, and then perform polling within interactive shell session.
Basic mode
textboxes:
- title: MongoDB polling
rate-ms: 500
init: mongo --quiet --host=localhost test # executes only once to start the interactive session
sample: Date.now(); # executes with a required rate, in scope of the interactive session
transform: echo result = $sample # executes in scope of local session, $sample variable is available for transformationPTY mode
In some cases interactive shell won't work, because its stdin is not a terminal. We can fool it, using PTY mode:
textboxes:
- title: Neo4j polling
pty: true # enables pseudo-terminal mode, default = false
init: cypher-shell -u neo4j -p pwd --format plain
sample: RETURN rand();
transform: echo "$sample" | tail -n 1
- title: Top on a remote server
pty: true # enables pseudo-terminal mode, default = false
init: ssh -i ~/user.pem ec2-user@1.2.3.4
sample: top Multistep init
It is also possible to execute multiple init commands one after another, before you start sampling.
textboxes:
- title: Java application uptime
multistep-init:
- java -jar jmxterm-1.0.0-uber.jar
- open host:port # or local PID
- bean java.lang:type=Runtime
sample: get UptimeVariables
If the configuration file contains repeated patterns, they can be extracted into the variables section.
Also variables can be specified using -v/--variable flag on startup, and any system environment variables will also be available in the scripts.
variables:
mongoconnection: mongo --quiet --host=localhost test
barcharts:
- title: MongoDB documents by status
items:
- label: IN_PROGRESS
init: $mongoconnection
sample: db.getCollection('events').find({status:'IN_PROGRESS'}).count()
- label: SUCCESS
init: $mongoconnection
sample: db.getCollection('events').find({status:'SUCCESS'}).count()
- label: FAIL
init: $mongoconnection
sample: db.getCollection('events').find({status:'FAIL'}).count()Color theme
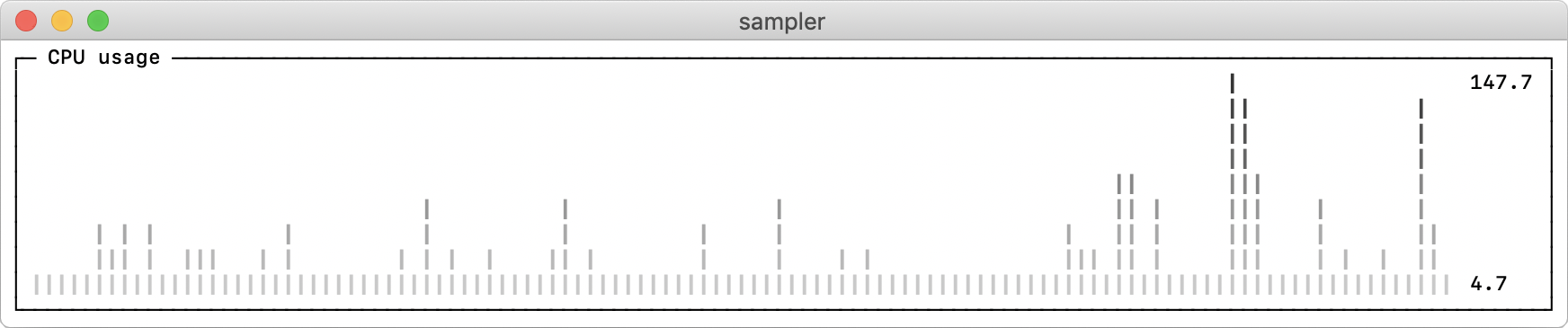
theme: light # default = dark
sparklines:
- title: CPU usage
sample: ps -A -o %cpu | awk '{s+=$1} END {print s}'Real-world recipes
Databases
The following are different database connection examples. Interactive shell (init script) usage is recommended to establish connection only once and then reuse it during sampling.