
@storyblok/react
The React plugin you need to interact with Storyblok API and enable the Real-time Visual Editing Experience. This package helps you integrate Storyblok with React along with all types of React based frameworks like Next.js, Remix etc. This SDK also includes the support for React Server Side Components.
Kickstart a new project
Are you eager to dive into coding? Follow these steps to kickstart a new project with Storyblok and React, and get started in just a few minutes!
5-minute Tutorial
Are you looking for a hands-on, step-by-step tutorial? The React 5-minute Tutorial has you covered! It provides comprehensive instructions on how to set up a Storyblok space and connect it to your React project.
Ultimate Tutorial
Are you looking for a hands-on, step-by-step tutorial? The Next.js Ultimate Tutorial has you covered! It provides comprehensive instructions on building a complete, multilingual website using Storyblok and Next.js from start to finish.
Installation
Install @storyblok/react:
npm install @storyblok/react
// yarn add @storyblok/react⚠️ This SDK uses the Fetch API under the hood. If your environment doesn't support it, you need to install a polyfill like isomorphic-fetch. More info on storyblok-js-client docs.
From a CDN
Install the file from the CDN:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@storyblok/react"></script>Initialization
Register the plugin on your application and add the access token of your Storyblok space. You can also add the apiPlugin in case that you want to use the Storyblok API Client:
import { apiPlugin, storyblokInit } from '@storyblok/react'
/** Import your components */
import Page from './components/Page'
import Teaser from './components/Teaser'
// import FallbackComponent from "./components/FallbackComponent";
storyblokInit({
accessToken: 'YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
use: [apiPlugin],
components: {
page: Page,
teaser: Teaser,
},
// bridge: false,
// apiOptions: {},
// richText: {},
// enableFallbackComponent: false,
// customFallbackComponent: FallbackComponent,
})Note: This is the general way for initalizing the SDK, the initialization might be a little different depending upon the framework. You can see how everything works according to the framework in their respective sections below.
Add all your components to the components object in the storyblokInit function.
That's it! All the features are enabled for you: the Api Client for interacting with Storyblok CDN API, and Storyblok Bridge for real-time visual editing experience.
You can enable/disable some of these features if you don't need them, so you save some KB. Please read the "Features and API" section
Region parameter
Possible values:
eu(default): For spaces created in the EUus: For spaces created in the USap: For spaces created in Australiaca: For spaces created in Canadacn: For spaces created in China
Full example for a space created in the US:
import { apiPlugin, storyblokInit } from '@storyblok/react'
storyblokInit({
accessToken: 'YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
use: [apiPlugin],
apiOptions: {
region: 'us',
},
components: {},
})Note: For spaces created in the United States or China, the
regionparameter must be specified.
@storyblok/react does three actions when you initialize it:
- Provides a
getStoryblokApiobject in your app, which is an instance of storyblok-js-client. - Loads the Storyblok Bridge for real-time visual updates.
- Provides a
storyblokEditablefunction to link editable components to the Storyblok Visual Editor.
For every component you've defined in your Storyblok space, call the storyblokEditable function with the blok content:
import { storyblokEditable } from '@storyblok/react'
const Feature = ({ blok }) => {
return (
<div {...storyblokEditable(blok)} key={blok._uid} data-test="feature">
<div>
<div>{blok.name}</div>
<p>{blok.description}</p>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default FeatureWhere blok is the actual blok data coming from Storyblok's Content Delivery API.
Note: The
storyblokEditablefunction works the same way for all the frameworks and components created.
Getting Started
This SDK provides you the support to work with React and all React Frameworks such as Next.js, Remix etc. Depending upon these different frameworks and versions, the way to use the SDK and the functionalities it provides differ.
Below is the guide and examples on how to use it with different frameworks -
React
The initalization remains the same when you work with React. You can intialze the SDK in the index.js file. Please refer to the 'Initialization' section above to read more.
Fetching Content and Listening to Storyblok Visual Editor events
Use useStoryblok to fetch the content as well as enable live editing. You need to pass the slug as the first parameter, apiOptions as the second parameter, and bridgeOptions as the third parameter, which is optional if you want to set the options for the bridge by yourself. Check the available apiOptions (passed to storyblok-js-client) and bridgeOptions (passed to the Storyblok Bridge).
import { StoryblokComponent, useStoryblok } from '@storyblok/react'
function App() {
const story = useStoryblok('react', { version: 'draft' })
if (!story?.content) {
return <div>Loading...</div>
}
return <StoryblokComponent blok={story.content} />
}
export default AppStoryblokComponent renders the route components dynamically, using the list of components loaded during the initialization inside the storyblokInit function.
This is how you can pass the Bridge options as a third parameter to useStoryblok:
useStoryblok(
story.id,
{ version: 'draft', resolveRelations: ['Article.author'] },
{
resolveRelations: ['Article.author'],
resolveLinks: 'url',
preventClicks: true,
}
)Check out our React Boilerplate here, or read on how to add Storyblok to React in 5 mins here You can also take a look at the React Playground in this repo.
Learn: Next.js 13 and 14 Data Fetching and Caching Behavior
When using Next.js 13 or 14 with the App Router, ensure that you include cache: "no-store" in your requests when fetching data from Storyblok. This prevents data caching, ensuring that you always receive the most up-to-date content from Storyblok.
For more details, refer to the Next.js documentation on opting out of caching.
Note: In Next.js 15, this will no longer be necessary, as the default caching behavior has been adjusted based on community feedback.
Example
Here's how you can fetch data from Storyblok with cache: "no-store":
export async function fetchData() {
const sbParams: ISbStoriesParams = { version: 'draft' }
const storyblokApi: StoryblokClient = getStoryblokApi()
return storyblokApi.get(`cdn/stories/home`, sbParams, {
cache: 'no-store', // This prevents Next.js 13, 14 default caching behaviour
})
}Next.js using App Router
The components in the app directory are by default React Server Side Components, which limits the reactivity. You can enable Storyblok Visual Editor's live editing with React Server Components by rendering them inside a wrapper (StoryblokPovider) on the client. The SDK allows you to take full advantage of the Live Editing, but the use of Server Side Components is partial, which will be still better than the older Next.js approach performance-wise. The next section explains about how to use complete server side approach.
The SDK has a special module for RSC. Always import
@storyblok/react/rscwhile using Server Components.
1. Initialize
Create a new file lib/storyblok.js and initialize the SDK. Make sure you export the getStoryblokApi function, which is an instance of storyblok-js-client that is shared by client and server components.
// lib/storyblok.js
import Page from '@/components/Page';
import Teaser from '@/components/Teaser';
import { apiPlugin, storyblokInit } from '@storyblok/react/rsc';
export const getStoryblokApi = storyblokInit({
accessToken: 'YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
use: [apiPlugin],
components: {
teaser: Teaser,
page: Page,
},
});In app/layout.jsx, wrap your whole app using a StoryblokProvider component (this provider is created in the next step) :
// app/layout.jsx
import { apiPlugin, storyblokInit } from '@storyblok/react/rsc'
import StoryblokProvider from '../components/StoryblokProvider'
export default function RootLayout({ children }) {
return (
<StoryblokProvider>
<html lang="en">
<body>{children}</body>
</html>
</StoryblokProvider>
)
}2. Create StoryblokProvider and Import your Storyblok Components
Create the components/StoryblokProvider.jsx file. Re-initalize the connection with Storyblok (this time, on the client) using the getStoryblokApi function imported from the lib/storyblok file. This will enable the client-side compoenents to interact with the Storyblok API, including the Visual Editor.
// components/StoryblokProvider.jsx
'use client';
import { getStoryblokApi } from '@/lib/storyblok';
export default function StoryblokProvider({ children }) {
getStoryblokApi();
return children;
}3. Fetch Content and Render Components
The getStoryblokApi function can now be used inside your Story components to fetch the data from Storyblok. In app/page.jsx, use it as follows:
import { StoryblokClient, ISbStoriesParams } from '@storyblok/react';
import { StoryblokStory } from '@storyblok/react/rsc';
import { getStoryblokApi } from '@/lib/storyblok'; // Remember to import from the local file
export default async function Home() {
const { data } = await fetchData();
return (
<div>
<StoryblokStory story={data.story} />
</div>
);
}
export async function fetchData() {
let sbParams: ISbStoriesParams = { version: 'draft' };
const storyblokApi: StoryblokClient = getStoryblokApi();
return storyblokApi.get(`cdn/stories/home`, sbParams);
}StoryblokStory keeps the state for thet story behind the scenes and uses StoryblokComponent to render the route components dynamically, using the list of components loaded during the initialization inside the storyblokInit function. You can use the StoryblokComponent inside the components to render the nested components dynamically. You can also pass bridge options to StoryblokStory using the prop bridgeOptions.
const bridgeOptions = { resolveRelations: ['article.author'] }
<StoryblokStory story={data.story} bridgeOptions={bridgeOptions} />[!IMPORTANT] When you render components, you must use
StoryblokServerComponentexported from@storyblok/react/rscinstead ofStoryblokComponent, even when you declare a client component with"use client". This is because the components are always rendered on the server side.
import { StoryblokServerComponent } from '@storyblok/react/rsc';
export default function Page({ blok }) {
return <StoryblokServerComponent blok={blok} />;
}[!NOTE] To use this approach (with
getStoryblokApi), you need to include theapiPluginmodule when callingstoryblokInitfunction. If you don't useapiPlugin, you can use your preferred method or function to fetch your data.
To try this setup, take a look at the Next 13 Live Editing Playground in this repo.
Next.js using Pages Router
In this section, we'll see how to use the React SDK with the pages directory approach.
The initalization remains the same when you work with Next.js. You can intialze the SDK in the _app.js file. Please refer to the 'Initialization' section above to read more.
1. Fetching Content
The SDK provides a getStoryblokApi object in your app, which is an instance of storyblok-js-client. This can be used to fetch the content from Storyblok. You can use it in functions like getStaticProps, getStaticPaths, getServerSideProps etc.
import { getStoryblokApi } from '@storyblok/react'
// At the required place
const storyblokApi = getStoryblokApi()
const { data } = await storyblokApi.get('cdn/stories', { version: 'draft' })Note: To use this approach, you need to include the
apiPluginmodule when callingstoryblokInitfunction. If you don't useapiPlugin, you can use your preferred method or function to fetch your data.
2. Listening to Storyblok Visual Editor events
The SDK also provides you with the useStoryblokState hook. It works similarly to useStoryblok for live editing, but it doesn't fetch the content. Instead, it receives a story object as the first parameter. You can also pass the Bridge Options as the second parameter.
import { StoryblokComponent, useStoryblokState } from '@storyblok/react'
export default function Home({ story: initialStory }) {
const story = useStoryblokState(initialStory)
if (!story.content) {
return <div>Loading...</div>
}
return <StoryblokComponent blok={story.content} />
}In this case, the story is being passed as a prop that can be coming from where the story is being fetched. A complete example would look like this-
import {
getStoryblokApi,
StoryblokComponent,
useStoryblokState,
} from '@storyblok/react'
export default function Home({ story: initialStory }) {
const story = useStoryblokState(initialStory)
if (!story.content) {
return <div>Loading...</div>
}
return <StoryblokComponent blok={story.content} />
}
export async function getStaticProps({ preview = false }) {
const storyblokApi = getStoryblokApi()
const { data } = await storyblokApi.get(`cdn/stories/react`, {
version: 'draft',
})
return {
props: {
story: data ? data.story : false,
preview,
},
revalidate: 3600, // revalidate every hour
}
}StoryblokComponent renders the route components dynamically, using the list of components loaded during the initialization inside the storyblokInit function.
Check out the code for the first part of our Next.js + Storyblok Ultimate Tutorial. Or you can also read on how to add Storyblok to a Next.js project in 5 minutes here
3. Adding components per page
If you are using the pages router, you might want to load your components per page, instead of all in the _app file.
If you load all components in the _app file with storyblokInit funciton, the JavaScript for all of those components will be loaded on every page, even on pages where most of these components might not be used.
A better approach is to load these components on a per-page basis, reducing the JS bundle for that page, improving your load time, and SEO.
Simply execute storyblokInit in the _app file as you did before, but omit the components object and the component imports like so:
import { storyblokInit, apiPlugin } from "@storyblok/react";
/** Import your components */
-import Page from "./components/Page";
-import Teaser from "./components/Teaser";
storyblokInit({
accessToken: "YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN",
use: [apiPlugin],
- components: {
- page: Page,
- teaser: Teaser,
- },
});After that, use the setComponent method in each of your pages, to only load the components you need for that particular page:
import React from "react";
import Teaser from "../components/teaser";
import Grid from "../components/grid";
import Page from "../components/page";
import Feature from "../components/feature";
import {
useStoryblokState,
StoryblokComponent,
+ setComponents,
} from "@storyblok/react";
export default function Home({
story: initialStory,
}: InferGetStaticPropsType<typeof getStaticProps>) {
+ setComponents({
+ teaser: Teaser,
+ grid: Grid,
+ feature: Feature,
+ page: Page,
+ })
const story = useStoryblokState(initialStory);
if (!story.content) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
return <StoryblokComponent blok={story.content} />;
}Features and API
You can choose the features to use when you initialize the plugin. In that way, you can improve Web Performance by optimizing your page load and save some bytes.
Storyblok API
You can use an apiOptions object. This is passed down to the storyblok-js-client config object:
storyblokInit({
accessToken: 'YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
apiOptions: {
// storyblok-js-client config object
cache: { type: 'memory' },
},
use: [apiPlugin],
components: {
page: Page,
teaser: Teaser,
grid: Grid,
feature: Feature,
},
})If you prefer to use your own fetch method, just remove the apiPlugin and storyblok-js-client won't be added to your application.
storyblokInit({})Storyblok Bridge
If you don't use registerStoryblokBridge, you still have access to the raw window.StoryblokBridge:
const sbBridge = new window.StoryblokBridge(options)
sbBridge.on(['input', 'published', 'change'], (event) => {
// ...
})Rendering Rich Text
You can easily render rich text by using the renderRichText function that comes with @storyblok/react:
import { renderRichText } from '@storyblok/react'
const renderedRichText = renderRichText(blok.richtext)You can set a custom Schema and component resolver globally at init time by using the richText init option:
import { RichTextSchema, storyblokInit } from '@storyblok/react'
import cloneDeep from 'clone-deep'
const mySchema = cloneDeep(RichTextSchema) // you can make a copy of the default RichTextSchema
// ... and edit the nodes and marks, or add your own.
// Check the base RichTextSchema source here https://github.com/storyblok/storyblok-js-client/blob/main/src/schema.ts
storyblokInit({
accessToken: '<your-token>',
richText: {
schema: mySchema,
resolver: (component, blok) => {
switch (component) {
case 'my-custom-component':
return `<div class="my-component-class">${blok.text}</div>`
default:
return 'Resolver not defined'
}
},
},
})You can also set a custom Schema and component resolver only once by passing the options as the second parameter to renderRichText function:
import { renderRichText } from '@storyblok/react'
renderRichText(blok.richTextField, {
schema: mySchema,
resolver: (component, blok) => {
switch (component) {
case 'my-custom-component':
return `<div class="my-component-class">${blok.text}</div>`
default:
return `Component ${component} not found`
}
},
})We also recommend using the Storyblok Rich Text Renderer for React by Claus for rendering your Storyblok rich text content to React elements and Next.js applications.
Using fallback components
By default, @storyblok/react returns an empty <div> if a component is not implemented. Setting enableFallbackComponent to true when calling storyblokInit bypasses that behavior, rendering a fallback component in the frontend instead. You can use the default fallback component, or create a custom React fallback component in your project and use it by setting customFallbackComponent: [YourFallbackComponent].
Efficiently Loading Storyblok Components in React
When using Storyblok with React, the general approach is to load all the Storyblok components when initializing Storyblok, usually in a layout page to ensure all pages have access to all of them:
storyblokInit({
accessToken,
use: [apiPlugin],
components: {
// all your React components
},
})Storyblok's React SDK automatically renders these predefined components based on your page content. While this is convenient, it can lead to larger bundle sizes and slower page speeds, especially for larger sites or when using heavy JavaScript libraries that are only needed on specific pages or a specific component.
Solutions
-
Storyblok's
setComponentsFunction: Storyblok SDK provides a function calledsetComponentsthat allows you to load only the components needed for each route instead of defining all components during initialization. This approach is useful but might not be practical if you use a catch-all route, which is common in many React frameworks. -
React's
react.lazy: React offers a built-in solution calledreact.lazyfor code splitting. Instead of directly importing components, you can do the following:'use client' import { apiPlugin, storyblokInit } from '@storyblok/react/rsc' import { lazy } from 'react' const lazyComponents = { page: lazy(() => import('./components/Page')), // other lazy-loaded components } storyblokInit({ accessToken, use: [apiPlugin], components: lazyComponents, })This approach enables automatic code splitting and loads only the necessary JavaScript for each page. However,
react.lazyhas some limitations when used with SSR (Server-Side Rendering). -
Using
@loadable/component: For cases where SSR is needed, or in general, you can use the@loadable/componentlibrary, which offers similar functionality and better SSR support. This library is framework-agnostic and can be used with any React framework. Loadable Components Documentation -
Next.js Dynamic Import: Next.js has a built-in
dynamicpackage that provides dynamic imports for lazy loading. Next.js Dynamic Import Documentation
By using these techniques, you can ensure that only the necessary components and dependencies are loaded for each page, improving your site's performance and speed.
The Storyblok JavaScript SDK Ecosystem
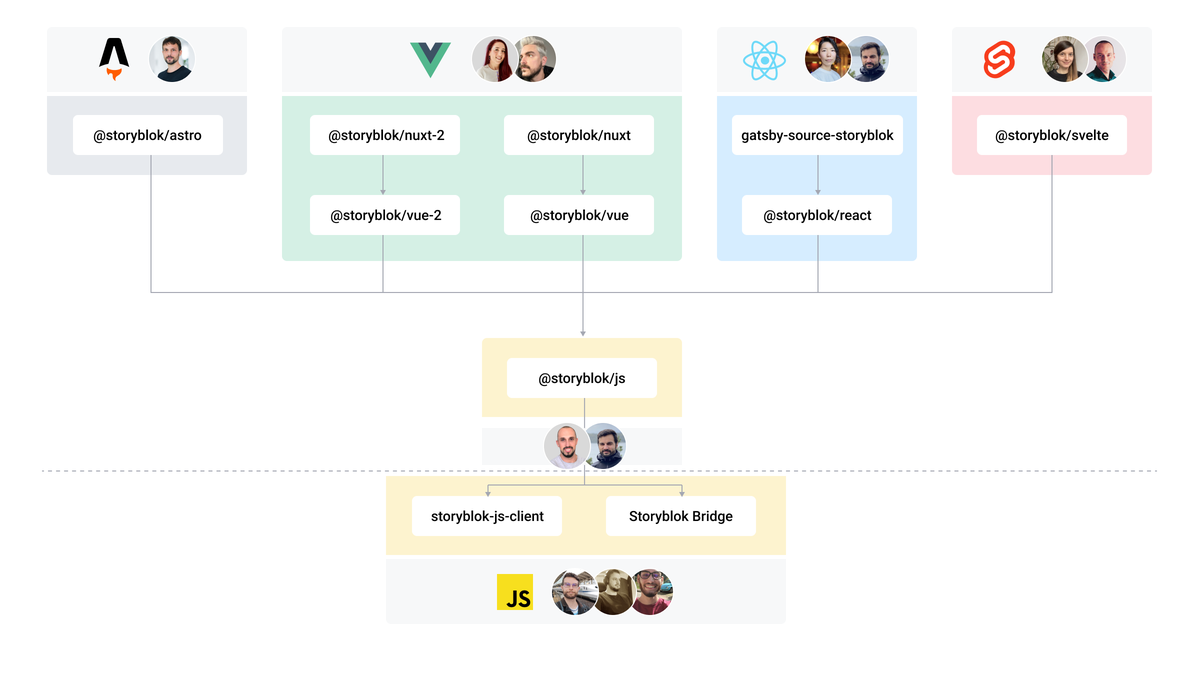
Further Resources
Support
- Bugs or Feature Requests? Submit an issue.
- Do you have questions about Storyblok or you need help? Join our Discord Community.
Contributing
Please see our contributing guidelines and our code of conduct. This project use semantic-release for generate new versions by using commit messages and we use the Angular Convention to naming the commits. Check this question about it in semantic-release FAQ.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.




