TableModel - Live Demo
TableModel is an in-memory data model that automatically calculates your data based on provided equations. It keeps track of dependencies between data and equations and automatically updates cells quickly and efficiently.
TableModel works especially well with UI components like AgGrid because it simplifies your data flow and can add additional features such as predicting which cells in your table are going to be impacted by a change (see below).
Preview: AgGrid powered by TableModel (AgGrid not included)
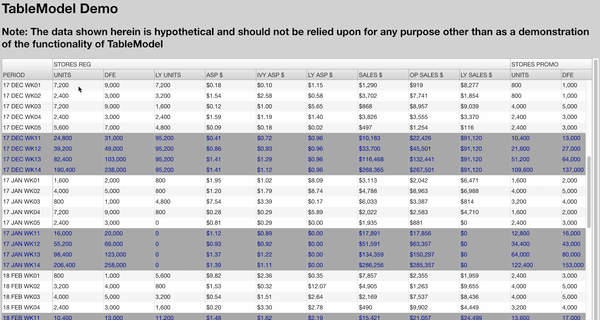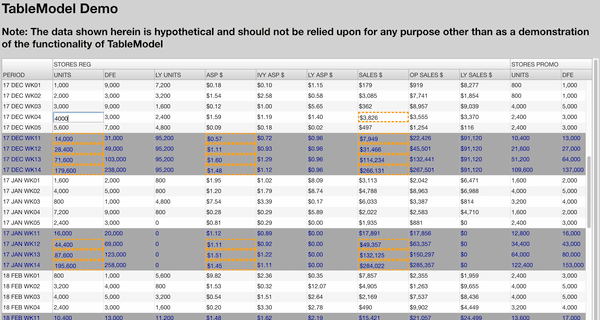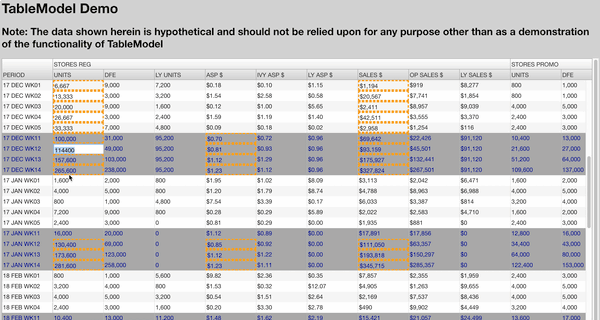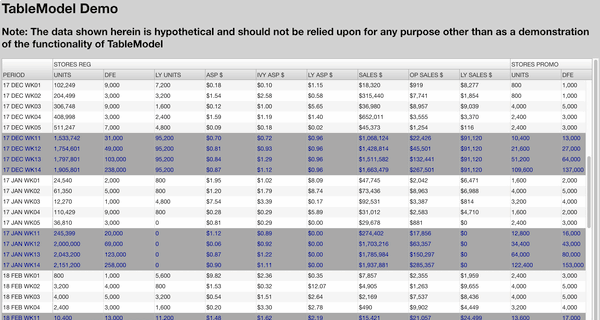
Getting Started
Install table-model:
npm install --save-dev table-modelImport the 'table-model' module into your project:
ES6+
import TableModel from 'table-model';CommonJS
const TableModel = require('table-model');Usage
A unit test of the following example can be found at src/example.spec.js
// Formulas
const totalEquation = d => d.row('a') + d.row('b') + d.row('c');
const extraEquation = d => d.row('b') * d.row('c');
// This builds a formula that matches a given color
const colorTotals = color => {
return d => {
// Get the 'total's from all rows with the matching color
const numbers = d.rowsWhere({ type: color }, 'total');
// Sum up the numbers to get to total
return numbers.reduce((total, num) => total + num, 0);
};
};
// This array contains a list of our rows and their cells
const rowDefs = [
// Row 1
{
meta: { id: 1, type: 'red' },
cells: { a: 10, b: 20, c: 30, total: totalEquation }
},
// Row 2
{
meta: { id: 2, type: 'green' },
// Rows don't have to have the same types of cells
cells: { a: 12, b: 45, c: 38, d: 1234, total: totalEquation, extra: extraEquation }
},
// Row 3
{
meta: { id: 3, type: 'red' },
cells: { a: 100, b: 200, c: 300, total: totalEquation }
},
// Totals
{
meta: { id: 4 },
cells: { redTotal: colorTotals('red'), greenTotal: colorTotals('green') }
}
];
const listener = updates => console.log('UPDATES:', updates);
const table = TableModel({ rowDefs, listener });
// Output: All cell values are included in the first update
// UPDATES: {
// 1: { a: 10, b: 20, c: 30, total: 60 },
// 2: { a: 12, b: 45, c: 38, d: 1234, total: 95, extra: 1710 },
// 3: { a: 100, b: 200, c: 300, total: 600 },
// 4: { redTotal: 660, greenTotal: 95 }
// });
table.update({ 2: { c: 123 } });
// Output: Only cells that were impacted by the update are included after that
// UPDATES: {
// 2: { c: 123, total: 180, extra: 5535 },
// 4: { greenTotal: 180 }
// });Docs
Cell Definitions
TableModel API
Built-in Helper Functions
Why?
Fast
Because TableModel analyzes your equations, it knows which other values and equations are impacted by any given change. This ensures that when a change happens, TableModel only does the minimum amount of work it needs to do.
Testable
If you're using a UI library like AgGrid to do your calculations for you, it can add an additional layer of complexity when trying to test. AgGrid requires a DOM to run and test with. This is not ideal for the simplicity and performance of your tests.
By using TableModel to handle your data, you can write units tests for your equations which are simple and easy to write, and decoupled from the view. See an example TableModel unit test at
src/example.spec.js.
Maintainable
If your data model has a lot of calculations your code base can get complicated very quickly, for example, maintaining the proper order of the calculations, and determining which values need to be recalculated (or not) when another values changes.
TableModel abstracts all this complexity away for you. All you have to do is define simple equations, feed TableModel your data, and it'll take care of the rest. TableModel automatically manages the dependencies between your equations. If you need to make changes down the road, you only have to update your equations.
Separation of Concerns -or- "Do one thing and do it well"
If you're using a library like AgGrid to render your data in a UI component, you might realize that AgGrid is REALLY good at presenting data, but has some limitations when trying to handle calculations, for example, trying to operate on data in multiple rows.
By using TableModel with AgGrid, you can use AgGrid to do what it does best (display data - the View) and let TableModel take care of what it does best (calculation and data management - the Model).
Features
- Automatic Updates
- Setter Functions
- Update Prediction
- Custom Helpers Functions
- Custom PreLink Callback for Optimization
- AgGrid Support
Who uses TableModel?
- Target
- ... that's it so far. (Send a PR if you use TableModel 😎)