ArduinoYaml A.K.A YAMLDuino
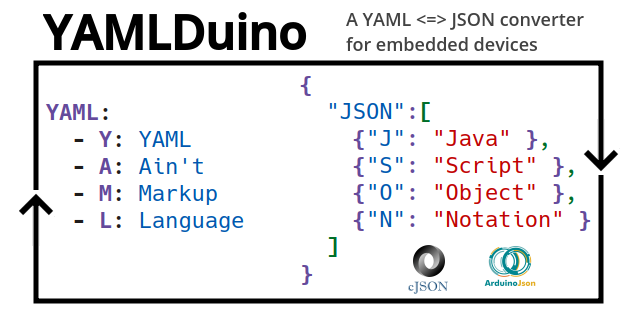
This arduino library is based on libyaml.
Supported platforms:
- ESP32
- RP2040
- ESP8266
- SAMD
- TeensyDuino
Features:
- YAML➔JSON and JSON➔YAML conversion
- Accepts valid JSON or YAML as the input.
- Standalone serializers/deserializers
- ArduinoJson serializers/deserializers
- cJSON serializers/deserializers
- Node accessors
- l10n style gettext()
- i18n loader
Usage
#include <ArduinoYaml.h>or
#include <YAMLDuino.h>Pure libyaml implementation
YAML is a superset of JSON, so native conversion from/to JSON is possible without any additional JSON library.
// Available values for output format:
// OUTPUT_YAML (default)
// OUTPUT_JSON
// OUTPUT_JSON_PRETTY
// JSON/YAML document to YAML/JSON string
size_t serializeYml( yaml_document_t* src_doc, String &dest_string, OutputFormat_t format=OUTPUT_YAML );
// JSON/YAML object to YAML/JSON stream
size_t serializeYml( yaml_document_t* src_doc, Stream &dest_stream, OutputFormat_t format=OUTPUT_YAML );
// YAML stream to YAML document
int deserializeYml( YAMLNode& dest_obj, const char* src_yaml_str );
// YAML string to YAML document
int deserializeYml( YAMLNode& dest_obj, Stream &src_stream );
Convert YAML to JSON
String yaml_str = "hello: world\nboolean: true\nfloat: 1.2345";
YAMLNode yamlnode = YAMLNode::loadString( yaml_str );
serializeYml( yamlnode.getDocument(), Serial, OUTPUT_JSON_PRETTY ); // pretty JSON
// serializeYml( yamlnode.getDocument(), Serial, OUTPUT_JSON ); // ugly JSONConvert JSON to YAML
String json_str = "{\"hello\": \"world\", \"boolean\": true, \"float\":1.2345}";
YAMLNode yamlnode = YAMLNode::loadString( yaml_str );
serializeYml( yamlnode.getDocument(), Serial, OUTPUT_YAML );Bindings
ArduinoJson and cJSON bindings operate differently depending on the platform.
| ArduinoJson support | cJSON support | |
|---|---|---|
| ESP32 | detected (*) | implicit (built-in esp-idf) |
| ESP8266 | implicit | implicit (bundled) |
| RP2040 | implicit | implicit (bundled) |
| SAMD | implicit | implicit (bundled) |
(*) On ESP32 platform, the detection depends on __has_include(<ArduinoJson.h>) macro.
So all ArduinoJson functions will be disabled unless #include <ArduinoJson.h> is found before #include <ArduinoYaml.h>.
On ESP8266/RP2040/SAMD platforms it is assumed that ArduinoJson is already available as a dependency.
In order to save flash space and/or memory, the default bindings can be disabled independently by setting one or all of the following macros before including ArduinoYaml:
#define YAML_DISABLE_ARDUINOJSON // disable all ArduinoJson functions
#define YAML_DISABLE_CJSON // disable all cJSON functionsNote to self: this should probably be the other way around e.g. explicitely enabled by user.
Note to readers: should ArduinoJson and/or cJSON be implicitely loaded? Feedback is welcome!
ArduinoJson bindings
See the motivational post for this implementation.
ArduinoJson support is implicitely enabled on most platforms except for ESP32 where dependencies can be detected.
*ESP32 plaforms must include ArduinoJson.h before ArduinoYaml.h or bindings will be disabled!**
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include <ArduinoYaml.h>Enabling support will expose the following functions:
// ArduinoJSON object to YAML string
size_t serializeYml( JsonVariant src_obj, String &dest_string );
// ArduinoJSON object to YAML stream
size_t serializeYml( JsonVariant src_obj, Stream &dest_stream );
// Deserialize YAML string to ArduinoJSON object
DeserializationError deserializeYml( JsonObject &dest_obj, const char* src_yaml_str );
// Deserialize YAML stream to ArduinoJSON object
DeserializationError deserializeYml( JsonObject &dest_obj, Stream &src_stream );
// Deserialize YAML string to ArduinoJSON document
DeserializationError deserializeYml( JsonDocument &dest_doc, Stream &src_stream );
// Deserialize YAML string to ArduinoJSON document
DeserializationError deserializeYml( JsonDocument &dest_doc, const char *src_yaml_str) ;
cJSON bindings
cJSON support is implicitely enabled on most platforms, and will use the bundled cJSON version unless ESP32 platform is detected. ESP32 will use the built-in cJSON version from esp-idf instead of the YAMLDuino bundled version.
⚠️ Both versions of cJSON have a memory leak with floats, the leak happens only once though, and may be avoided by quoting the float, which won't affect yaml output.
Enabling support will expose the following functions:
// cJSON object to YAML string
size_t serializeYml( cJSON* src_obj, String &dest_string );
// cJSON object to YAML stream
size_t serializeYml( cJSON* src_obj, Stream &dest_stream );
// YAML string to cJSON object
int deserializeYml( cJSON* dest_obj, const char* src_yaml_str );
// YAML stream to cJSON object
int deserializeYml( cJSON* dest_obj, Stream &src_stream );
// YAML document to cJSON object
int deserializeYml( cJSON** dest_obj, yaml_document_t* src_document );
String/Stream helper
Although const char* is an acceptable source type for conversion, using Stream is recommended as it is more memory efficient.
The StringStream class is provided with this library as a helper.
String my_json = "{\"blah\":true}";
StringStream json_input_stream(my_json);
String my_output;
StringStream output_stream(my_output);
The StringStream bundled class is based on Arduino String and can easily be replaced by any class inheriting from Stream.
class StringStream : public Stream
{
public:
StringStream(String &s) : str(s), pos(0) {}
virtual ~StringStream() {};
virtual int available() { return str.length() - pos; }
virtual int read() { return pos<str.length() ? str[pos++] : -1; }
virtual int peek() { return pos<str.length() ? str[pos] : -1; }
virtual size_t write(uint8_t c) { str += (char)c; return 1; }
virtual void flush() {}
private:
String &str;
unsigned int pos;
};See ArduinoStreamUtils for other types of streams (i.e. buffered).
Output decorators
JSON and YAML indentation levels can be customized:
void YAML::setYAMLIndent( int spaces_per_indent=2 ); // min=2, max=16
void YAML::setJSONIndent( const char* spaces_or_tabs="\t", int folding_depth=4 );
Set custom JSON indentation and folding depth:
// this set two spaces per indentation level, unfolds up to 8 nesting levels
YAML::setJSONIndent(" ", 8 ); // lame fact: folds on objects, not on arrays
Set custom YAML indentation (minimum=2, max=16):
// annoy your friends with 3 spaces indentation, totally valid in YAML
YAML::setYAMLIndent( 3 );
YAML gettext Module
The gettext module is a member of YAMLNode object.
class YAMLNode
{
// (...)
public:
const char* gettext( const char* path, char delimiter=':' );
// YAMLNode objects also bring few interesting methods to scope:
const char* scalar();
size_t size();
bool isScalar();
bool isSequence();
bool isMap();
bool isNull();
// (...)
}Usage (persistent)
Load from string:
YAMLNode yamlnode = YAMLNode::loadString( yaml_or_json_string );Load from stream:
YAMLNode yamlnode = YAMLNode::loadStream( yaml_or_json_stream );Access a value:
const char* text = yamlnode.gettext( "path:to:property:name" );Usage (non persistent)
YAMLNode supports chaining:
// load yaml and extract value from 'stuff'
YAMLNode::loadString("blah:\n stuff:\n true\n").gettext("blah:stuff");
// load json and extract value from 'stuff'
YAMLNode::loadString("{\"blah\":{\"stuff\":\"true\"}}").gettext("blah:stuff");I18N/L10N with gettext Module
Note: i18n Support is disabled with WIO Terminal (platform needs a proper fs::FS filesystem implementation).
WIO Terminal can still use the native YAMLNode::gettext() though.
Usage
- Include ArduinoJson and a
fs::FSfilesystem first - Create an i18n instance and assign the filesystem
i18n_t i18n( &LittleFS );. - Load
en-GBlocale withi18n.setLocale("en-GB"). - Use
i18n.gettext()to access localized strings.
Example
YAML Sample /lang/en-GB.yml stored in LittleFS:
en-GB:
hello: world
blah:
my_array:
- first
- second
- third
Load the language file and access translations:
#include <LittleFS.h> // Mandatory filestem (can be SPIFFS, SD, SD_MMC, LittleFS)
#include <YAMLDuino.h> // Load the library
i18n_t i18n( &LittleFS ); // Create an i18n instance attached to filesystem
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
LittleFS.begin();
// i18n.setFS( &SD ); // change filesystem to SD
i18n.setLocale("en-GB"); // This will look for "en-GB.yml" language file in "/lang/" folder and set "en-GB" as locale
// i18n.setLocale("/lang/en-GB.yml"); // This will load "/lang/en-GB.yml" language file and set "en-GB" as locale
// i18n.setLocale("en-GB", "/non-locale/file.yml"); // This will set "en-GB" as locale and load arbitrary "/non-locale/file.yml" language file
Serial.println( i18n.gettext("hello" ) ); // prints "world"
Serial.println( i18n.gettext("blah:my_array:2" ) ); // prints "third"
}
void loop()
{
delay(1000);
}Debug
The debug level can be changed at runtime:
void YAML::setLogLevel( LogLevel_t level );Set library debug level:
//
// Accepted values:
// LogLevelNone : No logging
// LogLevelError : Errors
// LogLevelWarning : Errors+Warnings
// LogLevelInfo : Errors+Warnings+Info
// LogLevelDebug : Errors+Warnings+Info+Debug
// LogLevelVerbose : Errors+Warnings+Info+Debug+Verbose
YAML::setLogLevel( YAML::LogLevelDebug );Support the Project
There are a few things you can do to support the project:
- Star 🌟 this repository and/or follow me on GitHub
- Share and upvote on sites like Twitter, Reddit, and Hacker News
- Report any bugs, glitches, or errors that you find
These things motivate me to to keep sharing what I build, and they provide validation that my work is appreciated! They also help me improve the project. Thanks in advance!
Credits and special thanks to:
Additional resources:
- ArduinoJson : https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson
- ArduinoStreamUtils : https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoStreamUtils
- cJSON : https://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON
- libyaml : https://github.com/yaml/libyaml