PagedDataTable
Completely customisable data table which supports cursor and offset pagination, filters and horizontal scrolling out-of-the-box. It's written from scratch, no dependency from Flutter's DataTable nor Table.
Designed to follow Google's Material You style.
Online demo
Features
- Horizontal scrolling, allowing you to define columns wider than the viewport width.
- Fixed columns, to scroll horizontally only a set of columns.
- Row updating on demand, preventing you to create other views for updating fields of a class. Now you can update an object from the table directly.
- Cursor and offset pagination, you decide how to paginate your data.
- Filtering by date, text, number, whatever you want!
- Sorting by predefined columns
- Page modification using controller, to add or remove items to the current page without reloading the entire table.
- Themeable, allowing you to change colors, fonts, text styles, and more!
Table Of Contents
Setup
Everything you need is a PagedDataTable<K, T> widget, which accepts two generic arguments, K and T, the type of object you will use as paging key and the type of object you will be showing in the table.
Keep in mind that
Kmust extendsComparable.
There are only two required parameters: columns and fetcher.
PagedDataTable<String, Post>(
fetcher: (int pageSize, SortModel? sortModel, FilterModel filterModel, String? pageToken) => ...,
columns: [...],
)Fetcher
The fetcher is a function that gets called every time a page is requested. It gives you the current page size, sort and filter models and the page token that is requested. It must return
a FutureOr<(List<T>, K?)>, so you can convert it to a Future and do async-like requests or simply return the data.
It expects a tuple, where the first value is the list of items and the second the next page token:
PagedDataTable<String, Post>(
fetcher: (int pageSize, SortModel? sortModel, FilterModel filterModel, String? pageToken) {
final result = await FetchService.listPosts();
return (result.data, result.nextPageToken);
},
columns: [...],
)By default, PagedDataTable does not copy the returned list, so, if it is a shared list, you or the table may modify the items. If you want, PagedDataTable can copy the list
if you specify it in the configuration property:
Note that
PagedDataTableDOES NOT cache pages.
PagedDataTable<String, Post>(
configuration: PagedDataTableConfiguration(
copyItems: true,
),
)Header
The header renders the column names, but also the FilterBar exists, which is an additional header that renders the filter picker and, optionally, you can display additional widgets aligned at the right of the bar.
Just pass your widget to the filterBarChild property. Naturally you would want to display a PopupMenuButton that will act as a menu.
Footer
Using the footer property you can render anything. If you don't pass it, it will render the DefaultFooter widget,
which again, if not specified, will display, aligned to the right, the following widgets:
- Refresh button: A button that can be used to refresh the current dataset.
- Page size selector: A dropdown that can be used to select the current page size to use, based on the
pageSizesproperty. - Current page display: Displays the current page number.
- Navigation buttons: will display the previous and next buttons as
IconButtons.
Custom footer
If you want your own footer widget but reuse some of the already existing widgets, they are named: RefreshButton, PageSizeSelector, CurrentPage and NavigationButtons.
Columns
There are two types of columns in PagedDataTable:
- ReadOnlyTableColumn<K, T>: renders a simple widget that does not allow edition.
- EditableTableColumn<K, T, V>: renders a simple widget too, but this can be modified in place and modify the dataset.
KandTare the same parameters defined in thePagedDataTablewidget.
Every column type has:
- title: the column's title. It is a widget but commonly it's a
Textwidget displaying the name. - size: configures the column's size. By default, it is a
FractionalColumnSize(.1), which means it will take 10% of the available width. You can useFixedColumnSize,FractionalColumnSize,RemainingColumnSizeandMaxColumnSize. - format: applies a transformation to the cell's widget. You have
NumericColumnFormat, which aligns content to the right andAlignColumnFormatwhich aligns cell's content to thealignmentproperty and you can implement your own implemeting theColumnFormatinterface. - sort and id: both properties are used to indicate that a column can be used for sorting. The
idis what you get in the Fetcher'sSortModel. To sort, you click the column's header. - There are other properties that you can use to play around and modify your columns. Check out the
ReadOnlyTableColumn's documentation.
If you want to fix columns at the left, you can specify the amount of columns to fix using the
fixedColumnCountproperty.
TableColumn<K, T>
Is the default ReadOnlyTableColumn that renders a cell using the cellBuilder property.
PagedDataTable<String, Post>(
columns: [
TableColumn(
title: const Text("Author"),
cellBuilder: (context, item, index) => Text(item.author),
),
],
)EditableTableColumn<K, T, V>
This abstract class provides two more properties, getter and setter. The first one is used to provide the value V to render and the second one
is the function used to set the new value. It must return a boolean indicating if the operation succeeded or not. If is true, the cell will update its
value, otherwise will keep the old one.
There are three built in editable columns, which are DropdownTableColumn which renders a dropdown; TextTableColumn which renders a Text until double-clicked, then it renders a TextField used to edit the cell's content; LargeTextTableColumn, which is the same as TextTableColumn but when
double-clicked, it opens an overlay, designed to edit large text cells.
You can create your own column.
Custom columns
To create your own columns, simply extend ReadOnlyTableColumn or EditableTableColumn depending on your needs.
For example:
class MyColumnType<K, T> extends ReadOnlyTableColumn<K, T> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, T item, int index) {
return MyCellWidget();
}
}If you want more examples, check out the implementation of the already existing column types.
Filters
PagedDataTable allows you to define a set of filters that you can use to interactively select them using a
popup overlay or a bottom sheet if you are in a small device.
To define filters, use the filters property:
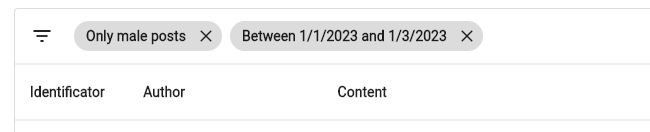
PagedDataTable<String, Post>(
...,
filters: [
TextTableFilter(
id: "content",
chipFormatter: (value) => 'Content has "$value"',
name: "Content",
),
DropdownTableFilter<Gender>(
items: Gender.values
.map((e) =>
DropdownMenuItem(value: e, child: Text(e.name)))
.toList(growable: false),
chipFormatter: (value) =>
'Author is ${value.name.toLowerCase()}',
id: "authorGender",
name: "Author's Gender",
),
],
)There are five built-in filter types:
TextTableFilter: renders aTextFieldto filter by raw text.DropdownTableFilter: renders aDropdownButtonwith a set of options.DateTimePickerTableFilter: renders aTextFieldthat, when tapped, opens theDateTimepicker dialog.DateRangePickerTableFilter: the same asDateTimePickerTableFilterbut selects aDateTimeRange.ProgrammingTextFilter: a filter that does not render nothing in the filter dialog but can be set using the controller.
Every filter type must define, at least, the id, the name and the chipFormatter properties. The first one is the identifier of the filter, used in the fetcher's FilterMode property. The name is the label displayed in the filter picker and the chipFormatter is a function that maps the actual selected value to a more user-friendly string that is displayed in the selected filter's chip.
Custom filters
To create your own filter, extend the TableFilter<T> abstract class, where T is the type of value the filter will handle. Then, implement the buildPicker function, which renders the actual filter picker.
The implementation of the TextTableFilter as an example:
final class TextTableFilter extends TableFilter<String> {
final InputDecoration? decoration;
const TextTableFilter({
this.decoration,
required super.chipFormatter,
required super.id,
required super.name,
super.initialValue,
super.enabled = true,
});
@override
Widget buildPicker(BuildContext context, FilterState<String> state) {
return TextFormField(
decoration: decoration ?? InputDecoration(labelText: name),
initialValue: state.value,
onSaved: (newValue) {
if (newValue != null && newValue.isNotEmpty) {
state.value = newValue;
}
},
);
}
}Controller
If you want to control the table programatically, provide your own PagedDataTableController<K, V> instance passing it to the controller property. It provides methods to interact with rows (selecting, unselecting, removing, inserting, updating), filters, sorting, pagination, and more.
Internationalization
Update your MaterialApp or CupertinoApp widget with the following:
localizationsDelegates: const [
PagedDataTableLocalization.delegate
],
And you're done.
At the moment of writing this, the supported locales are:
- es: Spanish
- en: English
- de: Deutsch
If you want more languages, you can contribute.
Screenshots
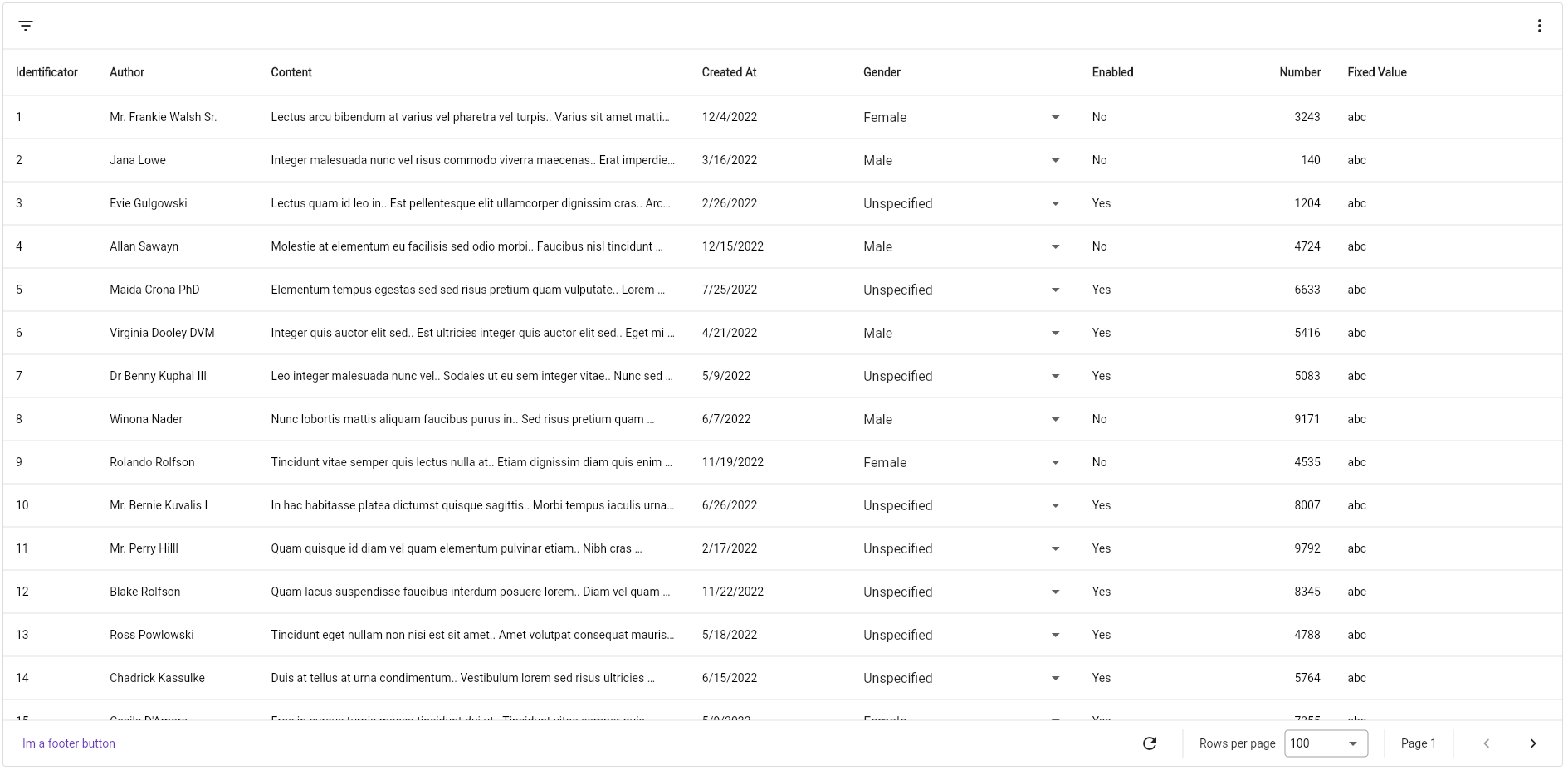
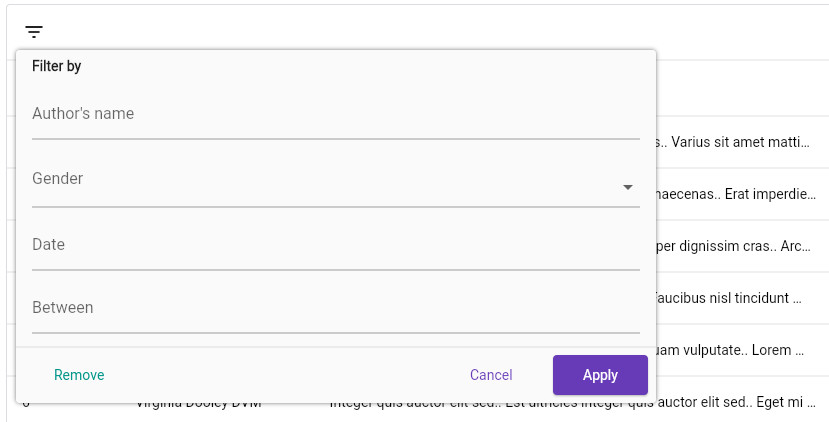
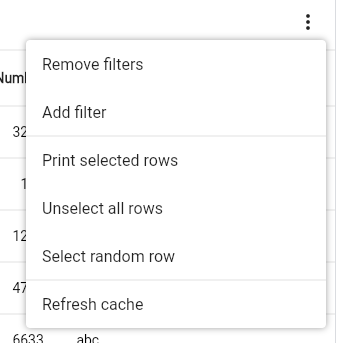
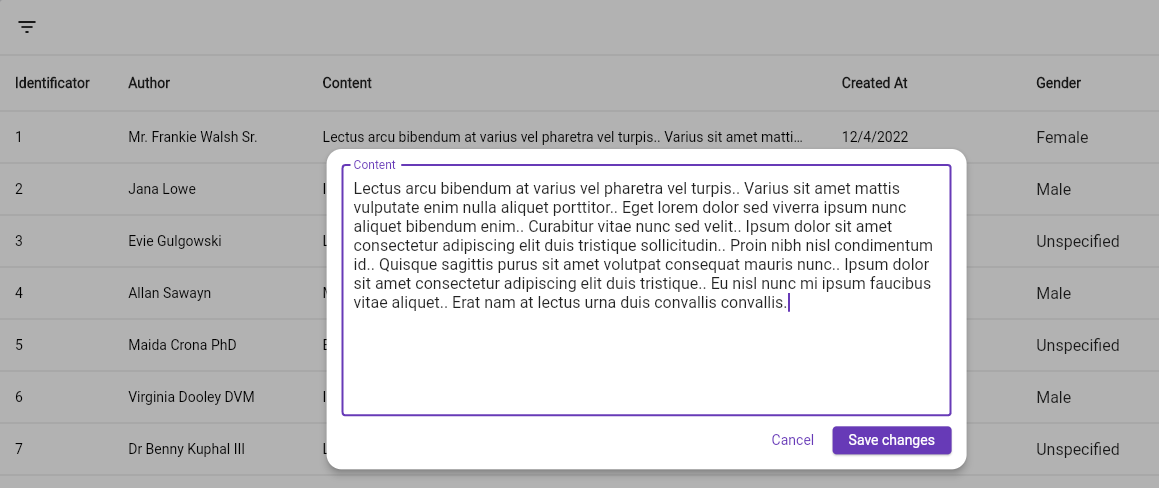
Contribute
Any suggestion to improve/add is welcome, if you want to make a PR, you are welcome :)
