IMPORTANT!!!
This project will not be further developed and bugs won't be fixed.
Instead, we advice you to use CityJSON (and convert your files with citygml-tools) and then use cjio export operator to get an OBJ file.
CityGML2OBJs
A robust semantic-aware utility to convert CityGML data to OBJ, featuring some additional options reflected through the suffix "s" in the name of the package:
- semantics -- decoupling of thematically structured surfaces in CityGML and converting them into separate OBJs (that's where the "OBJs" in the name come from).
- structured objects -- separation and storage of buildings into multiple objects in OBJ by structuring faces that belong to a building into the same group.
- "see" the attributes from a CityGML file -- the utility converts quantitative attributes into colours to support their visualisation.
- sturdy -- checks polygons for validity, considers different forms of geometry storage in GML, detects for lack of boundary surfaces, etc.
- solution to finally make use of those CityGML files (sarcasm is also an S word :-)). OBJ is probably the most supported 3D format, and converting your CityGML files to OBJ opens a door to a large number of software packages and uses.
Things to know
This is an experimental research software prototype. Therefore, support is limited, and the software is not without bugs. For instance, there are reports of crashes with large data sets and/or with invalid geometries.
If you'd like to learn more about OBJ, I recommend to read the Wikipedia entry and/or the specifications.
Publication and conditions for use
This software is free to use. You are kindly asked to acknowledge its use by citing it in a research paper you are writing, reports, and/or other applicable materials. If you used it for making a nice publication, please cite the following paper:
Biljecki, F., & Arroyo Ohori, K. (2015). Automatic semantic-preserving conversion between OBJ and CityGML. Eurographics Workshop on Urban Data Modelling and Visualisation 2015, pp. 25-30.
@inproceedings{Biljecki:2015vk,
author = {Biljecki, Filip and Arroyo Ohori, Ken},
title = {{Automatic Semantic-preserving Conversion Between OBJ and CityGML}},
booktitle = {Eurographics Workshop on Urban Data Modelling and Visualisation 2015},
year = {2015},
pages = {25--30},
address = {Delft, Netherlands},
doi = {10.2312/udmv.20151345},
month = nov
}Features explained in more details
- It re-uses repeating vertices, resulting in a reduced file size and redundancy, for which CityGML is not particularly known for.
- Validates polygon and skips them if they are not valid. Further, the tool supports multiple GML conventions for geometry (e.g.
<gml:posList>vs<gml:pos>). - The program is capable of batch processing of multiple files saving you time.
- Supports polygon holes by triangulating all surfaces. Besides the holes, this is done by default because some software handles OBJs only if the faces are triangulated, especially when it comes to the texture, so not only holey polygons are triangulated. OBJ does not support polygons with holes, which are common in CityGML files (
<gml:interior>), especially in LOD3 models due to doors, windows and holes left by building installations. For the Delaunay triangulation the tool uses Jonathan Richard Shewchuk's library, through its Python bindings Triangle. - It can store the semantic properties, and separate files for each of the thematic class, e.g. from the file
Delft.gmlit creates filesDelft-WallSurface.obj,Delft-RoofSurface.obj, ... - OBJ does not really support the concept of attributes, hence if the CityGML file contains an attribute, this is generally lost in the conversion. However, this converter is capable of converting a quantitative attribute to OBJ as a texture (colour) of the feature. For instance, if the attribute about the yearly solar irradiation is available for each polygon in the CityGML file, it is converted to a graphical information and attached to each polygon as a surface, so now you can easily visualise your attributes in CityGML. Please note that this is a very custom setting, and you will need to adapt the code to match your needs.
- Converts the coordinates to a local system.
- Supports both CityGML 1.0 and CityGML 2.0.
System requirements
Python packages:
- Numpy (likely already on your system)
- Triangle. If not on your system:
easy_install triangle - lxml
- Shapely
Optional:
OS and Python version
The software has been developed on Mac OSX in Python 2.7, and has not been tested with other configurations. Hence, it is possible that some of the functions will not work on Windows and on Python 3.
CityGML requirements
Mandatory:
- CityGML 1.0 or 2.0
- Files must end with
.gml,.GML,.xml, or.XML - Vertices in either
<gml:posList>or<gml:pos> - Your files must be valid (see the next section)
Optional, but recommended:
<gml:id>for each<bldg:Building>and other types of city objects<gml:id>for each<gml:Polygon>
About the validity of CityGML files
There have been reports that the code crashes for some CityGML files. Unfortunately, in some cases the triangulation code halts with a peculiar error as it encounters a weird geometry, that cannot be skipped (excepted). If your files won't convert, there's a chance that you have invalid CityGML files (albeit a CityGML2OBJs bug is not excluded). Please ensure that your files are valid. Alternatively, you can invoke the option -v 1 to skip such geometries--sometimes it works.
Hugo Ledoux built val3dity, a thorough GML validator which is available for free through a web interface. Use this tool to test your files.
Usage and options
Introduction
To simply convert CityGML data into OBJ type the following command:
python CityGML2OBJs.py -i /path/to/CityGML/files/ -o /path/to/new/OBJ/files/The tool will convert all CityGML files it finds in that folder. The command works also with relative paths.
Semantics
If you call the -s 1 option:
python CityGML2OBJs.py -i /path/to/CityGML/files/ -o /path/to/new/OBJ/files/ -s 1the tool will create an OBJ file for each of the boundary surfaces it encounters, e.g. Delft.gml containing RoofSurface, WallSurface and GroundSurface will result in: Delft-RoofSurface.obj, and so on.
Here is an example of the OBJ file representing the WallSurface:
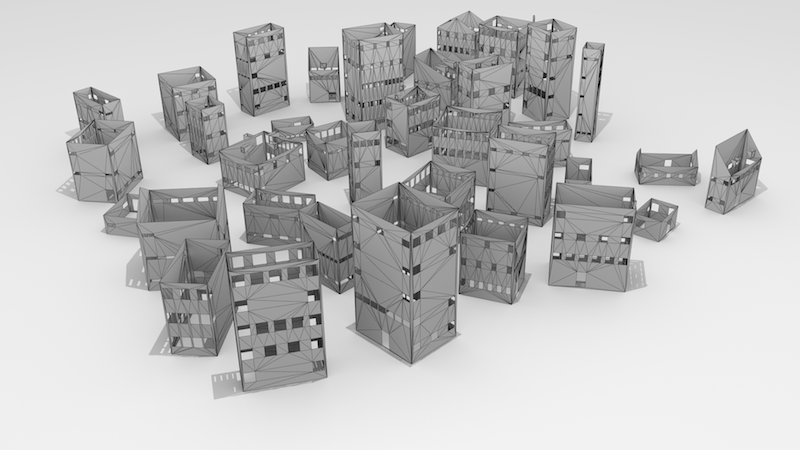

Regardless of the semantic option, the program always outputs the plain OBJ. This is a useful approach if you load data which does not have boundary surfaces (e.g. only a bunch of solids) so you'll always get something back. The tool detects if there are no thematic boundaries, so doesn't write empty OBJ files, for instance, an empty *-Window.obj for an LOD2 model.
Validate geometries
Call the -v 1 option:
python CityGML2OBJs.py -i /path/to/CityGML/files/ -o /path/to/new/OBJ/files/ -v 1in order to validate the geometries and skip invalid ones. The tool will report invalid geometries with their <gml:id>.
Objects
CityGML is a structured format. If you call the flag -g 1 you'll preserve the objects in the OBJ file
python CityGML2OBJs.py -i /path/to/CityGML/files/ -o /path/to/new/OBJ/files/ -g 1For the object option the name of the object will be derived from the <gml:id>, if not, an ordered list will be made starting from 1, and each object will be named as an integer from 1 to n, where n is the number of objects.
So this
<cityObjectMember>
<bldg:Building gml:id="ab76da5b-82d6-44ad-a670-c1f8b4f00edc">
<bldg:boundedBy>
<bldg:GroundSurface>
...becomes
o ab76da5b-82d6-44ad-a670-c1f8b4f00edc
f 635 636 637
f 636 635 638
f 639 640 641
...Conversion of coordinates
Normally CityGML data sets are geo-referenced. This may be a problem for some software packages. Invoke -t 1 to convert the data set to a local system. The origin of the local system correspond to the point with the smallest coordinates (usually the one closest to south-west).
Skip the triangulation
OBJ supports polygons, but most software packages prefer triangles. Hence the polygons are triangulated by default (another reason is that OBJ doesn't support polys with holes). However, this may cause problems in some instances, or you might prefer to preserve polygons. If so, put -p 1 to skip the triangulation. Sometimes it also helps to bypass invalid geometries in CityGML data sets.
Known limitations
- Some polygon normals sometimes get inverted. Usually a (wrong) normal is preserved from the data set, but in rare instances a bug may cause a correct normal to be inverted (and the other way around--in that case it's a feature!).
- Non-building thematic classes are not supported in the semantic sense (they will be converted together as
Otherclass). However, all geometry will be converted to the plain OBJ regardless of the theme, when the corresponding option is invoked). - The texture from the CityGML is not converted to OBJ (future work).
- The tool supports only single-LOD files. If you load a multi-LOD file, you'll get their union.
- If the converter crashes, it's probably because your CityGML files contain invalid geometries. Run the code with the
-v 1flag to validate and skip the invalid geometries. If that doesn't work, try to invoke the option-p 1. If that fails too, please report the error. XLinkis not supported, nor will be because for most files it will result in duplicate geometry.- The tool does not support non-convex polygons in the interior, for which might happen that the centroid of a hole is outside the hole, messing up the triangulation. This is on my todo list, albeit I haven't encountered many such cases.
- CityGML can be a nasty format because there may be multiple ways to store the geometry. For instance, points can be stored under
<gml:pos>and<gml:posList>. Check this interesting blog post by Even Rouault. I have tried to regard all cases, so it should work for your files, but if your file cannot be parsed, let me know. - Skipping triangulation does not work with polygons with holes.
Colour attributes
Please note that this is an experimental feature adapted to specific settings.
I have CityGML files with the attribute value of the solar potential (derived with Solar3Dcity, an experimental tool that I have recently developed and release soon) for each polygon. Normally these values cannot be visualised and are lost in the conversion to other formats. This tool solves this problem by normalising the quantitative attributes and colour them according to a colorbar, which is stored as a material (MTL) file.
Ancillary tools have been developed to make this feature use-friendly and visually appealing. Open each of these ancillary python files and fiddle with the values.
Generate the MTL library:
python generateMTL.pyPrint a colorbar with the transparent background:
python plotcolorbar.pyPut the newly generated MTL in the directory with the CityGML data and run the utility with the option -s 1 or -s 2 or -s 3:
python CityGML2OBJs.py -i /path/to/CityGML/files/ -o /path/to/new/OBJ/files/ -s 1Now the values of the solar potential of roof surfaces in the CityGML file are stored as textures (colours), and such can be easily visualised:
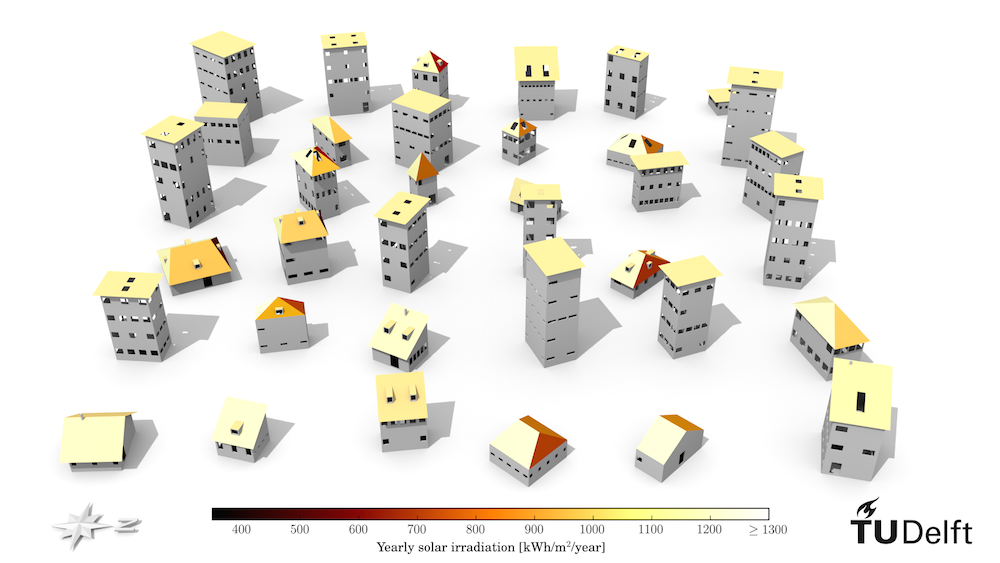
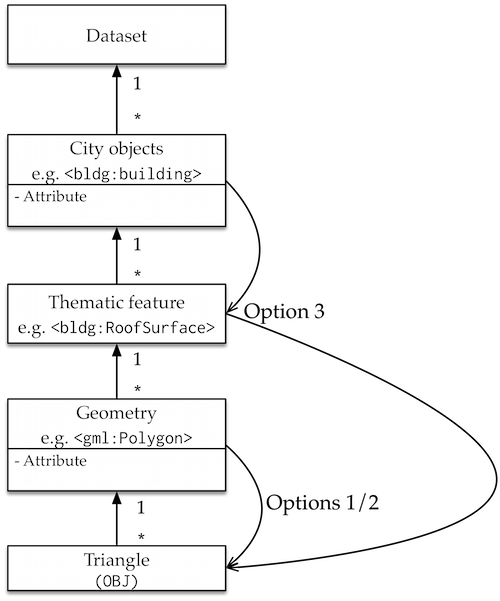
The different options are for transfering the values of attributes between different hierarchical levels. For instance, the option 3 takes the attribute assigned to the building, and colours only the triangles representing the RoofSurface, instead of all faces representing that building. If you want to discuss this in further details to accommodate your needs, do not hesitate to contact me.
Performance
The speed mainly depends on the invoked options and the level of detail of the data which substantially increases the number of triangles in the OBJ, mostly due to the openings.
For benchmarking, I have tested the tool with a CityGML data set of 100 buildings, and the performance is as follows:
- LOD2 (average 13 triangles per building)
- plain options: 0.004 seconds per building
- plain + semantics: 0.013 seconds per building
- LOD3 (average 331 triangles per building)
- plain options: 0.048 seconds per building
- plain + semantics: 0.0933 seconds per building
LOD0 and LOD1 have roughly the same performance as LOD2. Validation of polygons does not notably decrease the speed.
Contact for questions and feedback
Filip Biljecki
3D Geoinformation Research Group
Faculty of Architecture and the Built Environment
Delft University of Technology
email: fbiljecki at gmail dot com
Acknowledgments
-
This research is supported by the Dutch Technology Foundation STW, which is part of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO), and which is partly funded by the Ministry of Economic Affairs (project code: 11300).
-
Triangle, a 2D quality mesh generator and delaunay triangulator developed by Jonathan Shewchuk, and the Python bindings. CityGML2OBJs relies on this tool for triangulating the polygons, and its availability is highly appreaciated.
-
People who detected bugs and gave suggestions for improvements.
My colleagues:
-
Ravi Peters who developed a similar software citygml2obj in 2009, and gave me the permission to use the name of his software.