____ _ _ _
/ ___| ___ __ _ _ __ _ __ ___ __ _| \ | | ___ __| | ___
| | _ / _ \/ _` | '__| '_ ` _ \ / _` | \| |/ _ \ / _` |/ _ \
| |_| | __/ (_| | | | | | | | | (_| | |\ | (_) | (_| | __/
\____|\___|\__,_|_| |_| |_| |_|\__,_|_| \_|\___/ \__,_|\___|Node.js library for the Gearman distributed job system with support for multiple servers.
Breaking API change
- v0.2.0
- payload given back to client as
job.responseincomplete,workData,warningandexceptionevents: is instance ofBuffernow, unless you providetoStringEncodingoption insubmitJob
- payload given back to client as
Features
- fully implemented Gearman Protocol
- support for multiple job servers
- load balancing strategy (
sequenceorround-robin) - recover time (when a server node is down due to maintenance or a crash, load balancer will use the recover-time as a delay before retrying the downed job server)
- load balancing strategy (
- support for binary data and miscellaneous string encoding
- careful API documentation
- rock solid tests
- currently more than 130 test scenarios and 400 asserts
- in depth tested with gearman clients and workers written in other languages (Ruby, PHP, Java)
Installation
> npm install gearmanode- Node package published here: https://npmjs.org/package/gearmanode
Changelog
See version.js for detailed changelog.
Usage
- Client
var gearmanode = require('gearmanode');
var client = gearmanode.client();
var job = client.submitJob('reverse', 'hello world!');
job.on('workData', function(data) {
console.log('WORK_DATA >>> ' + data);
});
job.on('complete', function() {
console.log('RESULT >>> ' + job.response);
client.close();
});- Worker
var gearmanode = require('gearmanode');
var worker = gearmanode.worker();
worker.addFunction('reverse', function (job) {
job.sendWorkData(job.payload); // mirror input as partial result
job.workComplete(job.payload.toString().split("").reverse().join(""));
});TOC
See Geaman Manual to understand generic Gearman concepts. See example folder for more detailed samples.
Client
The client is responsible for creating a job to be run and sending it to a job server. The job server will find a suitable worker that can run the job and forwards the job on. -- Gearman Documentation --
Instance of class Client must be created to connect a Gearman job server(s) and to make requests to perform some function on provided data.
var gearmanode = require('gearmanode');
var client = gearmanode.client();By default, the job server is expected on localhost:4730. Following options can be used for detailed configuration of the client:
- host {string} hostname of single job server
- port {number} port of single job server
- servers {array} array of host,port pairs of multiple job servers
- loadBalancing {'Sequence'|'RoundRobin'} name of load balancing strategy
- recoverTime {number} delay in milliseconds before retrying the downed job server
// special port
client = gearmanode.client({port: 4732});
// two servers: foo.com:4731, bar.com:4732
client = gearmanode.client({servers: [{host: 'foo.com', port: 4731}, {host: 'bar.com', port: 4732}]});
// two servers with default values: foo.com:4730, localhost:4731
client = gearmanode.client({servers: [{host: 'foo.com'}, {port: 4731}]});Submit job
Client submits job to a Gearman server and futher processed by a worker via client#submitJob(name, payload, options)
where name is name of registered function a worker is to execute, payload is data to be processed
and options are additional options as follows:
- background {boolean} flag whether the job should be processed in background/asynchronous
- priority {'HIGH'|'NORMAL'|'LOW'} priority in job server queue
- encoding - {string} encoding if string data used, DEPRECATED: ignored, will be removed in next release, use Buffer with corresponding string encoding as payload
- unique {string} unique identifiter for the job
- toStringEncoding {string} if given received response will be converted to
Stringwith this encoding, otherwise payload turned over asBuffer
// by default foreground job with normal priority
var job = client.submitJob('reverse', 'hello world!');
// background job
var job = client.submitJob('reverse', 'hello world!', {background: true});
// full configured job
var job = client.submitJob('reverse', 'hello world!', {background: false, priority: 'HIGH', unique: 'FooBazBar', toStringEncoding: 'ascii'});Client-side processing of job is managed via emitted events. See Job events for more info.
var client = gearmanode.client();
var job = client.submitJob('reverse', 'hi');
job.on('complete', function() {
console.log('RESULT: ' + job.response);
client.close();
});A client object should be closed if no more needed to release all its associated resources and socket connections. See the sample above.
Client events
- socketConnect - when a job server connected (physical connection is lazy opened by first data sending), has parameter job server UID
- socketDisconnect - when connection to a job server terminated, has parameter job server UID and optional Error in case of an unexpected wrong termination
- socketError - when a socket problem occurs (connection failure, broken pipe, connection terminated by other end, ...), has parameter job server UID and Error
- jobServerError - when an associated job server encounters an error and needs to notify the client with packet ERROR (19), has parameters jobServerUid, code, message
- close - when Client#close() called to end the client for future use and to release all its associated resources
- error - when an unrecoverable error occured (e.g. illegal client's state, malformed data ...), has parameter Error
Worker
The worker performs the work requested by the client and sends a response to the client through the job server. -- Gearman Documentation --
Instance of class Worker must be created to connect a Gearman job server(s), where it then informs the server(s) of all different functions the Worker is capable of doing.
var gearmanode = require('gearmanode');
var worker = gearmanode.worker();By default, the job server is expected on localhost:4730. Following options can be used for detailed configuration of the worker:
- host see Client
- port see Client
- servers see Client
- withUnique {boolean} flag whether a job will be grabbed with the client assigned unique ID
Register function
A function the worker is able to perform can be registered via worker#addFunction(name, callback, options)
where name is a symbolic name of the function, callback is a function to be run when a job will be received
and options are additional options as follows:
- timeout {number} timeout value in seconds on how long the job is allowed to run, thereafter the job server will mark the job as failed and notify any listening clients
- toStringEncoding {string} if given received payload will be converted to
Stringwith this encoding, otherwise payload turned over asBuffer
The worker function callback gets parameter Job which is:
- job event emitter (see Job events)
- value object to turn over job's parameters
- interface to send job notification/information to the job server
worker.addFunction('reverse', function (job) {
var rslt = job.payload.toString().split("").reverse().join("");
job.workComplete(rslt);
});
// or with Timeout and conversion to String
worker.addFunction('reverse', function (job) {
var rslt = job.payload.toString().split("").reverse().join("");
job.workComplete(rslt);
}, {timeout: 10, toStringEncoding: 'ascii'});
It tries to connect to ALL job servers and fires error if one registration fails.
A registered function can be unregistered via worker#removeFunction.
Call Worker#resetAbilities to notify the server(s) that the worker is no longer able to do any functions it previously registered.
Set Worker ID
This method sets the worker ID in all job servers so monitoring and reporting commands can uniquely identify the various workers.
Parameter workerId has to be a non-blank string with no whitespaces.
worker.setWorkerId('FooBazBar');Worker events
- socketConnect - when a job server connected (physical connection is lazy opened by first data sending), has parameter job server UID
- socketDisconnect - when connection to a job server terminated, has parameter job server UID and optional Error in case of an unexpected wrong termination
- socketError - when a socket problem occurs (connection failure, broken pipe, connection terminated by other end, ...), has parameter job server UID and Error
- jobServerError - whenever an associated job server encounters an error and needs to notify the worker with packet ERROR (19), has parameters jobServerUid, code, message
- close - when Worker#close() called to close the worker for future use and to release all its associated resources
- error - when a fatal error occurred while processing job (e.g. illegal worker's state, socket problem, ...) or job server encounters an error and needs to notify client, has parameter Error
Job
The Job object is an encapsulation of job's attributes and interface for next communication with job server.
Additionally is the object en emitter of events corresponding to job's life cycle (see Job events).
The job has following getters
- name - name of the function, [Client/Worker]
- payload - transmited/received data (Buffer or String) [Client/Worker]
- response - data that is returned to the client as a response if job is done by a worker [Client]
- jobServerUid - unique identification (UID) of the job server that transmited the job [Client/Worker]
- handle - unique handle assigned by job server when job created [Client/Worker]
- encoding - encoding to use [Client] DEPRECATED: ignored, will be removed in next release, use Buffer with corresponding string encoding as payload
- unique - unique identifier assigned by client [Worker]
and methods
- getStatus - sends request to get status of a background job [Client]
- workComplete - sends a notification to the server (and any listening clients) that the job completed successfully [Worker]
- sendWorkData - sends updates or partial results [Worker]
- reportStatus - reports job's status to the job server [Worker]
- reportWarning - sends a warning explicitly to the job server [Worker]
- reportError - to indicate that the job failed [Worker]
- reportException - to indicate that the job failed with exception (deprecated, provided for backwards compatibility) [Worker]
Job events
- submited - when job submited via a job server; server UID stored on the job; has no parameter [Client]
- created - when response to one of the SUBMIT_JOB* packets arrived and job handle assigned; has no parameter [Client]
- status - to update status information of a submitted jobs [Client]
- in response to a client's request for a background job
- status update propagated from worker to client in case of a non-background job
- has parameter status with attributes: known, running, percent_done_num, percent_done_den (see protocol specification for more info)
- workData - to update the client with partial data from a running job, has parameter data [Client]
- warning - to update the client with a warning, has parameter data [Client]
- complete - when the non-background job completed successfully, has no parameter [Client]
- failed - when a job has been canceled by invoking Job#reportError on worker side, has no parameter [Client]
- exception - when the job failed with the an exception, has parameter text of exception [Client]
- timeout - when the job has been canceled due to timeout, has no parameter [Client/Worker]
- close - when Job#close() called or when the job forcible closed by shutdown of client or worker, has no parameter [Client/Worker]
- error - when communication with job server failed, has parameter Error object [Client/Worker]
Job server
Class JobServer represents an abstraction to Gearman job server (gearmand).
Accessible job server(s) are stored in array jobServer on instance of Client/Worker.
The class introduces following methods:
- echo - sends the job server request that will be echoed back in response
- setOption - sends the job server request to set an option for the connection in the job server
var client = gearmanode.client();
var js = client.jobServers[0];
js.once('echo', function(resp) {
console.log('ECHO: response=' + resp);
client.close();
});
js.echo('ping')Job server events
- echo - when response to ECHO_REQ packet arrived, has parameter data which is opaque data echoed back in response
- option - issued when an option for the connection in the job server was successfully set, has parameter name of the option that was set
- jobServerError - whenever the job server encounters an error, has parameters code, message
Binary data
Both binary data and text with various encoding are supported. By default the data delivered to client and worker are Buffer objects.
You can change this approach by providing toStringEncoding option in Client#submitJob or Worker#addFunction.
See following snippets of code or test-all-stack.js for more inspiration.
// send text with default encoding; Job#response will be a Buffer object
client.submitJob('reverse', '123');
// send text with given encoding; Job#response will be a Buffer object
client.submitJob('reverse', Buffer('123', 'ascii').toString());
// send text with given encoding; Job#response will be a String object with ASCII encoding
client.submitJob('reverse', '123', {toStringEncoding: 'ascii'});
// and receive text on Worker; Job#payload will be a String object with ASCII encoding
worker.addFunction('reverse', function (job) {
job.workComplete(job.payload.split("").reverse().join(""))
}, {toStringEncoding: 'ascii'});
// send binary data
client.submitJob('reverse', new Buffer([49, 50, 51]));Multiple servers
Many of Gearman job servers can be started for both high-availability and load balancing.
Client is able to communicate with multiple servers with one of the following load balancing strategy:
- default mode is
Sequencewhich calls job server nodes in the order of nodes defined by the client initialization (next node will be used if the current one fails) RoundRobinassigns work in round-robin order per nodes defined by the client initialization.
// default load balancer
client = gearmanode.client({ servers: [{host: 'foo.com'}, {port: 4731}] });
// desired load balancer and recover time
client = gearmanode.client({ servers: [{host: 'foo.com'}, {port: 4731}], loadBalancing: 'RoundRobin', recoverTime: 10000 });Worker can be initialized with multiple servers in order to register a function on each of them.
Error handling
Although exceptions are supported in JavaScript and they can be used to communicate an error, due to asynchronous concept of Node.js it can be a bad idea. According to Node.js best practices following error handling is introduced in GearmaNode.
Synchronous errors
A synchronous code returns an Error object if something goes wrong. This happens mostly in input value validation.
Asynchronous errors
In asynchronous code an error event will be emitted via EventEmitter on corresponding object if something goes wrong.
This happens mostly by network communication failure or if a gearman service fails.
Configuration
Logger
Winston library is used for logging. See the project page for details.
The GearmaNode library registers following loggers:
- Client
- Worker
- JobServer
- Job
- LBStrategy
- protocol
You can configure the logger in this way:
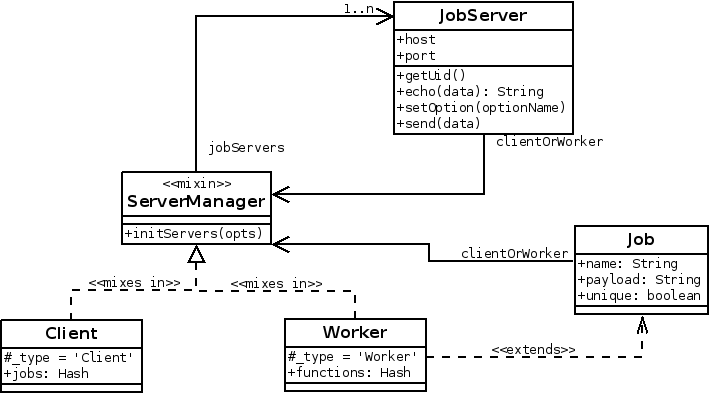
gearmanode.Client.logger.transports.console.level = 'info';Class diagram
Tests
> cd /path/to/repository
> mochaMake sure before starting the tests:
- job server is running on localhost:4730
mochatest framework is installed
Author
- vaclav.sykora@gmail.com
- https://plus.google.com/115674031373998885915
License
- Apache License, Version 2.0
- see LICENSE file for more details