WHY
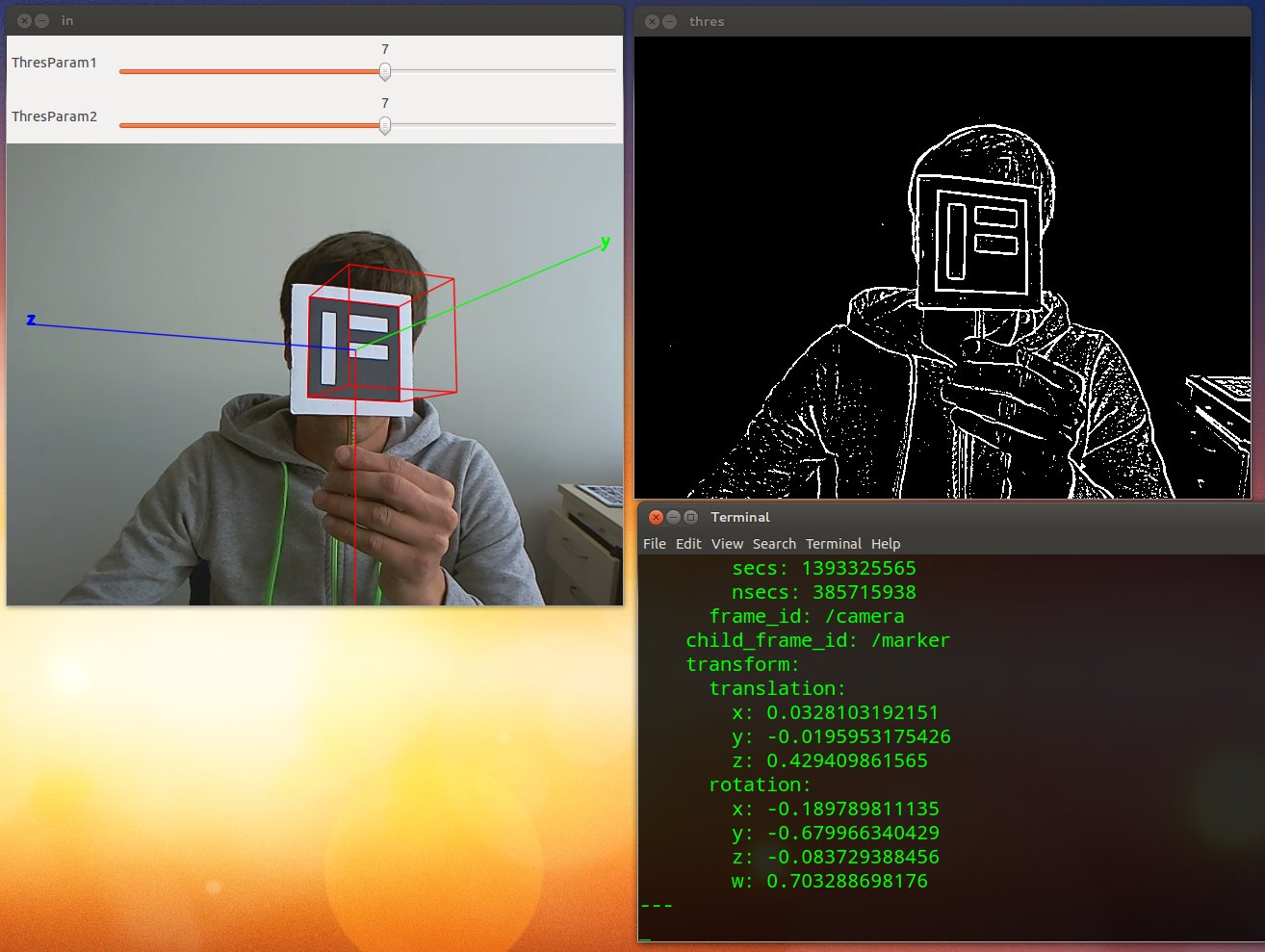
This is a ros package wrapping the lightweight and fast ArUco[1] marker tracking library. The usage of this package is, on purpose, straight forward and the features are simple/limited. This software tracks a single marker and publishes its ROTATION and TRANSLATION coordinates via ROS middleware (TF and Pose). The main advantages of this package are a) publishing of "real world" coordinates, i.e., distance in metres b) high frequency data streaming of coodinates, the bottleneck currently is the FPS count of your camera. Marker detection and tracking only consumes ~5ms per frame [intel i5] and c) easy deployment, if you are already using ROS.
An extension including detection and tracking of multiple markers should be an relatively easy task. Feel free to fork me.
[1] http://www.uco.es/investiga/grupos/ava/node/26
BUILDING AND USAGE
1) Install ROS, if neccessary. http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/Installation
2) Create a catkin workspace, if you don't already have one. http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/Tutorials/create_a_workspace
3) Download and install ArUco, you will need cmake >=2.8 and OpenCV >= 2.3.1 Basically: Download, extract, mkdir build, cd build, cmake .., make, make install (maybe sudo) Please remember the install location, i.e., "/usr/local", you will need the path later on. http://www.uco.es/investiga/grupos/ava/node/26
3a) Create a marker as explained in the README, use: aruco_create_marker
4) cd ~/catkin_ws/src (your catkin workspace)
5) mkdir -p ros_aruco && cd ros_aruco
6) git clone https://github.com/warp1337/ros_aruco.git .
7) source /opt/ros/YOUR_DISTRIBUTION/setup.bash
cd ~/catkin_ws/ && catkin_make --pkg ros_aruco -DARUCO_PATH=/usr/local
You will need to reference the location of your ArUco installation by providing:
-DARUCO_PATH=/PATH/TO/ARUCO
Hint: --pkg ros_aruco just builds the ros_aruco executable, not your whole catkin_workspace.
8) Start a roscore in a separate shell.
source /opt/ros/YOUR_DISTRIBUTION/setup.bash
roscore
8) cd ~/catkin_ws/build/ros_aruco
9) Now you will be able to run the tracker, as a first example just run:
source /opt/ros/YOUR_DISTRIBUTION/setup.bash
./ros_aruco live
You should now be able to track an ArUco marker, however you will not get any real world coordinates because your camera is probably not properly calibrated. You can use the OpenCV calibration tool for that. If you are familiar with it, go on, if not please refer to: https://github.com/warp1337/opencv_cam_calibration
10) In case you calibrated your camera please measure the size of your marker (in metres). Now fire up the tracker and provide the camera calibration file (obtained during calibration) and the size of your marker as parameters:
./ros_aruco live /path/to/calibration/file MARKERSIZE
./ros_aruco live ../../src/ros_aruco/data/logitech_9000_intrinsics.yml 0.08
An exemplary calibration file (for the Logitech 9000 HD web cam) is located in this git repo (data folder).
11) In another shell source the setup.bash as explained earlier and fire up:
rostopic echo /tf
rostopic echo /aruco_pose
Real world coordinates of your marker are published in this topic.
12) Have fun.
TODO
Add install target for CMAKE file ;)