Important Notice
As the Istio community is moving away from the Mixer Adapter approach, WSO2 does not recommend to use the approach mentioned in this istio-apim github repository. The recommended approach for applying API Management in Istio service mesh is to use the API Operator for Kubernetes. Please refer API Operator for Istio
Introduction
WSO2 API Manager is a full lifecycle API Management solution which has an API Gateway and a Microgateway. Istio is a service mesh solution which helps users to deploy and manage a collection of microservices. Service meshes in their native form have an “API Management gap” that requires to be filled. These are related to exposing services to external consumers (advanced security, discovery, governance, etc.), business insights, policy enforcement, and monetization. This explains how WSO2 API Manager plans to integrate with Istio and manage services deployed in Istio as APIs.
Background
When users move towards a microservice architecture from monolithic app architecture, it can result in a considerable number of fine-grained microservices. Therefore, it was a challenge to manage all these microservices. As a solution, Istio was able to provide a platform to connect, manage, and secure all these microservices, while reducing the complexity of deployments. In addition, Istio includes APIs that let it integrate in to any logging platform, telemetry, or policy system.
However, when users need to expose these microservices to the outside in a secured controlled manner, API Management comes into picture. Most of the time we need to create APIs (for microservices) and share them with other developers who might be part of your organization or external organizations. Therefore, API Management within a service mesh solution is required in order to operate successfully. You can use this capability to expose one or more services from an Istio service mesh as APIs by adding API management capabilities.
Approach
While Istio provides data plane (DP) and control plane (CP), WSO2 API Manager provides management plane capabilities to manage microservices.
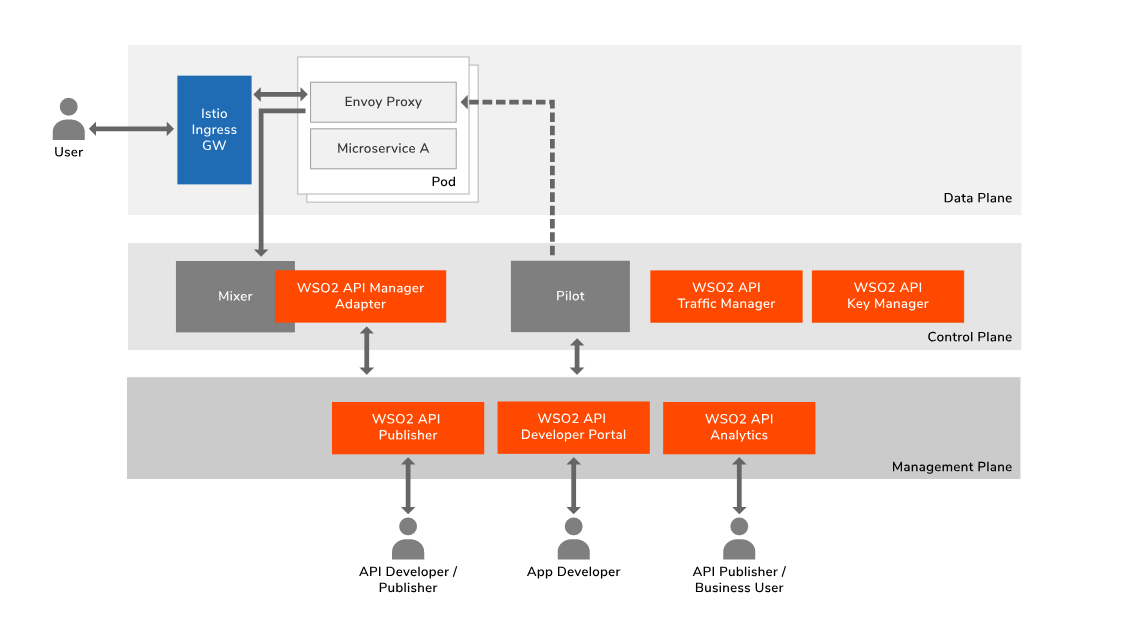
Role of the Istio Mixer plugin
The Mixer is a core Istio component which runs in the control plane of the service mesh. The Mixer plugin model enables new rules and policies to be added to groups of services in the mesh without modifying the individual services or the nodes where they run. API management policies such as authentication (by API key validation), rate-limiting, etc. can be deployed and managed by WSO2 API Manager without doing any changes to the actual microservice or sidecar proxy.
API management for Istio
When you need to expose this service to the outside in a managed way, the API developer can use the WSO2 API Publisher portal to create the API by attaching necessary policies like security, rate limiting etc. The Publisher is capable of pushing all these policies in to the Envoy proxy via the Pilot and Mixer in order for them to take action with regard to policy enforcement. After publishing this the API, it will appear in the WSO2 API Developer Portal. Thereafter, the app developer can discover these APIs and use them in their application along with all the capabilities provided by the developer portal such as, getting a subscription plan, adding application security etc. If you are a business user, you can use WSO2 API Analytics to get more business insights by looking at the API Analytics.
Route of a successful request
Let us now see how service calls work with this solution and at which point API related quality of services gets applied. As you can see in the diagram below, when a request comes from the outside it first goes to the Istio proxy (Envoy) and then it will communicate with the Mixer in order to perform policy checks. Based on the outcome of the policy checks, the request may be routed to the service or an error should be sent back to the client. For more information, see the diagram and the detailed steps.
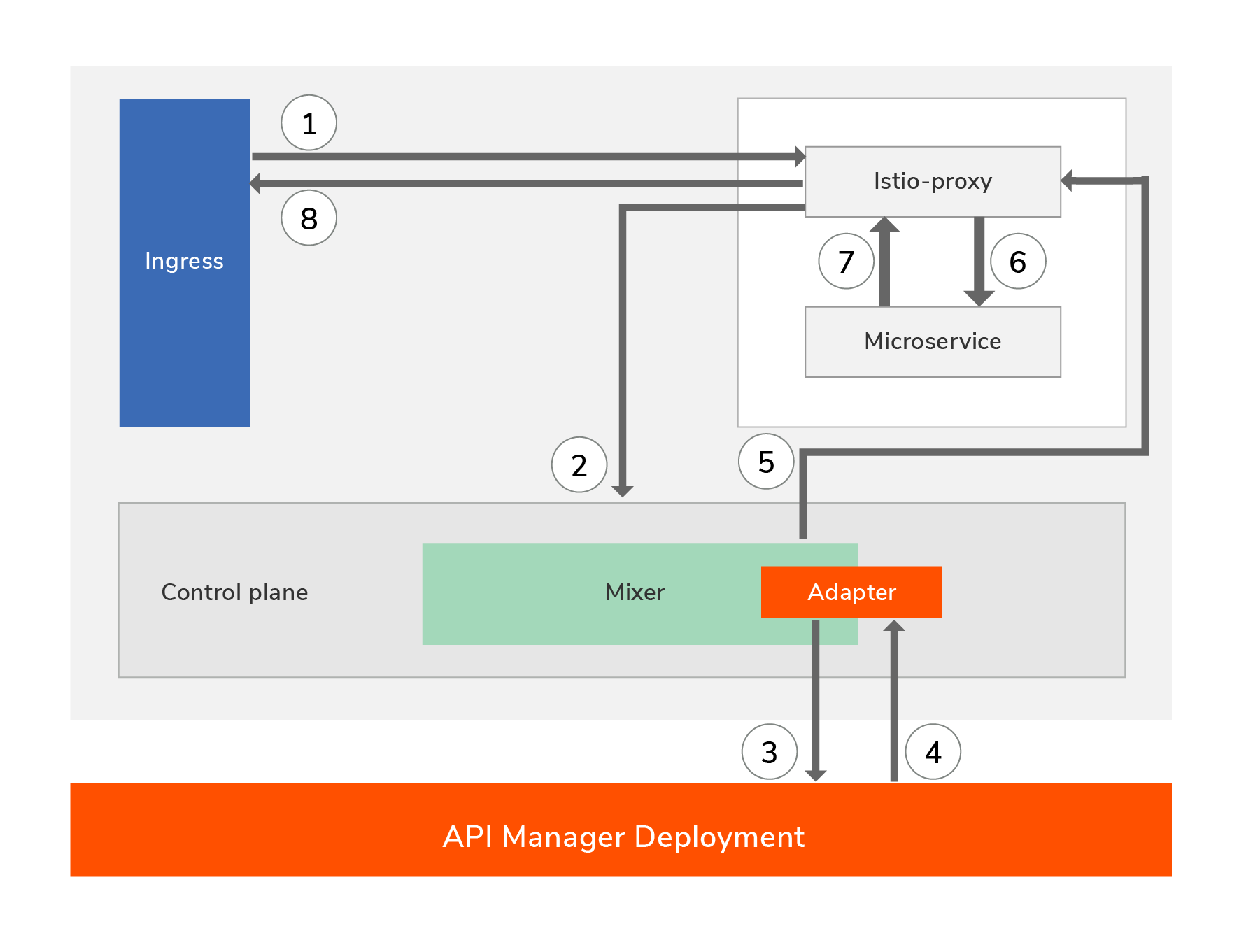
- The client sends the request to the service (Istio capture the request and redirects it to the Istio-proxy). This enters the Kubernetes (K8s) cluster via an ingress point.
- The Istio proxy captures a wealth of signal and sends it to the Mixer as attributes.
- The Mixer adapter then calls WSO2 API Manager for various types of policy checks and verifications.
- WSO2 API Manager performs the policy checks and responds back to the Mixer.
- The Mixer communicates the outcome of the policy checks to the Istio proxy.
- When there are no policy validation failures, the request is routed to the microservice.
- The microservice executes the service logic and sends the response.
- The response is sent out to the client.
Istio mixer adapter for WSO2 API Manager
Using WSO2 adapter, users can do the following.
- Secure services with JWT and OAuth2 tokens
- Validate API subscriptions
- Validate scopes
- Use WSO2 API Manager Analytics for business insights
- WSO2 API Manager integration automates HTTPAPISpec, HTTPAPISpecBinding and rules creation for APIs
Quick Start Guide
Step 1 - Install Istio 1.1 or above
NOTE:
- Make sure the Kubernetes (K8s) cluster has at least 8GB of memory.
- In the default profile of Istio installation, the policy check is disabled by default. However, in a production environment it is mandatory to use the Mixer Adapter; therefore, in such a scenario you need to explicitly enable the policy check. For more information, see Enable Policy Enforcement.
Step 2 - Install WSO2 API Manager Analytics
-
Install Istio-apim release: wso2am-istio-1.0.zip.
The wso2am-istio-1.0.zip contains installation artifacts that you need to deploy in Istio, WSO2 API Manager, and WSO2 API Manager Analytics as explained in the subsequent steps. -
Extract wso2am-istio-1.0.zip and navigate to the \
/ directory.
cd <APIM-ISTIO-HOME>/
Note: You need to run allkubectlcommands from within the \/ directory. -
Deploy Kubenetes (K8s) artifacts for Analytics.
kubectl apply -f <config-file-path>- \
- Enter the filename, directory, or URL to the files that contains the configuration that you need to apply.
kubectl apply -f install/analytics/k8s-artifacts/Output
namespace "wso2" created deployment.apps "wso2apim-with-analytics-apim-analytics-deployment" created service "wso2apim-with-analytics-apim-analytics-service" createdStep 3 - Install WSO2 API Manager
- \
-
Deploy the required config maps for WSO2 API Manager.
kubectl create configmap <configmap-name> --from-file=<key-file-path> -n <namespace>- \
- You can specify the key file by using its file path.
kubectl create configmap apim-conf --from-file=./install/api-manager/resources/conf/ -n wso2 kubectl create configmap apim-lifecycles --from-file=./install/api-manager/resources/lifecycles/ -n wso2Output
configmap "apim-conf" created configmap "apim-lifecycles" created - \
-
Deploy K8s artifacts for WSO2 API Manager.
kubectl apply -f <config-file-path>- \
- Enter the filename, directory, or URL to the files that contains the configuration that you need to apply.
kubectl apply -f install/api-manager/k8s-artifacts/
Outputnamespace "wso2" configured serviceaccount "wso2svc-account" created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "crd-deploy" created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "crd-deploy-binding" created deployment.apps "wso2apim-with-analytics-apim" created service "wso2apim-with-analytics-apim-service" created - \
-
Access WSO2 API Manager.
WSO2 API Manager is exposed as NodePort service type. Therefore, you can use any K8s node IP to access it.-
Add the node IP to the \/etc/hosts file as follows:
`wso2apim ` -
Access WSO2 API Manager.
Publisherhttps://wso2apim:32001/publisherStore
https://wso2apim:32001/storeAdmin
https://wso2apim:32001/adminStep 4 - Install WSO2 Istio Mixer Adapter
-
-
Create a K8s secret in the istio-system namespace for the public certificate of WSO2 API Manager as follows:
kubectl create secret generic <secret-name> --from-file=<key-file> -n istio-system- \
- Enter the path and name of the key file.
kubectl create secret generic server-cert --from-file=./install/adapter-artifacts/server.pem -n istio-systemNOTE: The public certificate for the WSO2 API Manager 2.6.0 GA release is in the install/adapter-artifacts/server.pem file.
Output
secret "server-cert" created - \
-
Deploy the wso2-adapter as a cluster service.
The Docker image of WSO2 Mixer Adapter, which is referred to when deploying this cluster service, is available in DockerHub.
kubectl apply -f <config-file-path>-
\
- Enter the filename, directory, or URL to the files that contains the configuration that you need to apply.
kubectl apply -f install/adapter-artifacts/Output
attributemanifest.config.istio.io "istio-proxy" created attributemanifest.config.istio.io "kubernetes" configured template.config.istio.io "authorization" created template.config.istio.io "metric" created secret "wso2server-secret" created service "wso2adapterservice" created deployment.apps "wso2adapter" created handler.config.istio.io "wso2-handler" created instance.config.istio.io "wso2-authorization" created instance.config.istio.io "wso2-metrics" created adapter.config.istio.io "wso2" createdStep 5 - Deploy a microservice in Istio
-
-
Enable Istio sidecar injection for the default namespace if it not already enabled.
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
Outputnamespace "default" labeled -
Deploy the httpbin sample service.
kubectl create -f <config-file>- \
- Enter the filename, directory, or URL to the files that you need to use to create the resource.
kubectl create -f samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml
Outputservice "httpbin" created deployment.apps "httpbin" created - \
-
Expose the httpbin sample service via Istio ingress gateway to be able to access it from outside.
kubectl create -f <config-file>- \
- Enter the filename, directory, or URL to the files that you need to use to create the resource.
kubectl create -f samples/httpbin/httpbin-gw.yaml
Outputgateway.networking.istio.io "httpbin-gateway" created virtualservice.networking.istio.io "httpbin" created - \
-
Access the httpbin sample service via Istio ingress gateway.
curl http://$<ingress_gateway_host>:<ingress_gateway_port>/headersYou can identify the value of the \
and \ as follows.
For more information, go to the Istio guide.-
Use EXTERNAL-IP as the \
based on the output of the following command.
kubectl get svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system -
Use the output of the following command as the \
value.
kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}'NOTE: If you are using a Mac OS and you are running Istio under Docker for desktop’s built-in Kubernetes, the \
value will always be port 80. Output
{ "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Content-Length": "0", "Host": "", "User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0", "X-B3-Parentspanid": "ab2e9a9eed908d7c", "X-B3-Sampled": "1", "X-B3-Spanid": "bda5158fae7fde30", "X-B3-Traceid": "a79c3a7318eb25ecab2e9a9eed908d7c", "X-Envoy-Internal": "true" } } -
Step 6 - Apply API Management for microservices
You need to secure the service by either using OAuth2 or JWT tokens.
In addition, you need to also validate the subscription for the API and validate the scope for the resources.
Step 6.1 - Create and publish an API in WSO2 API Manager Publisher
-
Sign in to WSO2 API Manager Publisher and create a REST API with the following details.
For more information, go to Create and Publish an API in the WSO2 API Manager documentation.- API Name : HttpbinAPI
- API Context : /httpbin
- API Version : 1.0.0
- Production Endpoint : http://httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local
Make sure you provide the production endpoint for the API in the following format.
http://<service_name>.<namespace_of_the_service>.svc.cluster.local
Add the following resources with these scopes.
NOTE: When adding a scope, it is mandatory to select a role that corresponds to the scope.Resource Request Type Scope Scope - Role /ip GET scope_ip admin /headers GET scope_headers admin /delay/{delay} GET - - /status/{status_code} GET - - When you create an API, WSO2 API Manager automatically creates and deploy Istio resources for the API.
Step 6.2 - Access the Service
You can access the service either using a JWT token or an OAuth2 token as follows:
-
Using a JWT Token to access the service
- Sign in to WSO2 API Manager Publisher and create an application by selecting JWT as Token Type.
- Subscribe to the API (httpbinAPI) by selecting the application that you created.
- Select the relevant scopes and generate an access token.
- Access the service by providing the authorization header as follows:
curl http://$<ingress_gateway_host>:<ingress_gateway_port>/headers -H "Authorization: Bearer <JWT_access_token>"
Output
{ "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Authorization": "Bearer <JWT_access_token>", "Content-Length": "0", "Host": "localhost", "User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0", "X-B3-Parentspanid": "e7d9530be32b57e9", "X-B3-Sampled": "1", "X-B3-Spanid": "f15dc7333dff51cb", "X-B3-Traceid": "84ce2c827154abc6e7d9530be32b57e9", "X-Envoy-Internal": "true" } } -
Using an OAuth2 token to access the service
- Create an application by selecting OAuth2 as the Token Type.
- Subscribe to the API (httpbinAPI) by selecting the application that you created.
- When generating the token, select the relevant scopes and generate an access token.
-
When accessing the service, provide the authorization header as follows:
curl http://$
: /headers -H "Authorization: Bearer "
Output
{ "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Authorization": "Bearer <OAuth2_access_token>", "Content-Length": "0", "Host": "localhost", "User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0", "X-B3-Parentspanid": "64939801f6f62add", "X-B3-Sampled": "1", "X-B3-Spanid": "1f8e7fb9db647aaf", "X-B3-Traceid": "0c3b98c396045dcc64939801f6f62add", "X-Envoy-Internal": "true" } }
Step 6.3 - Access Analytics for Business Insights
Access the WSO2 API Manager Publisher and Store for analytics.
Cleanup
kubectl delete -f samples/httpbin/
kubectl delete -f install/adapter-artifacts/
kubectl delete secrets server-cert -n istio-system
kubectl delete -f install/analytics/k8s-artifacts/
kubectl delete -f install/api-manager/k8s-artifacts/
kubectl delete configmap apim-conf -n wso2
kubectl delete configmap apim-lifecycles -n wso2Advanced Guide
You can customize and deploy WSO2 Servers by following this guide.
Troubleshooting Guide
-
Figure out the pod name for wso2adapter.
kubectl get pods -n istio-system -l app=wso2adapter -
Browse the wso2adapter log.
kubectl logs -f <pod_name> -n istio-system -
How can I overcome the following error?
Error from server (AlreadyExists): secrets "<cert-name>" already exists
This error occurs when you try to create another certificate with the same name in a namespace. To overcome this error you need to first delete the existing certificate and then add the new certificate, which has the same name. Run the following command to delete the existing certificate.
kubectl delete secrets <cert-name> -n <namespace>
kubectl delete secrets server-cert -n istio-system