
What is YugabyteDB?
YugabyteDB is a PostgreSQL-compatible, high-performance, cloud-native, distributed SQL database. It combines the benefits of traditional relational databases with the scalability of NoSQL systems, making it suitable for applications that require both transactional consistency and the ability to handle large amounts of data. It is best suited for cloud-native OLTP (that is, real-time, business-critical) applications that need absolute data correctness and require at least one of the following: scalability, high tolerance to failures, or globally-distributed deployments.
- Core Features
- Get Started
- Build Apps
- Current Roadmap
- Recent features
- Architecture
- Need Help?
- Contribute
- License
- Read More
Core Features
-
Powerful RDBMS capabilities Yugabyte SQL (YSQL for short) reuses the PostgreSQL query layer (similar to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL), thereby supporting most of its features (datatypes, queries, expressions, operators and functions, stored procedures, triggers, extensions, and so on).
-
Distributed transactions The transaction design is based on the Google Spanner architecture. Strong consistency of writes is achieved by using Raft consensus for replication and cluster-wide distributed ACID transactions using hybrid logical clocks. Snapshot, serializable and read committed isolation levels are supported. Reads (queries) have strong consistency by default, but can be tuned dynamically to read from followers and read replicas.
-
Continuous availability YugabyteDB is extremely resilient to common outages with native failover and repair. YugabyteDB can be configured to tolerate disk, rack, node, zone, region, and cloud failures automatically. For a typical deployment where a YugabyteDB cluster is deployed in one region across multiple zones on a public cloud, the RPO is 0 (meaning no data is lost on failure) and the RTO is 3 seconds (meaning the data being served by the failed node is available in 3 seconds).
-
Horizontal scalability Scaling a YugabyteDB cluster to achieve more IOPS or data storage is as simple as adding nodes to the cluster.
-
Geo-distributed, multi-cloud YugabyteDB can be deployed in public clouds and natively inside Kubernetes. It supports deployments that span three or more fault domains, such as multi-zone, multi-rack, multi-region, and multi-cloud deployments. It also supports xCluster asynchronous replication with unidirectional master-slave and bidirectional multi-master configurations in two-region deployments. Read replicas are also a supported to serve (stale) data with low latencies.
-
Multi API design The YugabyteDB query layer is built to be extensible. Currently, YugabyteDB supports two distributed SQL APIs: Yugabyte SQL (YSQL), a fully relational API that re-uses the PostgreSQL query layer, and Yugabyte Cloud QL (YCQL), a semi-relational SQL-like API with documents/indexing support with Apache Cassandra QL roots.
-
100% open source YugabyteDB is fully open-source under the Apache 2.0 license. The open-source version has powerful enterprise features such as distributed backups, encryption of data at rest, in-flight TLS encryption, change data capture, read replicas, and more.
YugabyteDB was created with several key design goals in mind, aiming to address the challenges faced by modern, cloud-native applications while maintaining the familiarity and power of traditional relational databases. Read more about these in our Design goals.
Get Started
- Quick Start
- Try running a real-world demo application:
Can't find what you're looking for? Have a question? Post your questions or comments on our Community Slack or Forum.
Build Applications
YugabyteDB supports many languages and client drivers, including Java, Go, NodeJS, Python, and more. For a complete list, including examples, see Drivers and ORMs.
Current Roadmap
The following is a list of some of the key features being worked on for upcoming releases.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| PostgreSQL 15 Compatibility | For latest features, new PostgreSQL extensions, performance, and community fixes. |
| PostgreSQL Publication/Replication slot API in CDC | PostgreSQL has a huge community that needs a PG-compatible API to set up and consume database changes. |
| Bitmap scan | Bitmap Scan support for using Index Scans, remote filter and enhanced Cost Model. |
| Cost based optimizer(CBO) | Efficient query plans based on statistics (such as table size, number of rows) and data distribution. |
| Parallel query execution | Higher query performance by splitting a single query for execution across different CPU cores. |
| pgvector extension | Support for vector data types, enabling efficient storage and querying of high-dimensional vectors. |
| Connection Management | Server side connection management enabling upto 30K connections per node |
Refer to roadmap tracker for the list of all items in the current roadmap.
Recently released features
v2.23 (Preview) - Sep, 2024
v2.23 is the current Preview release. This includes features under active development and is recommended for development and testing only. For the full list of features and improvements in this release, see Release notes - v2.23. Here are some of the prominent features.
Instant database cloning
Quickly create independent copies of your database for data recovery, development, and testing.
pg_cron extension
Use pg_cron to schedule YSQL commands using familiar cron syntax, including jobs on intervals as fine as seconds.
Semi-automatic xCluster replication
Simplified management of YSQL transactional xCluster replication by operating at the database level instead of the table level.
Improvement to backward scans
Improvements to backward scan performance now allows such queries to be 10X faster out of the box!
v2024.1 (Stable) - Jun, 2024
v2024.1 is the current stable release. Stable releases undergo rigorous testing for a longer period of time and are ready for production use. For the full list of features and improvements in this release, see Release notes - v2024.1. Here are some of the prominent features.
Enhanced Postgres Compatibility Mode
Enables you to take advantage of many new improvements in both PostgreSQL compatibility and performance parity, making it even easier to lift and shift your applications from PostgreSQL to YugabyteDB. When this mode is turned on, YugabyteDB uses the Read-Committed isolation mode, the Wait-on-Conflict concurrency mode for predictable P99 latencies, and the new Cost Based Optimizer.
Rollback after upgrade
Seamlessly roll back to the pre-upgrade version if you're not satisfied with the upgraded version.
Batched nested loop joins
A join execution strategy that improves on Nested Loop joins by sending one request to the inner table per batch of outer table tuples instead of once per individual outer table tuple.
Enhanced Explain Analyze output
Explain Analyze, when used with DIST option, will also show the rows read from the storage layer, which can help diagnosing the query performance.
Architecture
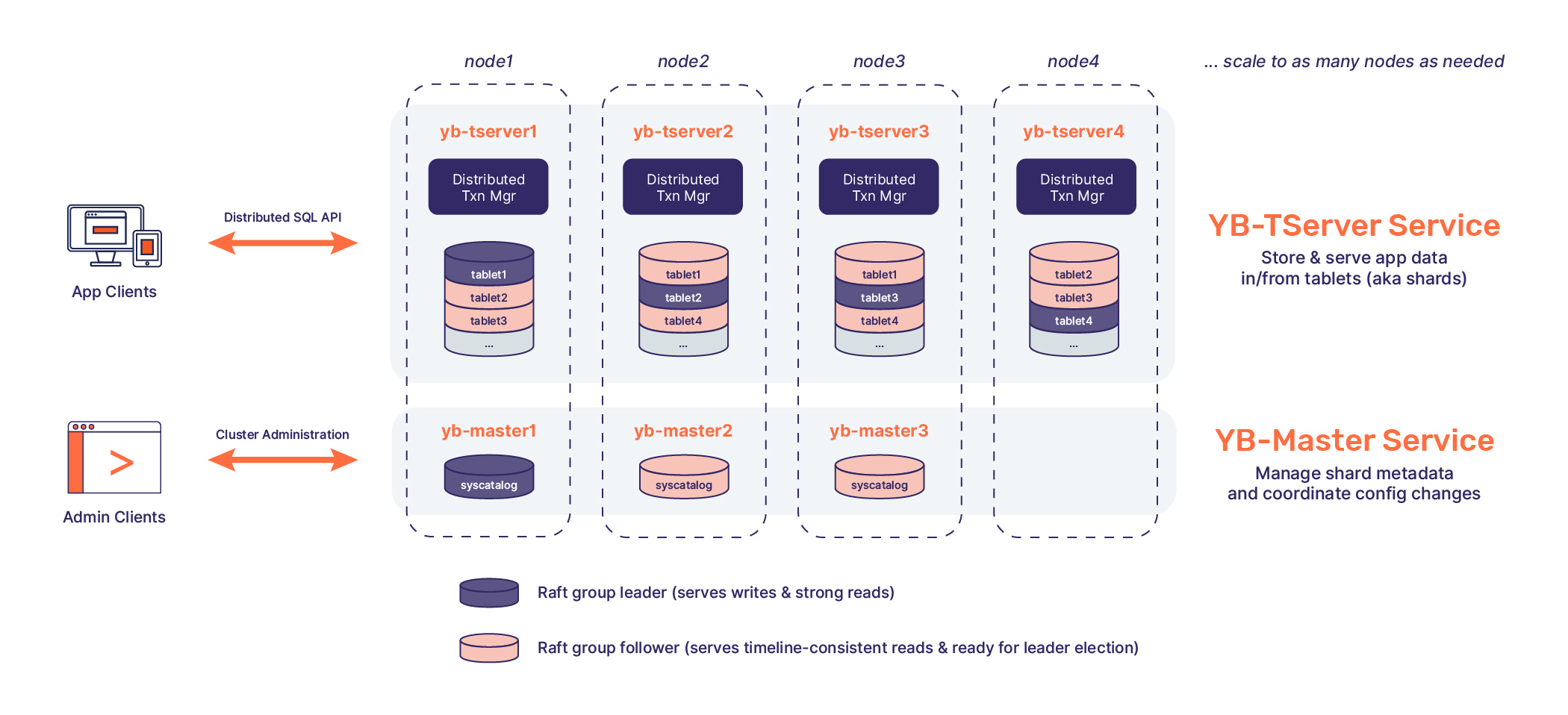
Review detailed architecture in our Docs.
Need Help?
-
You can ask questions, find answers, and help others on our Community Slack, Forum, Stack Overflow, as well as Twitter @Yugabyte.
-
Use GitHub issues to report issues or request new features.
-
To troubleshoot YugabyteDB and cluster/node-level issues, refer to Troubleshooting documentation.
Contribute
As an open-source project with a strong focus on the user community, we welcome contributions as GitHub pull requests. See our Contributor Guides to get going. Discussions and RFCs for features happen on the design discussions section of our Forum.
License
Source code in this repository is variously licensed under the Apache License 2.0 and the Polyform Free Trial License 1.0.0. A copy of each license can be found in the licenses directory.
The build produces two sets of binaries:
- The entire database with all its features (including the enterprise ones) is licensed under the Apache License 2.0
- The binaries that contain
-managedin the artifact and help run a managed service are licensed under the Polyform Free Trial License 1.0.0.
By default, the build options generate only the Apache License 2.0 binaries.
Read More
- To see our updates, go to the Distributed SQL Blog.
- For in-depth design and architecture details, see our design specs.
- Tech Talks and Videos.
- See how YugabyteDB compares with other databases.


