Welcome to dotnet-shell the C# script compatible shell
dotnet-shell is a replacement for your *Unix shell (bash,sh,dash etc) that brings C#/Dotnet to the command line in a familiar and Bash-like syntax. It combines the best of C# with the shell commands you already know. If you've used dotnetscript or nake you will feel right at home. Best of all it is easy to take your existing Unix shell scripts and port them to dotnet-shell format.
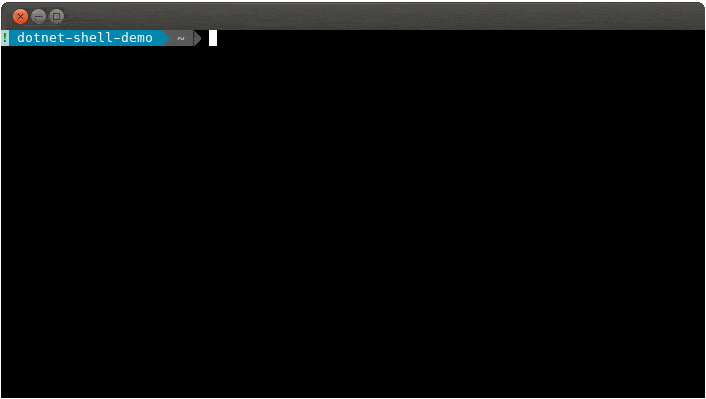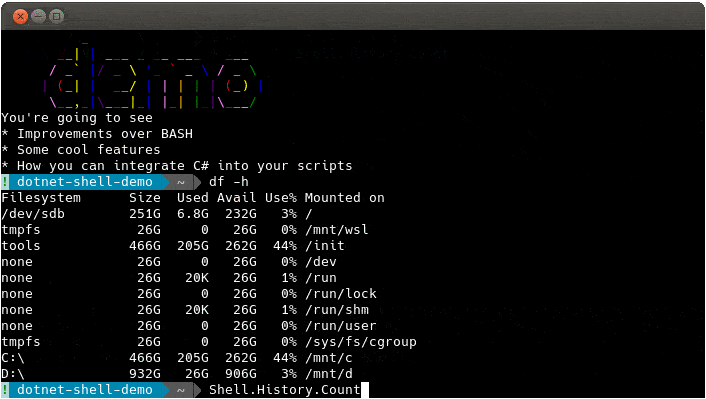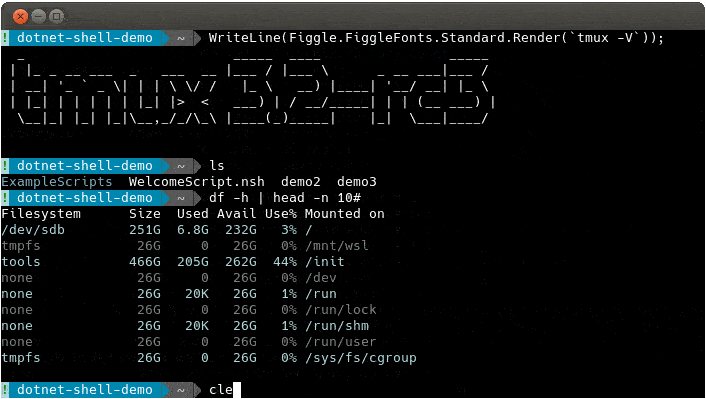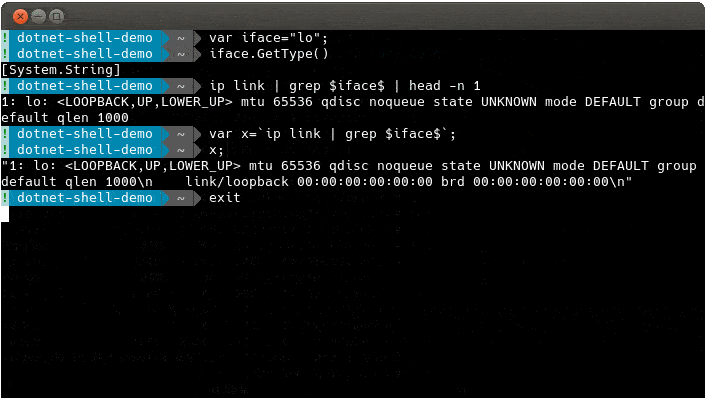
dotnet-shell acts as a meta shell that sits on top of your system shell (Bash/PowerShell etc). It replaces hard to remember loop/if syntax with C# and enables you to use the shell constructs that you know and can't unlearn! It works in both interactive and script modes allowing you to build variables and arguments in C# and use them easily in shell commands.
It is fully featured, supporting:
- Bash-style tab completion augmented with C# autocompletion
- Advanced history searching with an improved UX (helped by tmux if desired)
- Support for loading Nugets, DLLs and other scripts
- Powerline, command aliasing
Comparison to other projects / check these out too
Since the dotnet runtime enabled REPL (Read Evaluate Print Loop) support there have been a few different projects that have evolved to use it, some of the best are:
- dotnet-script - A great scripting environment which we use internally to run commands. The UX however is not designed for everyday use and the command line environment lacks an easy way to run system commands.
- Nake - Another great project focused on build scripts instead of interactive shell environments.
- Orbital Shell - A great project but focused on being cross platform, supporting the same commands on multiple platforms, as such 'OS' commands have been reimplemented. We took the view of keeping existing logic/syntax similar enough to aid porting.
How to install
First you need to install the .NET6. runtime. this is usually easiest via your OS' package manager. Next run:
dotnet --infoIf you see a lot of .NET version information that starts with 6.0 then you have a working copy of the .NET runtime. dotnet-shell is a dotnet tool. It is installed by:
dotnet tool install -g dotnet-shell| OS | Status |
|---|---|
| Linux | Stable |
| Windows | In-Testing |
| Mac | Should work untested |
| BSD | Unsupported |
There is now initial support for Windows execution via PowerShell. Executing commands works as does variable capture.
Syntax cheatsheet
In general dotnet-shell uses the same syntax of dotnetscript. To make some operations easier this has been extended so that:
- shell commands are created from any line that doesn't end with a ';' or part of existing C# syntax - just like in Bash
- backtick characters allow you to execute a command and capture its stdout (rather than letting it go to the screen)
- nake style variables \$...\$ allow you to take variables from C# and include these in your system commands
A key point to note is that in generally a line needs to end with a ';' to be interpreted as C# (unless it is part of loop, class etc)
| File extension | Usage |
|---|---|
| CSX | File contains dotnetscript syntax - no dotnet-shell extension can be used |
| nsh | CSX script syntax with our extensions |
| CS | Can be loaded and executed with #load |
| DLL | Can be loaded with #r |
The ExampleScripts repo is a good place to see what you can do.
#!/usr/bin/env dotnet-shell
#r "System.Xml.Linq" // reference assemblies
#r "nuget: Newtonsoft.Json" // and nuget packages is fully supported
#load "Other.csx" // You can load other script files
#load ~/ExampleScripts/CmdSyntax.nsh // (both absolute and relative paths are fine)
using System; // many namespaces are loaded by default
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using Microsoft.CSharp;
using static System.Console; // static members smake your scripts shorter
WriteLine("Are you ready? Y/N:");
// You can run a system command just like in Bash
echo "Hello world"
// Wrapping a command in ``(backticks) allows you to capture the output
var x = `ps`; // but default this is a string
// You can also create more complex objects
DirectoryInfo dir = `/bin/echo /bin/`;
FileInfo file = `/bin/echo /bin/ls`;
int aNumber=`/bin/echo 500`;
// You can combine these into something quite powerful
List<string> z=`dmesg`; z.Distinct().Count();
var variable = "Lets say you have a variable";
// This is how you pass it into a system command
echo $variable$
Useful tips and tricks
Escaping input automatically - the following one liner will print escaped C#. Great for copy and pasting into your codebase.
Console.ReadLine();Command line help
-v, --verbose (Default: false) Set output to verbose messages.
--earlyDebuggerAttach (Default: false) Enables early debugging for initialization related issues
--showPreProcessorOutput (Default: false) Outputs preprocessed scripts and commands to StdOut prior to execution
-x, --ux (Default: Enhanced) The user experience mode the shell starts in
--profile The path to the personal initialization script file (core.nsh)
-s, --subShell Path to the sub shell to invoke commands with
-a, --subShellArgs Arguments to the provided to the SubShell, this MUST include the format specifier {0}
-u, --using Additional 'using' statements to include
--popupCmd (Default: tmux popup -KER '{0}' -x 60 -y 0 -w 60% -h 100%) Command to run to raise a system popup window, must include {0} format specifier for the dotnet-shell command
--historyCmd (Default: dotnet {0} --history --apiport {1} --token {2}) dotnet-shell command line to execute when the history subprocess. Must include {0} format specifier for DLL location, {1} for port and {2} for token parameters
--additionalHistory Path to additional OS specific history files
--historyPath Path to CSX history file
--nowizard (Default: false) Do not try and run the initial set up wizard
--help Display this help screen.
--version Display version information.How to build from source
Visual Studio solutions and VS Code projects are published with this repo. Otherwise you can checkout the repo and run:
dotnet build
dotnet src/Shell/bin/Debug/net6.0/dotnet-shell.dllAuthor
i-am-shodan
- Twitter: @therealshodan
- Github: @i-am-shodan
Contributing
Contributions, issues and feature requests are welcome!
Feel free to check issues page.
License
Copyright © 2021 i-am-shodan.
This project is MIT licensed.
This README was generated by readme-md-generator


