PySC2 - StarCraft II Learning Environment
PySC2 is DeepMind's Python component of the StarCraft II Learning Environment (SC2LE). It exposes Blizzard Entertainment's StarCraft II Machine Learning API as a Python RL Environment. This is a collaboration between DeepMind and Blizzard to develop StarCraft II into a rich environment for RL research. PySC2 provides an interface for RL agents to interact with StarCraft 2, getting observations and sending actions.
We have published an accompanying blogpost and paper, which outlines our motivation for using StarCraft II for DeepRL research, and some initial research results using the environment.
About
Disclaimer: This is not an official Google product.
If you use the StarCraft II Machine Learning API and/or PySC2 in your research, please cite the StarCraft II Paper
You can reach us at pysc2@deepmind.com.
Quick Start Guide
Get PySC2
PyPI
The easiest way to get PySC2 is to use pip:
$ pip install pysc2That will install the pysc2 package along with all the required dependencies.
virtualenv can help manage your
dependencies. You may also need to upgrade pip: pip install --upgrade pip
for the pysc2 install to work. If you're running on an older system you may
need to install libsdl libraries for the pygame dependency.
Pip will install a few of the binaries to your bin directory. pysc2_play can
be used as a shortcut to python -m pysc2.bin.play.
From Source
Alternatively you can install latest PySC2 codebase from git master branch:
$ pip install --upgrade https://github.com/deepmind/pysc2/archive/master.zipor from a local clone of the git repo:
$ git clone https://github.com/deepmind/pysc2.git
$ pip install --upgrade pysc2/Get StarCraft II
PySC2 depends on the full StarCraft II game and only works with versions that include the API, which is 3.16.1 and above.
Linux
Follow Blizzard's documentation to
get the linux version. By default, PySC2 expects the game to live in
~/StarCraftII/. You can override this path by setting the SC2PATH
environment variable or creating your own run_config.
Windows/MacOS
Install of the game as normal from Battle.net. Even the
Starter Edition will work.
If you used the default install location PySC2 should find the latest binary.
If you changed the install location, you might need to set the SC2PATH
environment variable with the correct location.
PySC2 should work on MacOS and Windows systems running Python 3.8+, but has only been thoroughly tested on Linux. We welcome suggestions and patches for better compatibility with other systems.
Get the maps
PySC2 has many maps pre-configured, but they need to be downloaded into the SC2
Maps directory before they can be played.
Download the ladder maps
and the mini games
and extract them to your StarCraftII/Maps/ directory.
Run an agent
You can run an agent to test the environment. The UI shows you the actions of the agent and is helpful for debugging and visualization purposes.
$ python -m pysc2.bin.agent --map Simple64It runs a random agent by default, but you can specify others if you'd like, including your own.
$ python -m pysc2.bin.agent --map CollectMineralShards --agent pysc2.agents.scripted_agent.CollectMineralShardsYou can also run two agents against each other.
$ python -m pysc2.bin.agent --map Simple64 --agent2 pysc2.agents.random_agent.RandomAgentTo specify the agent's race, the opponent's difficulty, and more, you can pass
additional flags. Run with --help to see what you can change.
Play the game as a human
There is a human agent interface which is mainly used for debugging, but it can also be used to play the game. The UI is fairly simple and incomplete, but it's enough to understand the basics of the game. Also, it runs on Linux.
$ python -m pysc2.bin.play --map Simple64In the UI, hit ? for a list of the hotkeys. The most basic ones are: F4 to
quit, F5 to restart, F8 to save a replay, and Pgup/Pgdn to control the
speed of the game. Otherwise use the mouse for selection and keyboard for
commands listed on the left.
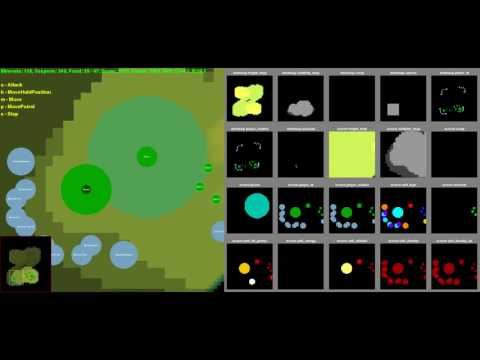
The left side is a basic rendering. The right side is the feature layers that the agent receives, with some coloring to make it more useful to us. You can enable or disable RGB or feature layer rendering and their resolutions with command-line flags.
Watch a replay
Running an agent and playing as a human save a replay by default. You can watch that replay by running:
$ python -m pysc2.bin.play --replay <path-to-replay>This works for any replay as long as the map can be found by the game.
The same controls work as for playing the game, so F4 to exit, pgup/pgdn
to control the speed, etc.
You can save a video of the replay with the --video flag.
List the maps
Maps need to be configured before they're known to the environment. You can see the list of known maps by running:
$ python -m pysc2.bin.map_listRun the tests
If you want to submit a pull request, please make sure the tests pass on both python 2 and 3.
$ python -m pysc2.bin.run_testsEnvironment Details
For a full description of the specifics of how the environment is configured, the observations and action spaces work read the environment documentation.
Note that an alternative to this environment is now available which provides an enriched action and observation format using the C++ wrappers developed for AlphaStar. See the converter documentation for more information.
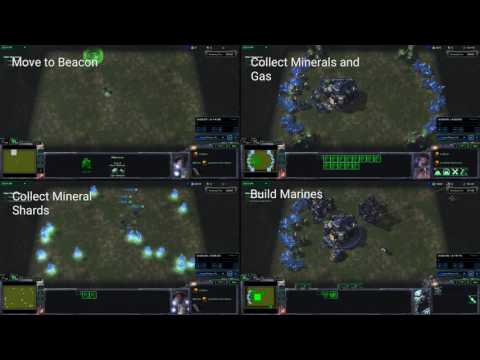
Mini-game maps
The mini-game map files referenced in the paper are stored under pysc2/maps/
but must be installed in $SC2PATH/Maps. Make sure to follow the download
instructions above.
Maps are configured in the Python files in pysc2/maps/. The configs can set
player and time limits, whether to use the game outcome or curriculum score, and
a handful of other things. For more information about the maps, and how to
configure your own, read the maps documentation.
Replays
A replay lets you review what happened during a game. You can see the actions and observations that each player made as they played.
Blizzard is releasing a large number of anonymized 1v1 replays played on the ladder. You can find instructions for how to get the replay files on their site. You can also review your own replays.
Replays can be played back to get the observations and actions made during that game. The observations are rendered at the resolution you request, so may differ from what the human actually saw. Similarly the actions specify a point, which could reflect a different pixel on the human's screen, so may not have an exact match in our observations, though they should be fairly similar.
Replays are version dependent, so a 3.16 replay will fail in a 3.16.1 or 3.17 binary.
You can visualize the replays with the full game, or with pysc2.bin.play.
Alternatively you can run pysc2.bin.replay_actions to process many replays
in parallel.