pysmartmeter
Collect data from Hichi Smartmeter aka volkszaehler.org (USB Version) and expose it via MQTT.
Discussion: https://www.photovoltaikforum.com/thread/188160-pysmartmeter (de)
In the end it can looks like the following Home Assistant dashboard screenshot, using MQTT integration:
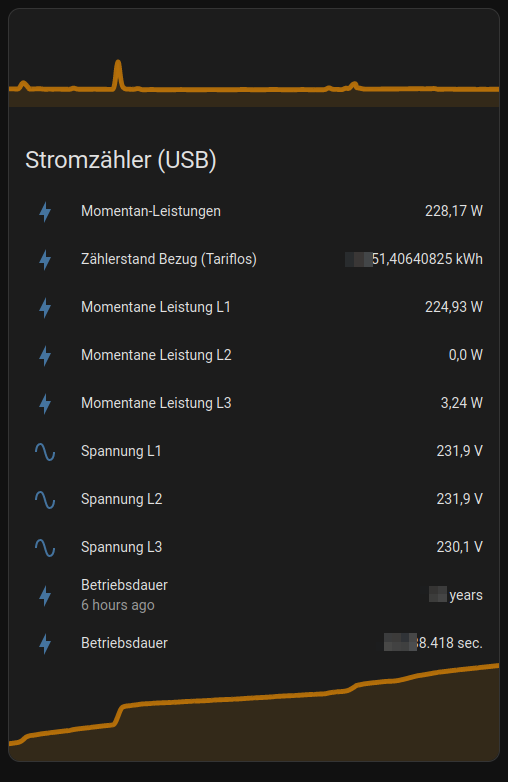
With my "eBZ DD3" energy meter by eBZ GmbH the values update live every second ;)
Currently only energy meters that send OBIS text protocol are supported! (Test this with ./cli.py dump)
TODO: #37 - Add support for SML (Smart Message Language) binary protocol
quickstart
prepare
Install minimum requirements, e.g.:
~$ sudo apt install python3-venvNote: If you using a Raspberry Pi: Check that https://www.piwheels.org/ are in use.
For this, just look into etc/pip.conf it should be looked like this:
~/pysmartmeter$ cat /etc/pip.conf
[global]
extra-index-url=https://www.piwheels.org/simpleclone and start
Clone sources and install project:
~$ git clone https://github.com/jedie/pysmartmeter.git
~$ cd pysmartmeter
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py --helpThe output of ./cli.py --help looks like:
Usage: ./cli.py [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭─ Commands ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ debug-settings Display (anonymized) MQTT server username and password │
│ debug-systemd-service Just print the systemd service file content │
│ detect-serial Just print the detected serial port instance │
│ dump Just dump serial output │
│ publish-loop Publish current data via MQTT (endless loop) │
│ setup-systemd-service Setup PySmartMeter systemd services and starts it. │
│ store-settings Store MQTT server settings. │
│ systemd-restart Restart PySmartMeter systemd services │
│ systemd-status Call systemd status of PySmartMeter services │
│ systemd-stop Stop PySmartMeter systemd services │
│ test-mqtt-connection Test connection to MQTT Server │
│ version Print version and exit │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯Test if you Hichi Smartmeter with CP2102 USB to UART Bridge Controller will be found, e.g.:
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py detect-serialNote: It's a good idea to use the /dev/serial/by-id/{your-device-id} path as serial port, instead of /dev/ttyUSB1
Call udevadm info -n /dev/ttyUSB* to get information about all USB serial devices and ls -l /dev/serial/by-id/ to see the existing links.
Maybe you didn't have permissions to access the port, e.g.:
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py dump
...
try: /dev/ttyUSB0 CP2102 USB to UART Bridge Controller - CP2102 USB to UART Bridge Controller USB VID:PID=10C4:EA60
/dev/ttyUSB0 file mode: 0o20660
/dev/ttyUSB0 user ID: 0
/dev/ttyUSB0 user group ID: 20
/dev/ttyUSB0 user group: 'dialout'
ERROR: [Errno 13] could not open port /dev/ttyUSB0: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/dev/ttyUSB0'
...Fix fiy by add the user to the group, e.g.:
sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USERpublish smartmeter data via MQTT
You have to store your MQTT settings (host, port, username, password) one time, e.g.:
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py store-settingsThis will create a JSON file here: ~/.pysmartmeter
You can test reading this settings file with:
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py debug-settingsTest your MQTT settings with:
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py test-mqtt-connectionSetup systemd service:
~/pysmartmeter$ sudo ./cli.py setup-systemd-serviceThis will create a systemd service that automaticly starts on every boot.
Note: Before you start the systemd service, check if everything works correctly with ./cli.py dump and ./cli.py publish-loop
Otherwise you may start a services that will just deal wie gabage (e.g.: your energy meters speaks no OBIS text protocol) and restarts on and on again ;)
Check if service is running:
~/pysmartmeter$ sudo ./cli.py systemd-statusIf everything is fine: Go to your Home Assistant and check the MQTT integration The device discovery will be made automaticly.
Troubleshooting
If you have any trouble, try to recreate the Python Virtual Environment first. For this, just delete it and start the CLI to recreate it, e.g.:
~/pysmartmeter$ rm -Rf .venv-app/
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.pyStart hacking
~$ git clone https://github.com/jedie/pysmartmeter.git
~$ cd pysmartmeter
~/pysmartmeter$ ./dev-cli.py --helpUsage: ./dev-cli.py [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
╭─ Options ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ --help Show this message and exit. │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
╭─ Commands ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ check-code-style Check code style by calling darker + flake8 │
│ coverage Run tests and show coverage report. │
│ fix-code-style Fix code style of all pysmartmeter source code files via darker │
│ install Run pip-sync and install 'pysmartmeter' via pip as editable. │
│ mypy Run Mypy (configured in pyproject.toml) │
│ publish Build and upload this project to PyPi │
│ safety Run safety check against current requirements files │
│ test Run unittests │
│ tox Run tox │
│ update Update "requirements*.txt" dependencies files │
│ update-test-snapshot-files Update all test snapshot files (by remove and recreate all snapshot │
│ files) │
│ version Print version and exit │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯Backwards-incompatible changes
v0.4.x -> v0.5.x
We split the CLI files into:
./cli.py- Commands for end users./dev-cli.py- Commands for developers
v0.2.x -> v0.3.x
Packages changes:
- We switched from
poetrytopip-tools Makefilewas removed- "Renamed"
cli.shtocli.py
The Makefile is no longer needed, because "Bootstrapping" will be made, just by call cli.py
To migrate, just remove the existing .venv and create a fresh one, e.g.:
~$ cd pysmartmeter
~/pysmartmeter$ git pull origin main
~/pysmartmeter$ rm -Rf .venv
~/pysmartmeter$ ./cli.py --helpvarious links
- Discussion: https://www.photovoltaikforum.com/thread/188160-pysmartmeter (de)
- https://github.com/pyserial/pyserial
- https://github.com/eclipse/paho.mqtt.python
- https://github.com/eclipse/mosquitto
- https://dewiki.de/Lexikon/OBIS-Kennzahlen (de) | https://www.promotic.eu/en/pmdoc/Subsystems/Comm/PmDrivers/IEC62056_OBIS.htm (en)
- https://www.photovoltaikforum.com/thread/145886-habe-lesk%C3%B6pfe-mit-usb-%C3%BCber/ (de)
- https://www.heise.de/tests/Ausprobiert-Guenstiger-IR-Lesekopf-fuer-Smart-Meter-mit-Tastmota-Firmware-7065559.html (de)
- https://www.home-assistant.io


