Blazor Internationalization(I18n) Text 

📝 Summary
This package is another way to localize text in your Blazor Web App!
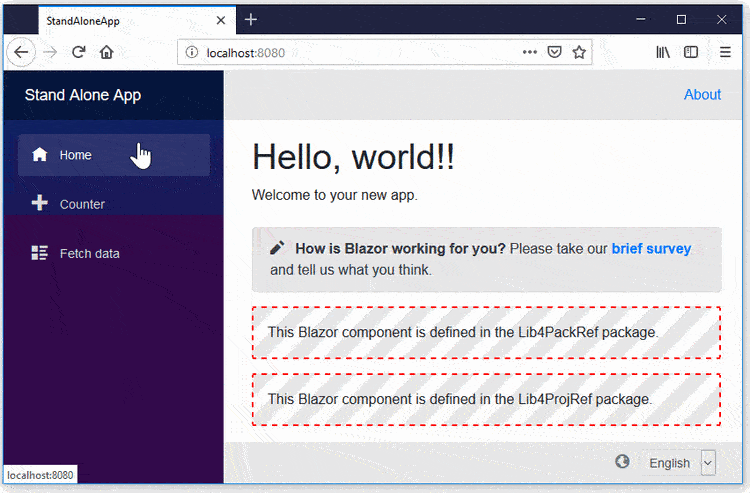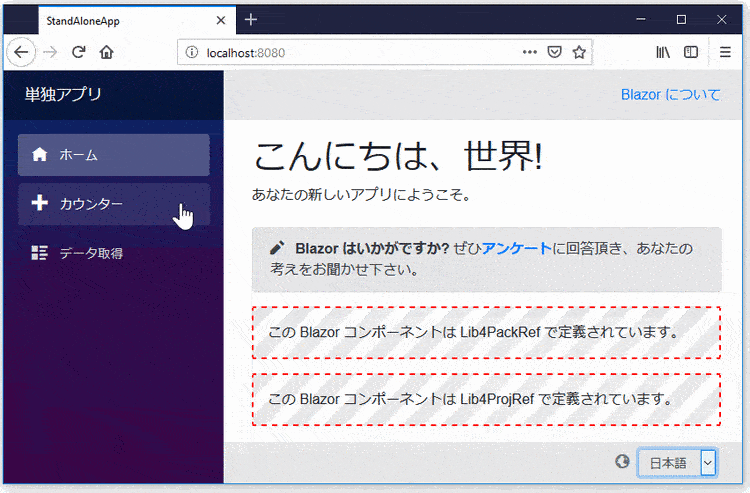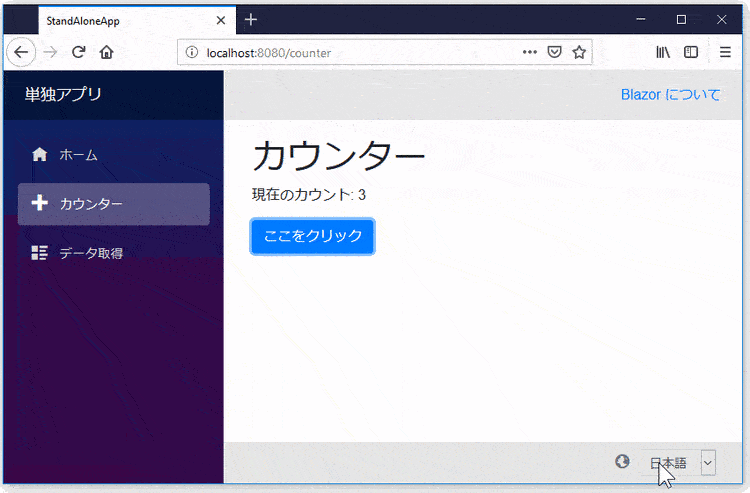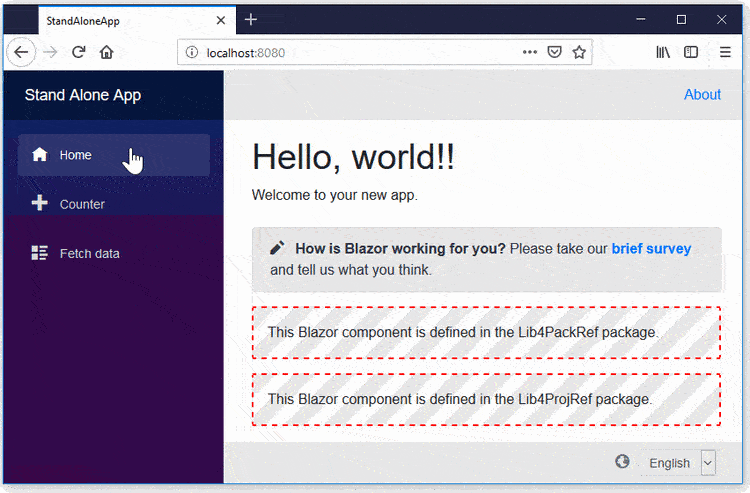
🎁 Features
- All of the render modes (SSR, Server, WebAssembly, and Auto) are supported.
- In Blazor Wasm, it works even on a static web host. (The ASP.NET Core host isn't required)
- Only needs a plain text editor - no need for .resx files
- Static Typing - IntelliSense, Code Hint, etc.
- It supports Blazor components libraries. You can create NuGet packages of your libraries that are localized with "Blazor I18nText".
📢 Notice
Blazor WebAssembly has started localization support officially since v.3.2 preview 4. It is based on .NET Standard IStringLocalizer and satellite assemblies with .resx.
However, I will continue to develop and maintain this package, because this package still has some advantages over the .NET standard implementation.

Supported .NET versions
.NET 6.0, 8.0, or later versions.
🚀 Quick Start
Step 1 - Add Package
Add Toolbelt.Blazor.I18nText NuGet package to your Blazor app project as shown below
dotnet add package Toolbelt.Blazor.I18nTextStep 2 - Create localized text source files as JSON or CSV
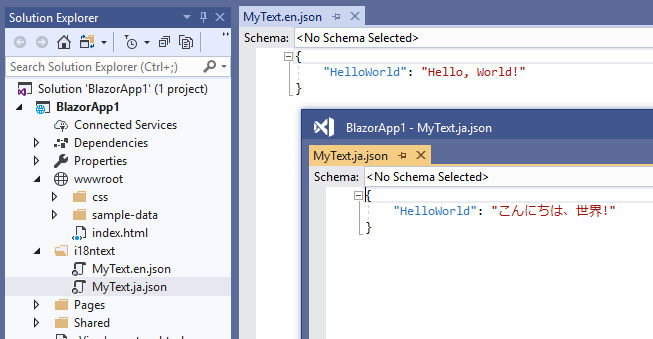
Add localized text source files for each language in an i18ntext folder under the project folder.
The localized text source files must be simple key-value only JSON files, as shown in the example below:
{
"Key1": "Localized text 1",
"Key2": "Localized text 2",
...
}or, an only 2-column CSV file without a header row as shown in the example below.
Key1,Localized text 1
Key2,Localized text 2[!IMPORTANT]
The encoding of the CSV and JSON files must be UTF-8.
The naming rule for the localized text source files must follow this format:
<Text Table Name>.<Language Code>.{json|csv}For example, the JSON-formatted localized text source file for the English language of the MyText Text Table class must be named MyText.en.json.
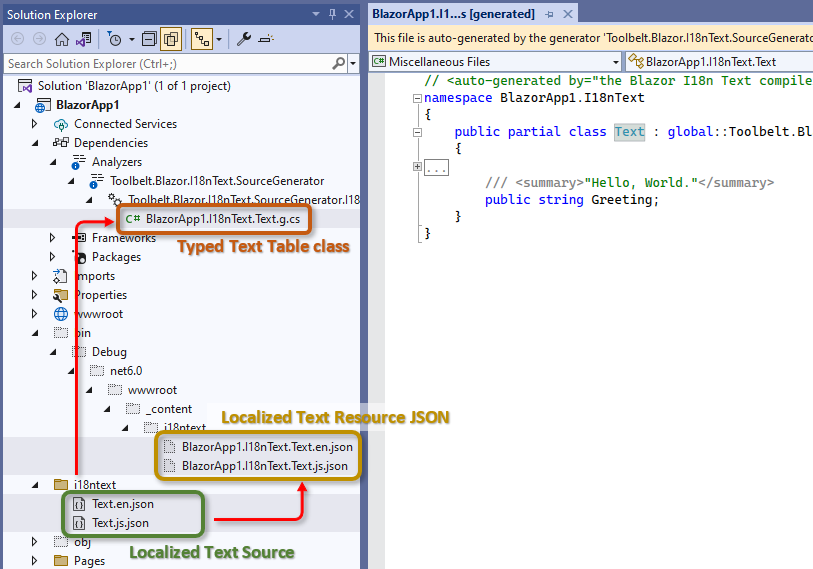
Step 3 - Build the project whenever localized text source files are created or updated.
Basically, after creating or updating those localized text source files, you may have to build your Blazor app project.
After that, "Typed Text Table class" C# source code will be generated by the C# "source generator" feature.
And also, "Localized Text Resource JSON" files will be generated in the output folder.
for Visual Studio IDE users
On Visual Studio IDE, the source generator will work automatically in the background. Therefore, Visual Studio IDE users usually do not need to build the project explicitly.
Localized text source files (.json or .csv) are recompiled into "Typed Text Table class" and "Localized Text Resource JSON" files automatically whenever they are updated.
for dotnet CLI users
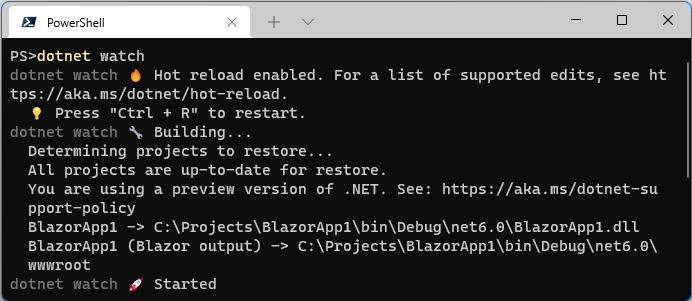
When you are developing on dotnet CLI and want to recompile localized text source files automatically whenever they are changed, you can use the dotnet watch command.
$ dotnet watchAfter entering that dotnet CLI command, the command window will stay in execution mode and watch for changes in the localized text source files.
When that dotnet CLI detects localized text source files changing, the dotnet CLI will recompile localized text source files into "Typed Text Table class" and "Localized Text Resource JSON" files.
Step 4 - Configure your app to use I18nText service
Edit the "Program.cs" file to register "I18nText" service, like this.
// in your Program.cs
using Toolbelt.Blazor.Extensions.DependencyInjection; // 👈 Add this, and...
...
var builder = WebApplication.CreateDefault(args);
...
// 👇 Add the following code to register the I18nText service.
builder.Services.AddI18nText(
options => options.PersistenceLevel = PersistanceLevel.Cookie);
...[!NOTE] If your Blazor app has SSR areas, we strongly recommend to use
PersistanceLevel.Cookieoption to keep the language settings, because it is the only way to keep the language settings in the SSR areas. If your Blazor app doesn't have any SSR areas, you can use other options, such asPersistanceLevel.Session, etc.
If your Blazor app has SSR areas, or the Server-side Pre-rendering is enabled, or the I18n Text options are configured to use cookies to persist language settings, you have to add the following code to configure the RequestLocalization middleware, and use the RequestLocalization middleware, like this.
// in your Program.cs
...
// 👇 Add the following code to configure
// the RequestLocalization middleware, and...
builder.Services.Configure<RequestLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
// This is an example.
// You should configure the supported cultures as you like.
var supportedCultures = new[] { "en", "ja" };
options.DefaultRequestCulture = new("en");
options.AddSupportedCultures(supportedCultures);
options.AddSupportedUICultures(supportedCultures);
});
...
var app = builder.Build();
...
// 👇 Add the following code to use the RequestLocalization middleware.
app.UseRequestLocalization();
...Step 5 - Get the "Text Table" object in your Blazor component
Open your Blazor component file (.razor) inside any editor, and do the following:
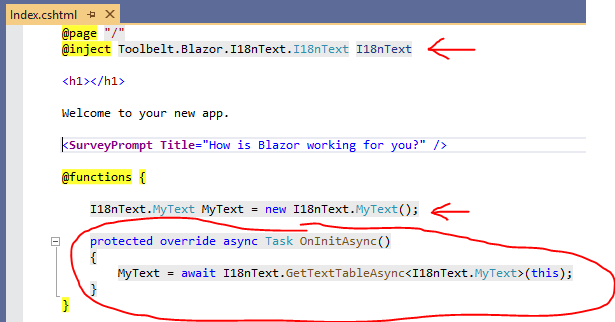
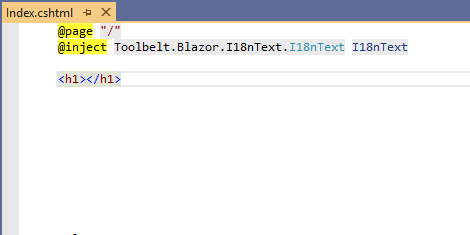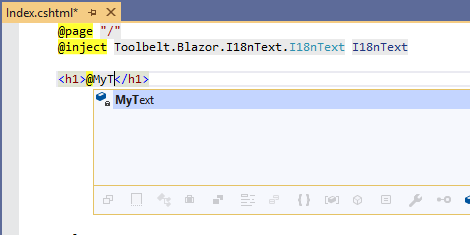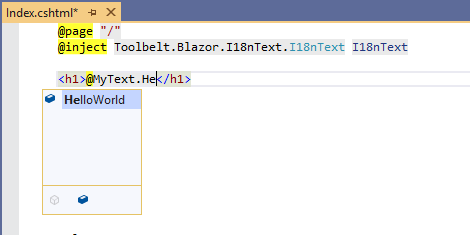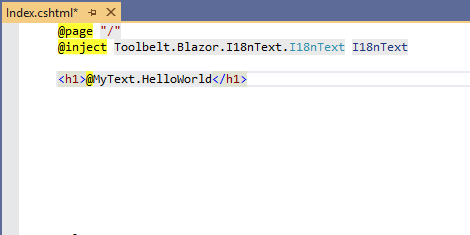
- Inject
Toolbelt.Blazor.I18nText.I18nTextservice into the component.
@inject Toolbelt.Blazor.I18nText.I18nText I18nText- Add a field of the Text Table class generated from localized text source files, and assign the default instance.
@code {
private I18nText.MyText MyText = new();
...[!NOTE] The namespace of the Text Table class is
<default namespace of your Blazor project>+"I18nText".
- Override
OnInitiallizedAsync()method of the Blazor component, and assign a Text Table object that's a return value ofGetTextTableAsync<T>()method ofI18nTextservice instance to the Text Table field.
...
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
MyText = await I18nText.GetTextTableAsync<I18nText.MyText>(this);
...
Step 6 - Use the Text Table
After doing these steps, you can reference a field of the Text Table object to get localized text.
If you are using Visual Studio in Windows OS or Visual Studio Code with the C# extension, you will get "IntelliSense" and "Document comment" support.
[!TIP] Text Table object allows you to get localized text by key string dynamically, with indexer syntax, like this.
<h1>@MyText["HelloWorld"]</h1>If you make some mistakes that typo of key string, it will just return the key string as is without any runtime exceptions.
Step 7 - Run it!
Build and run your Blazor app.
The I18nText service detects the language settings of the Web browser, and reads the localized text resource JSON which is most suitable for the language detected.
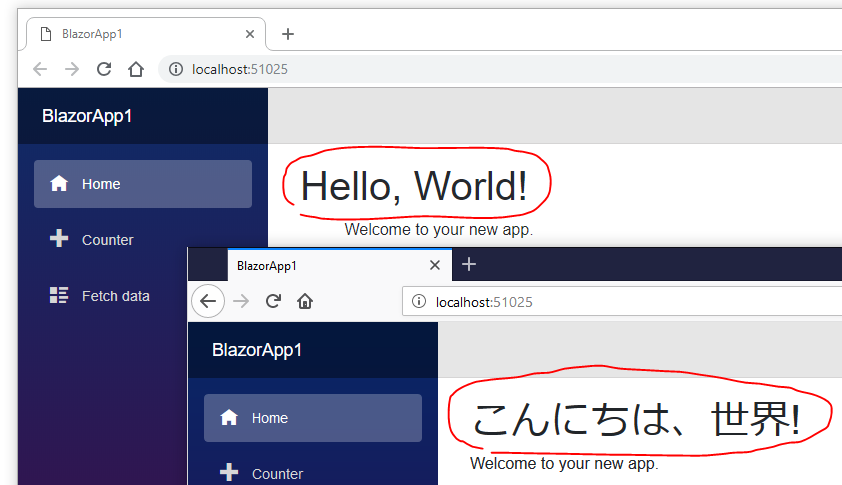
📌 Limitations
The following features are not supported in this version of I18Text library.
- Integration with ASP.NET Core localization (
IStringLocalizer<T>support) - Localize validation message
- Plural form support
- Text formatting by placeholder.
- Integration with
System.Globalization.Culture.CurrentUICulture.
The following features will not be supported forever, because these features are not the scope of this library, we think.
- Formatting of date, time, currency. (These features will be provided by
System.Globalization.Culture.)
⚙️ Configuration
🛠️ API Reference
Please see also "API Reference" on GitHub.
🎉 Release Notes
Release notes are here.