RPD — Reactive Patch Development v3.x
Important notice
This project has a successor now, named Noodle: https://github.com/shamansir/noodle, which is very close to be finished and released and, of course, have documentation, like RPD has. Noodle is written in PureScript, the very type-safe and pure functional language and so it is much more reliable and shouldn't cause runtime issues most of the time. It still has FFI to/from JavaScript, though. Another benefit — it can easily be used at server side and so the Networks require no rewriting at all, may be it will even get Terminal renderer at some point.
That way I wasn't supporting this project while I was writing the successor, and I am sorry for that. It should be working, but the features/fixes are freezed for the moment.
Official Documentation & Examples: http://shamansir.github.io/rpd
Latest Stable Version: v2.1.3
Version in development: v3.x.
(no semantic versioning was used before v2.0)
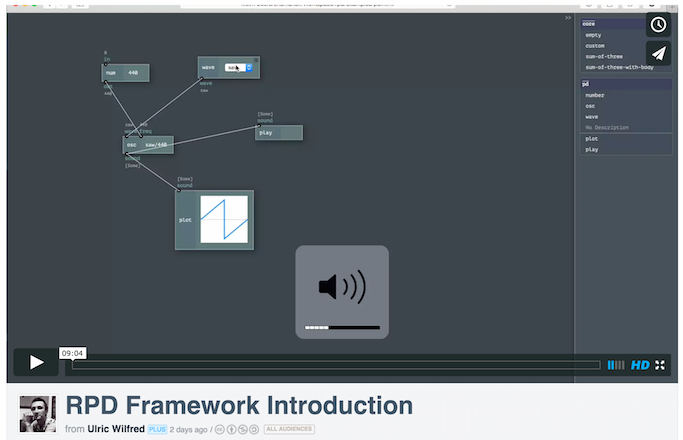
A video of the engine v0.1.0 in action, demonstrates some of its features: [ Watch ].
[ Play online ]
(NB: Only modern browsers are supported, tested most in Chrome and Safari, no mobile support for now)
Surely visit Documentation, Examples & More...
RPD is a super-minimal plugin-based Vanilla-JS-driven engine for Node-Based User Interfaces, or Flow-Based Programming Intefaces, this concept has a lot of names — namely, the ones like Pure Data, Quartz Composer, Reaktor, NodeBox, VVVV or any Shader/Material Composing View in your favorite 3D Editor.
And when I say minimal, I really mean it. Minimized and gzipped with its standard configuration, it takes no more than 10KB! (*)
(*) Excluding CSS file which usually takes 2-3 KB and Kefir.js requirement, which also usually takes ~10KB, minified and gzipped. Other configurations provided in repository may take from 10 to 20 KB, but users are free to use as many KB as they need.
Moreover, it's built with the help of Reactive programming (thanks to Kefir.js), and this way it allows a programmer to treat and process any data flow as a stream, so:
colorInlet.stream(Kefir.sequentially(500, ['red', 'navy']));Will send red and navy values every 500ms to a single color-value inlet in order. It's not the only feature you get with streams, of course, see below for much more.
Here are some GIFs in reduced quality, in addition to a video in rather good quality above, to help you decide if it worths to use this engine or not (also please take a look at code examples below!).
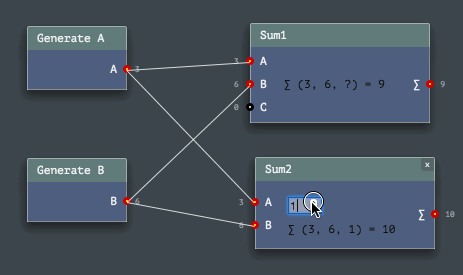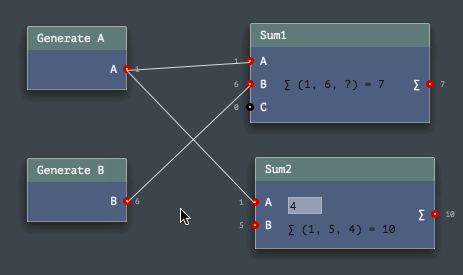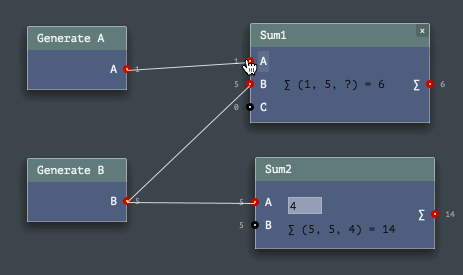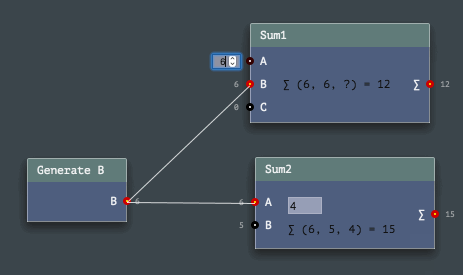
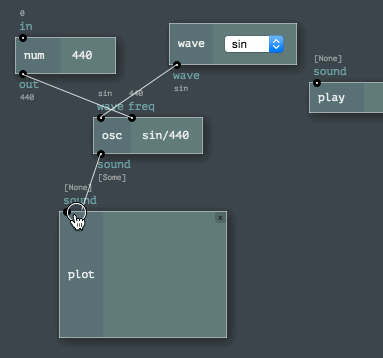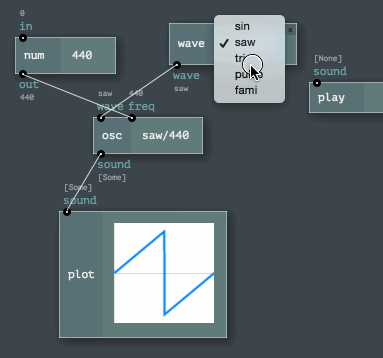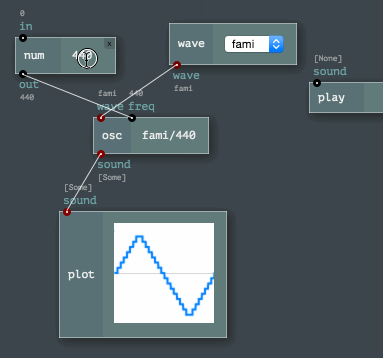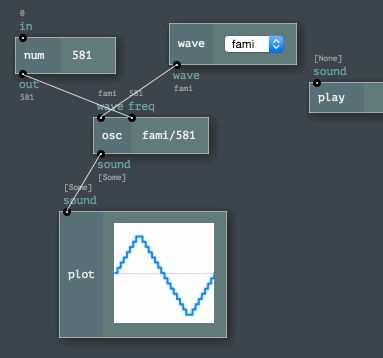
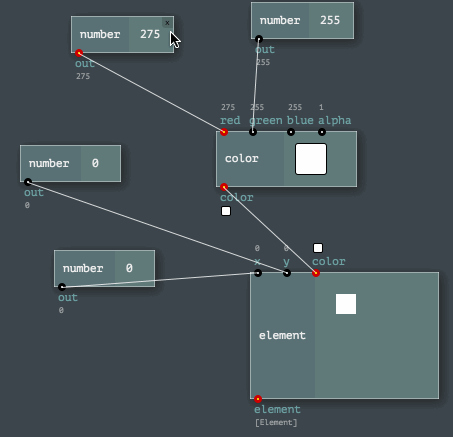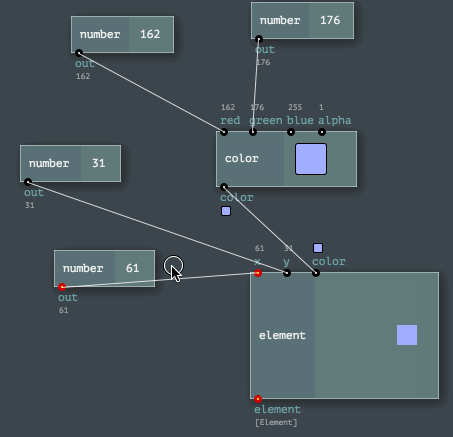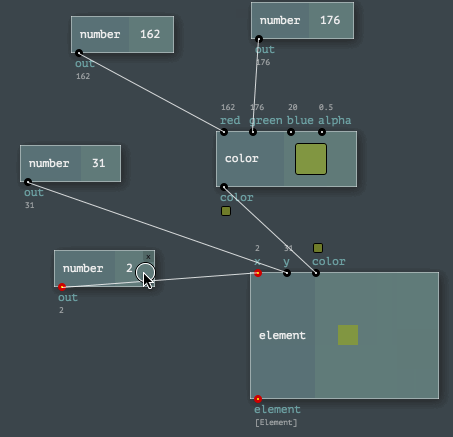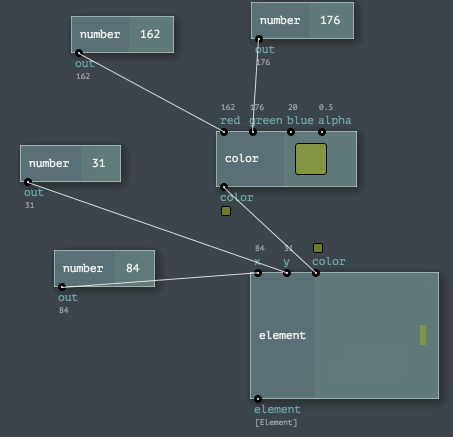
The Engine API provides easy ways to program node networks. Or to define a custom node or a channel type. Even node sets (named toolkits) are enormously easy to build!
Let's switch to some simple examples. Detailed stuff is under the links below.
Constructing a network of nodes:
var patch = Rpd.addPatch('Example');
var firstNode = patch.addNode('core/basic', 'Test');
var boolOutlet = firstNode.addOutlet('util/boolean', 'bool', {
default: true;
});
firstNode.addOutlet('util/number', { default: 1 });
firstNode.addOutlet('util/number');
var secondNode = patch.addNode('core/basic', 'Foo');
var boolInlet = secondNode.addInlet('util/boolean', 'bool');
var numInlet = secondNode.addInlet('util/number', 'num', {
allow: [ 'util/boolean' ],
adapt: function(val) { return (val === true) ? 1 : 0 }
});
boolOutlet.connect(boolInlet);
boolOutlet.connect(numInlet);
boolOutlet.send(false);
boolInlet.stream(Kefir.repeatedly(10, [true, false]));Creating custom node types is very easy:
Rpd.nodetype('util/sum-of-three', {
name: 'Sum of Three',
inlets: {
'a': { type: 'util/number', name: 'A', default: 1 },
'b': { type: 'util/number', name: 'B' },
'c': { type: 'util/number', name: 'C', hidden: true }
},
outlets: {
'sum': { type: 'util/number', name: '∑' }
},
process: function(inlets) {
return { 'sum': (inlets.a || 0) + (inlets.b || 0) + (inlets.c || 0) };
}
});Even very complex ones:
Rpd.nodetype('pd/play', function() {
var lastSound;
return {
name: 'play',
inlets: { 'sound': { type: 'pd/t-obj', default: null } },
tune: function(updates) { return updates.throttle(50); },
process: function(inlets, inlets_prev) {
if (inlets_prev.sound) inlets_prev.sound.pause();
if (inlets.sound) {
lastSound = inlets.sound;
inlets.sound.play();
}
},
handle: {
'node/turn-off': function() {
if (lastSound) lastSound.pause();
}
}
}
});Here's the engine code at a glance;
Features
RPD provides following features (though probably I forgot a dozen):
- User may observe nodes, manipulate nodes, connect inlets and outlets, effect is seen immediately; User may edit values on inlets, see results inside node bodies or additionally configure them there;
- Network model may be stored in a simple JS File;
- Developer may build custom node Toolkits to let user re-use them, in a very easy way; And it's not only restricted with configuring inlets and outlets—actually, every aspect of the node or a channel is configurable;
- Streams provide developer with an unlimited power in sending, queueing, filtering, mapping/reducing/flattening, packing and un-packing any data, basing on time periods or not; every aspect from Reactive Programming may be used to operate data streams;
- Plugin system allows to easily add renderers (HTML & SVG renderers are provided, Canvas renderer is planned), styles or importers/exporters for specific Toolkits;
- Styles allow easily and completely change a look of the interface, so your nodes may appear like ones in Blender or like ones in VVVV with just a few changes; 8 different styles are provided out-of-the-box; Also, styles are very easy to extend or create;
- Renderers do not use any direct style injection except some very minor cases, they only operate CSS classes, and it means you may completely redesign the look of your interface using only CSS;
- Developer is free to use any helper library (while RPD tries to use only Kefir and nothing else), and it is very easy: i.e. node renderers may easily use jQuery or d3.js;
- JSON and Plain Text Import/Export, both provided as an example, with the ability to write module which Imports/Exports from/to any format you want;
- Ability to be injected into any part of a page;
- Node model may be easily programmed and updated on-the-fly (i.e. while nodes already send some data);
- Node model has no side-effects in functional meaning, every change or update is provided through event streams, no data is stored or changed (expect construction); plugins, on the other hand, are completely free to use any programming model they prefer, and they are actually written in much more imperative style than the Engine, but yet they do not change the model;
- It is so easy to code for RPD, I hope community will be able and happy to write new toolkits, renderers and importers and help evolving the engine;
- PureData, Animatron and more Toolkits as an examples out-of-the-box;
- Supports Procedures (re-use node sub-trees by name);
- Smart layouting;
Using
See Setup and Network sections in Official Documentation.
Just as a quick note (detailed descriptions are for the pages mentioned above), RPD is available from NPM since latest versions, so just do:
npm install rpd --no-optionalOr, if you plan to run examples locally from node_modules, omit the --no-optional flag.
Participating
See Participation sections in Official Documentation.
Feel free to fix issues or do Pull Requests!