diff_drive_bot
This ROS package implements SLAM on a 2 wheeled differential drive robot to map an unknown environment. A joystick is used to teleoperate the robot in Gazebo. The map generated is then used for autonomous navigation using the ROS Navigation stack.
Installation
- Build package from source: navigate to the source folder of your catkin workspace and build this package using:
$ git clone https://github.com/devanshdhrafani/diff_drive_bot.git $ cd .. $ catkin_make - Install Required dependencies:
$ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-dwa-local-planner $ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-joy
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM)
The package uses slam_gmapping to map the environment. For the purpose of this demonstration, we use the Gazebo simulation environment to move around the robot.

- Load the robot in the Gazebo environment. Default model is the turtlebot3_house. You can change this from
/worlds/mybot.world. To continue with default model:$ roslaunch diff_drive_bot gazebo.launch - Launch the slam_gmapping node. This will also start rviz where you can visualize the map being created:
$ roslaunch diff_drive_bot gmapping.launch - Move the robot around. If you have a Joystick, use:
$ roslaunch diff_drive_bot joy_teleop_launch.launchOR teleop using keyboard:
$ rosrun diff_drive_bot keyboard_teleop.py - Move the robot in your environment till a satisfactory map is created.
- Save the map using:
$ rosrun map_server map_saver -f ~/test_map - Copy the map file to
~/diff_drive_bot/maps/directory and edit the .yaml file to match the path.
Autonomous Navigation
This package uses the ROS Navigation stack to autonomously navigate through the map created using gmapping.
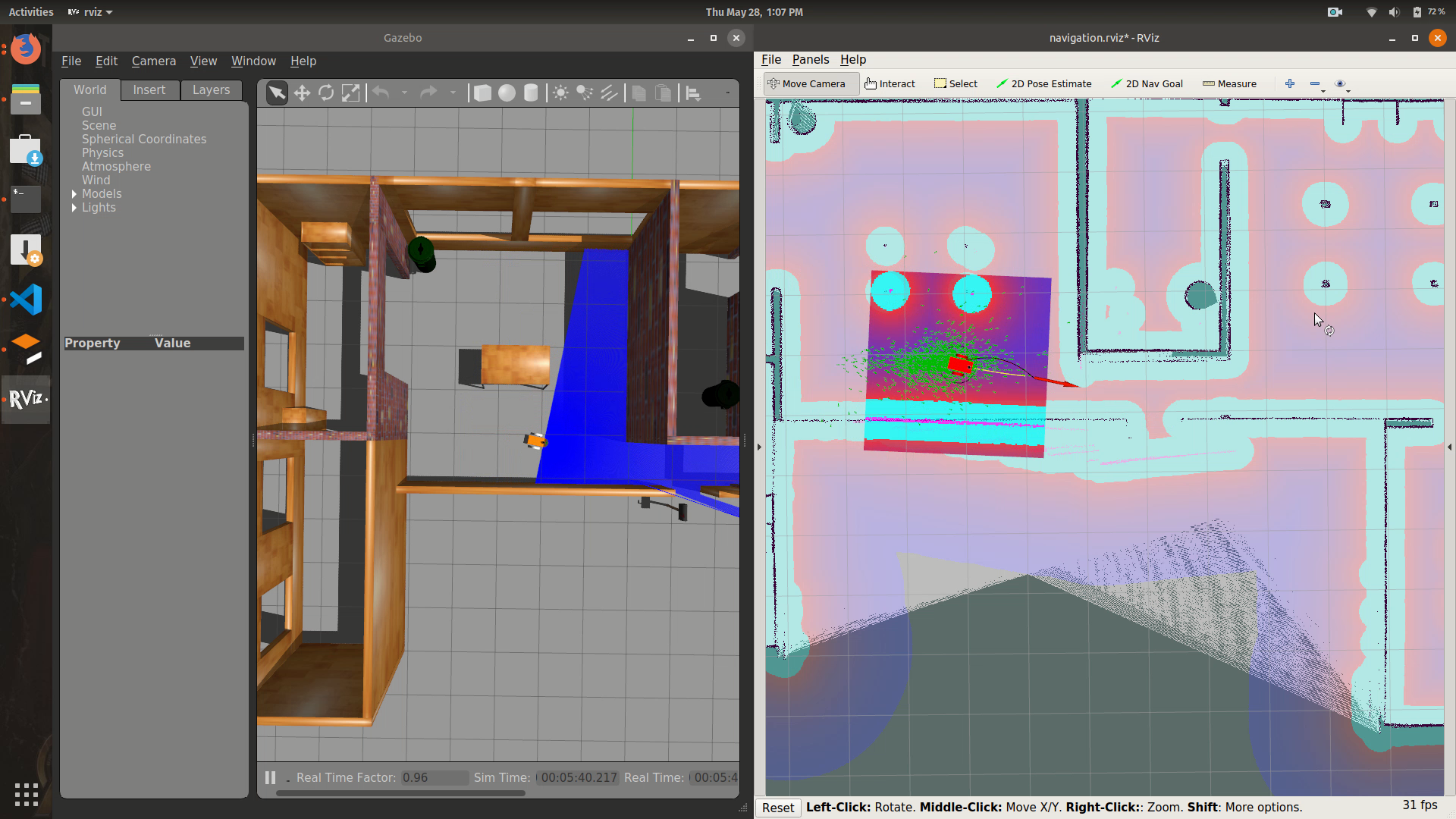
- To use your generated map, edit
/launch/amcl_move_base.launchand add map .yaml location and name to map_server node launch. - Load the robot in gazebo environment:
$ roslaunch diff_drive_bot gazebo.launch - Start the amcl, move_base and rviz nodes:
$ roslaunch diff_drive_bot amcl_move_base.launch - In rviz, click on 2D Pose Estimate and set initial pose estimate of the robot.
- To move to a goal, click on 2D Nav Goal to set your goal location and pose.
[Optional] Joystick Configuration
To make it easier to map environments, I added a joystick_teleop node to control the robot movement using my xbox controller. If you are using some other controller, you can easily map your buttons:
- Install the ROS joy package:
$ sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-joy - Connect your Jotstick to your machine and check if its detected:
$ ls /dev/input/ - If everything worked, your joystick should show up as jsX. In my case, it showed up as js1.
- Go to
/launch/joy_teleop_launch.launchand edit the dev parameter value to/dev/input/jsX. - Open the
joy_teleop.pyscript in the/scripts/folder. - Uncomment the print statements in the
joyCallback()function. - Save and run the script using:
$ roslaunch diff_drive_robot joy_teleop_launch.launch - You will see 2 arrays corresponding to the axes and buttons of your Joystick. Press each button/stick and find the index of your controls. Change the
joy_teleop.pyscript with your respective axes.