PyGPSClient
Current Status | Installation | Instructions | UBX Configuration | NTRIP Client | SPARTN Client | Socket Server / NTRIP Caster | GPX Track Viewer | Mapquest API Key | User-defined Presets | CLI Utilities | Known Issues | License | Author Information
PyGPSClient is a free, open-source, multi-platform graphical GNSS/GPS testing, diagnostic and UBX © (u-blox ™) device configuration application written entirely in Python and tkinter.
- Runs on any platform which supports a Python 3 interpreter (>=3.9) and tkinter (>=8.6) GUI framework, including Windows, MacOS, Linux and Raspberry Pi OS.
- Supports NMEA, UBX, RTCM3, NTRIP and SPARTN protocols.
- Capable of reading from a variety of GNSS data streams: Serial (USB / UART), Socket (TCP / UDP), binary data stream (terminal or file capture) and u-center (*.ubx) recording.
- Provides NTRIP and SPARTN client facilities.
- Can serve as an NTRIP base station with a compatible receiver (e.g. ZED-F9P).
- While not intended to be a direct replacement, the application supports most of the UBX configuration functionality in u-blox's Windows-only u-center © tool (only public-domain features are supported).
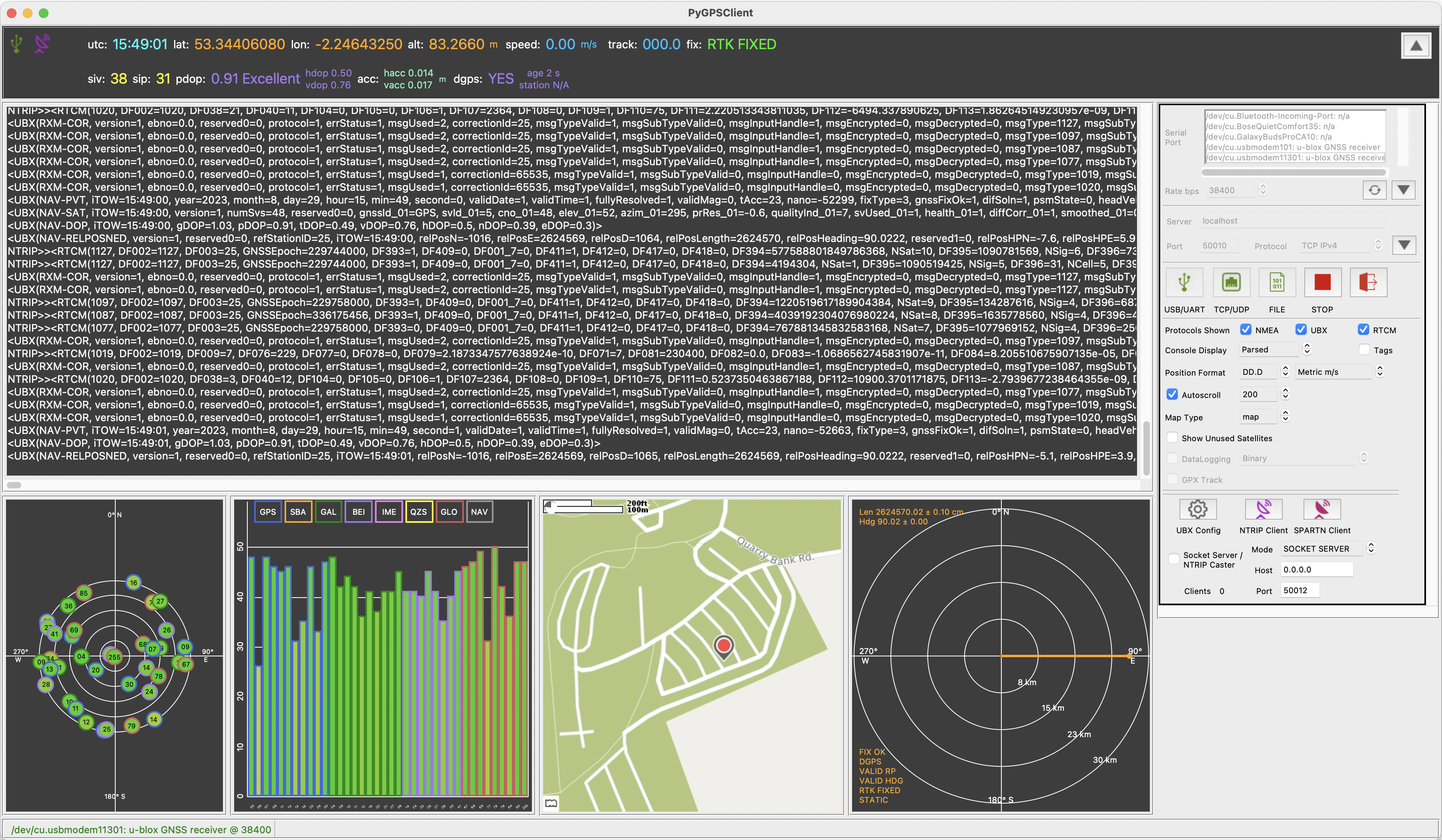
Screenshot showing mixed-protocol stream from u-blox ZED-F9P receiver, using PyGPSClient's NTRIP Client with a base station 26km to the west to achieve better than 2cm accuracy
The application can be installed using the standard pip Python package manager - see installation instructions below.
Current Status






The PyGPSClient home page is at PyGPSClient. For a general overview of GNSS, DGPS, RTK, NTRIP and SPARTN technologies and terminology, refer to GNSS Positioning - A Reviser. For practical tips on RTK, refer to Achieving cm Level GNSS Accuracy using RTK.
Sphinx API Documentation in HTML format is available at https://www.semuconsulting.com/pygpsclient.
Contributions welcome - please refer to CONTRIBUTING.MD.
For Bug reports, please use the template provided. For feature requests and general queries and advice, post a message to one of the PyGPSClient Discussions channels in the first instance.
This is an independent project and we have no affiliation whatsoever with u-blox.
Installation
The Quick Version
If you have an official Python >=3.9 with tkinter >=8.6 installed and the Python binaries folder is in your PATH, you can install PyGPSClient using pip:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pygpsclientand then run it by typing:
pygpsclientThe Longer Version
In the following, python3 & pip refer to the Python 3 executables. You may need to substitute python for python3, depending on your particular environment (on Windows it's generally python). It is strongly recommended that the Python 3 binaries and site_packages directories are included in your PATH (most standard Python 3 installation packages will do this automatically if you select the 'Add to PATH' option during installation).
Platform Dependencies
- Python 3.9 - 3.13¹
- Tk (tkinter) >= 8.6³
- Screen resolution >= 800 x 600; Ideally >= 1920 x 1080, though the main application window is resizeable and reconfigurable.
All platforms
¹ It is highly recommended to use the latest official Python.org installation package for your platform, rather than any pre-installed version.
- To enable automatic bounds detection in the Import Custom Map facility, the
rasteriolibrary must be installed:python3 -m pip install rasterio
Windows 10 or later:
Normally installs without any additional steps.
MacOS 12 or later:
³ The version of Python supplied with most Apple MacOS platforms includes a deprecated version of tkinter (8.5). Use an official Python.org installation package instead.
Linux (including Raspberry Pi OS):
⁴ Some Linux distributions may not include the necessary pip, tkinter or Pillow imaging libraries by default. They may need to be installed separately, e.g.:
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-tk python3-pil python3-pil.imagetk libjpeg-dev zlib1g-dev⁵ If you're compiling the latest version of Python 3 from source, you may also need to install tk-dev (or a similarly named package e.g. tk-devel) first. Refer to http://wiki.python.org/moin/TkInter for further details:
sudo apt install tk-dev⁶ On some 32-bit Linux platforms (e.g. Raspberry Pi OS 32), it may be necessary to install Rust compiler support and some additional build dependencies in order to install the cryptography library which PyGPSClient depends on to decrypt SPARTN messages (see pyspartn cryptography installation notes):
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
sudo apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev libffi-dev python3-dev pkg-configUser Privileges
To access the serial port on most Linux platforms, you will need to be a member of the
tty and/or dialout groups. Other than this, no special privileges are required.
usermod -a -G tty myuserInstall using pip
The easiest way to install the latest version of PyGPSClient is with pip:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pygpsclientIf required, PyGPSClient can also be installed into a virtual environment, e.g.:
python3 -m pip install --user --upgrade virtualenv
python3 -m virtualenv env
source env/bin/activate (or env\Scripts\activate on Windows)
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pygpsclient
...
deactivateThe pip installation process places an executable file pygpsclient in the Python binaries folder (../bin on Linux & MacOS, ..\Scripts on Windows).
Tip: The location of the relevant binaries folder can usually be found by executing one of the following commands:
Global installation:
python3 -c "import os,sysconfig;print(sysconfig.get_path('scripts'))"User installation:
python3 -c "import os,sysconfig;print(sysconfig.get_path('scripts',f'{os.name}_user'))"Typically:
- Windows:
C:\Users\myuser\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python3**\Scripts\pygpsclient.exe - MacOS:
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.**/bin/pygpsclient - Linux:
/home/myuser/.local/bin/pygpsclient - Virtualenv:
env/bin/pygpsclient(orenv\Scripts\pygpsclient.exeon Windows)
where ** signifies the Python version e.g. 3.12.
The PyGPSClient application may be started by double-clicking on this executable file from your file manager or, if the binaries folder is in your PATH, by opening a terminal and typing (all lowercase):
pygpsclientpygpsclient also accepts optional command line arguments for a variety of configurable parameters. These will override any saved configuration file settings. Type the following for help:
pygpsclient -hNB: If the Python 3 binaries folder is not in your PATH, you will need to add the fully-qualified path to the pygpsclient executable in the command above.
Creating A Desktop Application Launcher
The pip installation process does not automatically create a desktop application launcher, but this can be done manually:
Windows:
To create an application launcher for Windows, create a new Shortcut named PyGPSClient with the following properties (adapted for your particular environment):
- Target type: Application
- Target location: Scripts
- Target:
C:\Users\myuser\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python3**\Scripts\pygpsclient.exe - Start in:
C:\Users\myuser - Run: Minimized
and place this in the C:\Users\myuser\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs directory (you may need Administrator privileges to do this). To assign an icon to this shortcut, select Change Icon.. and Browse to the pygpsclient.ico file in the site_packages folder (e.g.C:\Users\myuser\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python3**\site-packages\pygpsclient\resources\pygpsclient.ico)
MacOS:
To create an application launcher for MacOS, use MacOS's Automator tool to create a "Run Shell Script" application and save this as PyGPSClient.app, e.g.
Shell: /bin/zsh
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.**/bin/pygpsclientTo assign an icon to this shortcut, right-click on the PyGPSClient entry in the Applications folder, select "Get Info" and drag-and-drop the pygpsclient.ico image file from the site-packages folder (e.g. /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.**/lib/python3.**/site-packages/pygpsclient/resources/pygpsclient.ico) to the default application icon at the top left of the "Get Info" panel.
Linux:
To create an application launcher for most Linux distributions, create a text file named pygpsclient.desktop with the following content (adapted for your particular environment) and copy this to the /home/myuser/.local/share/applications folder, e.g.
[Desktop Entry]
Type=Application
Terminal=false
Name=PyGPSClient
Icon=/home/myuser/.local/lib/python3.**/site-packages/pygpsclient/resources/pygpsclient.ico
Exec=/home/myuser/.local/bin/pygpsclientYou will need to logout and login for the launcher to take effect.
Instructions
-
To connect to a GNSS receiver via USB or UART port, select the device from the listbox, set the appropriate serial connection parameters and click
 . The application will endeavour to pre-select a recognised GNSS/GPS device but this is platform and device dependent. Press the
. The application will endeavour to pre-select a recognised GNSS/GPS device but this is platform and device dependent. Press the  button to refresh the list of connected devices at any point.
button to refresh the list of connected devices at any point. Rate bps(baud rate) is typically the only setting that might need adjusting, but tweaking thetimeoutsetting may improve performance on certain platforms. TheMsg Modeparameter defaults toGETi.e., periodic or poll response messages from a receiver. If you wish to parse streams of command or poll messages being sent to a receiver, set theMsg ModetoSETorPOLL. An optional serial or socket stream inactivity timeout can also be set (in seconds; 0 = no timeout). -
A custom user-defined serial port can also be passed via the json configuration file setting
"userport_s":, via environment variablePYGPSCLIENT_USERPORTor as a command line argument--userport. A special userport value of "ubxsimulator" invokes the experimentalpygnssutils.UBXSimulatorutility to emulate a GNSS NMEA/UBX serial stream. -
To connect to a TCP or UDP socket, enter the server URL and port, select the protocol (defaults to TCP) and click
 .
. -
To stream from a previously-saved binary datalog file, click
 and select the file type (
and select the file type (*.log, *.ubx, *.*) and path. PyGPSClient datalog files will be named e.g.pygpsdata-20220427114802.log, but any binary dump of an GNSS receiver output is acceptable, including*.ubxfiles produced by u-center. -
To disconnect from the data stream, click
 .
. -
Protocols Shown - Select which protocols to display; NMEA, UBX and/or RTCM3 (NB: this only changes the displayed protocols - to change the actual protocols output by the receiver, use the UBX Configuration Dialog).
-
Position Format and Units - Change the displayed position (D.DD / D.M.S / D.M.MM / ECEF) and unit (metric/imperial) formats.
-
Map Type - Select from "world", "map", "sat" or "custom". "map" and "sat" types require an Internet connection and free Mapquest API Key. "custom" offline map images can be imported and georeferenced using the Menu..Options..Import Custom Map facility.
-
Show Track - Tick to show track in map view. Map track will only be recorded while this checkbox is ticked.
-
Show Unused Satellites - Include or exclude satellites that are not used in the navigation solution (e.g. because their signal level is too low) from the graph and sky view panels.
-
DataLogging - Turn Data logging in the selected format on or off. You will be prompted to select the directory into which timestamped log files are saved.
-
GPX Track - Turn track recording (in GPX format) on or off. You will be prompted to select the directory into which timestamped GPX track files are saved.
-
To save the current configuration to a file, go to File..Save Configuration. NB: NTRIP and SPARTN client settings must be uploaded to the client handler (by clicking connect) before saving.
-
To load a saved configuration file, go to File..Load Configuration. The default configuration file location is
$HOME/pygpsclient.json. NB Any active serial or RTK connection must be stopped before loading a new configuration. -
Socket Server / NTRIP Caster facility with two modes of operation: (a) open, unauthenticated Socket Server or (b) NTRIP Caster (mountpoint =
pygnssutils). -
UBX Configuration Dialog, with the ability to send a variety of UBX CFG configuration commands to u-blox GNSS devices. This includes the facility to add user-defined commands or command sequences - see instructions under user-defined presets below. To display the UBX Configuration Dialog (only functional when connected to a UBX GNSS device via serial port), click
 , or go to Menu..Options..UBX Configuration Dialog.
, or go to Menu..Options..UBX Configuration Dialog. -
NTRIP Client facility with the ability to connect to a specified NTRIP caster, parse the incoming RTCM3 or SPARTN data and feed this data to a compatible GNSS receiver (requires an Internet connection and access to an NTRIP caster and local mountpoint). To display the NTRIP Client Configuration Dialog, click
 , or go to Menu..Options..NTRIP Configuration Dialog.
, or go to Menu..Options..NTRIP Configuration Dialog. -
SPARTN Client facility with the ability to configure an IP or L-Band SPARTN Correction source and SPARTN-compatible GNSS receiver (e.g. ZED-F9P) and pass the incoming correction data to the GNSS receiver (requires an Internet connection and access to a SPARTN location service). To display the SPARTN Client Configuration Dialog, click
 , or go to Menu..Options..SPARTN Configuration Dialog.
, or go to Menu..Options..SPARTN Configuration Dialog. -
GPX Track Viewer utility with elevation and speed profiles and track metadata (requires an Internet connection and free MapQuest API Key). To display the GPX Track viewer, go to Menu..Options..GPX Track Viewer.
| User-selectable 'widgets' | To show or hide the various widgets, go to Menu..View and click on the relevant hide/show option. |
|---|---|
 |
Expandable banner showing key navigation status information based on messages received from receiver. To expand or collapse the banner or serial port configuration widgets, click the |
 |
Configurable serial console widget showing all incoming data streams (both GNSS and RTK) in either parsed, binary or tabular hexadecimal formats. Double-click to copy contents of console to clipboard. The scroll behaviour and number of lines retained in the console can be configured via the settings panel. Supports user-configurable color tagging of selected strings for easy identification. Color tags are loaded from the "colortag_b": value (0 = disable, 1 = enable) and "colortags_l": list ([string, color] pairs) in your json configuration file (see example provided). If color is set to "HALT", streaming will halt on any match and a warning displayed. NB: color tagging does impose a small performance overhead - turning it off will improve console response times at very high transaction rates. |
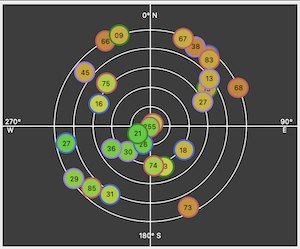 |
Skyview widget showing current satellite visibility and position (elevation / azimuth). Satellite icon borders are colour-coded to distinguish between different GNSS constellations. For consistency between NMEA and UBX data sources, will display GLONASS NMEA SVID (65-96) rather than slot (1-24). |
 |
Graphview widget showing current satellite reception (carrier-to-noise ratio or cnr). Double-click to toggle legend. |
 |
Map widget with various modes of display. Map Type = 'world': a static offline Mercator world map showing current global location. |
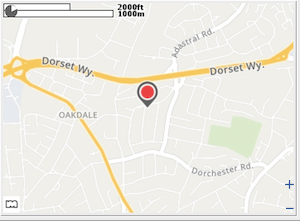 |
Map Type = 'map' or 'sat': Dynamic, online web map or satellite image via MapQuest API (requires an Internet connection and free Mapquest API Key). Left Click +/- to zoom in or out. Right click +/- to zoom in or out to maximum extent. By default, the web map will automatically refresh every 60 seconds (indicated by a small timer icon at the top left). The default refresh rate can be amended by changing the "mapupdateinterval_n": value in your json configuration file, but NB the facility is not intended to be used for real-time navigation. Double-click anywhere in the map to immediately refresh. |
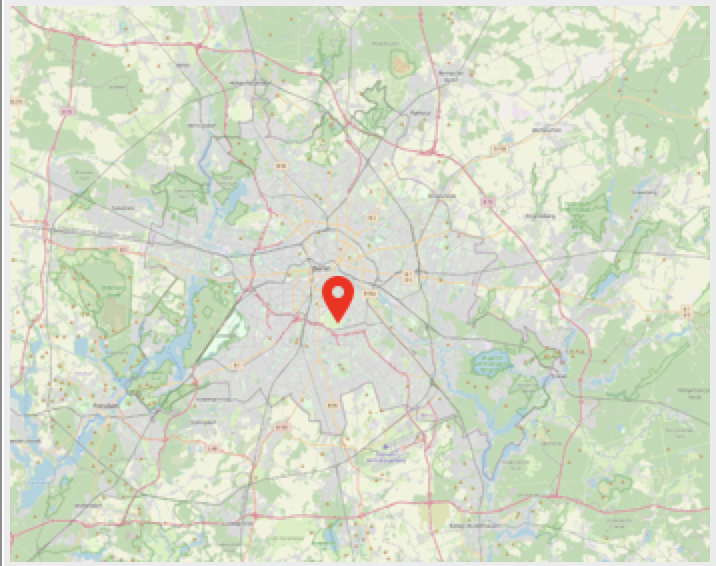 |
Map Type = 'custom': One or more user-defined custom offline maps can be imported using the Menu..Options..Import Custom Map facility, or by manually setting the usermaps_l field in the json configuration file. The usermaps_l setting represents a list of map paths and bounding boxes in the format ["path to map image", [minlat, minlon, maxlat, maxlon]] - see example configuration file. Map images must be a supported format and use a standard WGS84 Web Mercator projection e.g. EPSG:4326. |
 |
Import Custom Map dialog. Click - select Show Options to select any file suffix.*). If therasterio` library is installed and the image is georeferenced (e.g. using QGIS), the map extent will be automatically extracted - otherwise it must be entered manually. Import the custom map path anad extent settings by clicking |
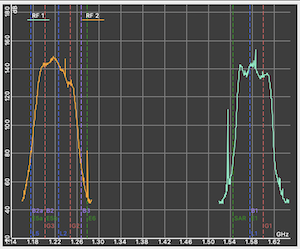 |
Spectrum widget showing a spectrum analysis chart (GNSS receiver must be capable of outputting UBX MON-SPAN messages). Clicking anywhere in the spectrum chart will display the frequency and decibel reading at that point. Double-clicking anywhere in the chart will toggle the GNSS frequency band markers (L1, G2, etc.) on or off. Right-click anywhere in the chart to capture a snapshot of the spectrum data, which will then be superimposed on the live data. Double-right-click to clear snapshot. NB: Some receivers (e.g. NEO-F10N) will not output the requisite MON-SPAN messages unless the port baud rate is at least 57,600. |
 |
System Monitor widget showing device cpu, memory and I/O utilisation (GNSS receiver must be capable of outputting UBX MON-SYS and/or MON-COMMS messages). Tick checkbox to toggle between actual (cumulative) I/O stats and pending I/O. |
 |
Scatterplot widget showing variability in position reporting over time. (Optional) Enter fixed reference position. Select Average to center plot on dynamic average position (displayed at top left), or Fixed to center on fixed reference position (if entered). Check Autorange to set plot range automatically. Set the update interval (e.g. 4 = every 4th navigation solution). Use the range slider or mouse wheel to adjust plot range. Right-click to set fixed reference point to the current mouse cursor position. Double-click clear existing plot. The default center mode, autorange, update increment, scale index and fixed reference position settings can be stored in the json configuration file as scattercenter_s/scatterautorange_b/scatterinterval_n/scatterscale_n/scatterlat_f/scatterlon_f. |
 |
Rover widget plots the relative 2D position, track and status information for the roving receiver in a fixed or moving base / rover RTK configuration. Can also display relative position of NTRIP mountpoint and receiver in a static RTK configuration. Double-click to clear existing plot. (GNSS rover receiver must be capable of outputting UBX NAV-RELPOSNED messages.) |
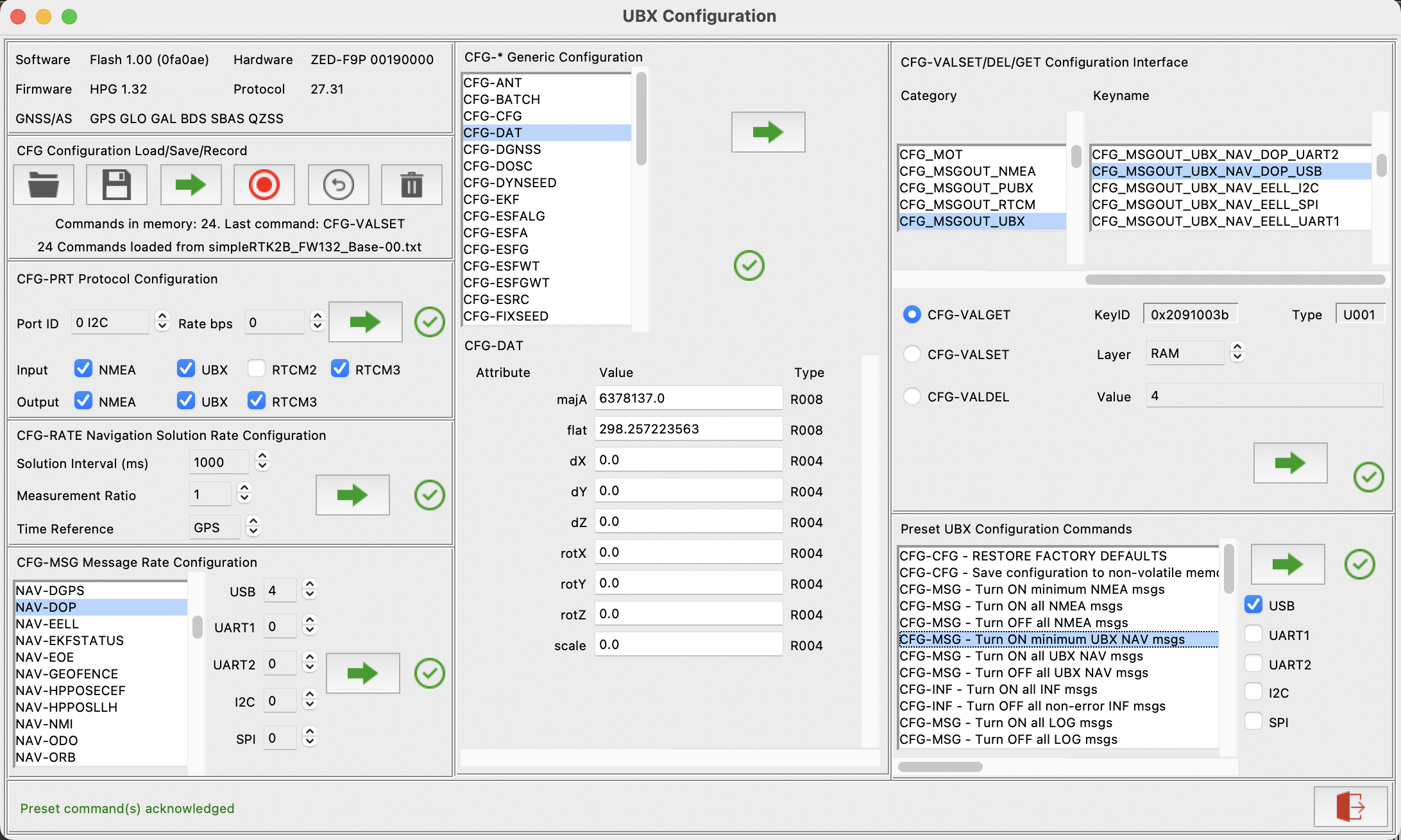
UBX Configuration Facilities
Pre-Requisites:
- u-blox GNSS receiver e.g. u-blox NEO-M8S, ZED-F9P, etc. connected to the workstation via USB or UART port.
Instructions:
The UBX Configuration Dialog currently provides the following UBX configuration panels:
- Version panel shows current device hardware/firmware versions (via MON-VER and MON-HW polls).
- CFG Configuration Load/Save/Record facility. This allows users to record
 a sequence of UBX CFG configuration commands, and to save
a sequence of UBX CFG configuration commands, and to save  this recording to a file (as binary CFG- messages). Saved files can be reloaded
this recording to a file (as binary CFG- messages). Saved files can be reloaded  and the configuration commands replayed
and the configuration commands replayed  . This provides a means to easily reproduce a given sequence of configuration commands, or copy a saved configuration between compatible devices. The Configuration Load/Save/Record facility can accept configuration files in either binary UBX format (*.ubx) or u-center text format (*.txt). Files saved using the ubxsave CLI utility (installed via the
. This provides a means to easily reproduce a given sequence of configuration commands, or copy a saved configuration between compatible devices. The Configuration Load/Save/Record facility can accept configuration files in either binary UBX format (*.ubx) or u-center text format (*.txt). Files saved using the ubxsave CLI utility (installed via the pygnssutilslibrary) can also be reloaded and replayed. Tip: The contents of a binary config file can be reviewed using PyGPSClient's file streaming facility, BUT* remember to set theMsg Modein the Settings panel toSETrather than the defaultGET .
. - Protocol Configuration panel (CFG-PRT) sets baud rate and inbound/outbound protocols across all available ports.
- Solution Rate panel (CFG-RATE) sets navigation solution interval in ms (e.g. 1000 = 1/second) and measurement ratio (ratio between the number of measurements and the number of navigation solutions, e.g. 5 = five measurements per navigation solution).
- For each of the panels above, clicking anywhere in the panel background will refresh the displayed information with the current configuration.
- Message Rate panel (CFG-MSG) sets message rates per port for UBX and NMEA messages. Message rate is relative to navigation solution frequency e.g. a message rate of '4' means 'every 4th navigation solution' (higher = less frequent).
- Generic configuration panel (CFG-*) providing structured updates for a range of legacy CFG- configuration commands for pre-Generation 9+ devices. Note: 'X' (byte) type attributes can be entered as integers or hexadecimal strings e.g. 522125312 or 0x1f1f0000.
- Configuration Interface widget (CFG-VALSET, CFG-VALDEL and CFG-VALGET) queries and sets configuration for Generation 9+ devices e.g. NEO-M9, ZED-F9P, etc.
- Preset Commands widget supports a variety of preset and user-defined commands - see user defined presets. The port checkboxes (USB, UART1, etc.) determine which device port(s) any preset message rate commands apply to (assuming the selected ports are physically implemented on the device). The selected port(s) may be saved as configuration parameter
defaultport_se.g. "USB,UART1".
An icon to the right of each 'SEND'
![]() button indicates the confirmation status of the configuration command;
(pending i.e. awaiting confirmation
button indicates the confirmation status of the configuration command;
(pending i.e. awaiting confirmation ![]() ,
confirmed
,
confirmed ![]() or
warning
or
warning ![]() ).
).
Note:
- The UBX protocol does not support synchronous command acknowledgement or unique confirmation IDs. Asynchronous command and poll acknowledgements and responses can take several seconds at high message transmission rates, or be discarded altogether if the device's transmit buffer is full (txbuff-alloc error). To ensure timely responses, try increasing the baud rate and/or temporarily reducing transmitted message rates using the configuration commands provided.
- A warning icon (typically accompanied by an ACK-NAK response) is usually an indication that one or more of the commands sent is not supported by your receiver.
NTRIP Client Facilities
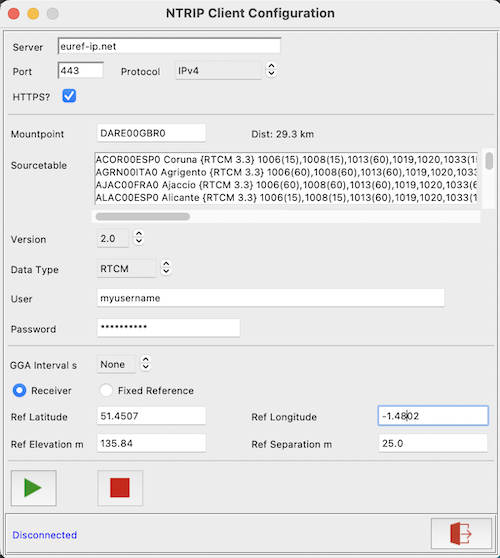
The NTRIP Configuration utility allows users to receive and process NTRIP RTK Correction data from an NTRIP caster to achieve cm level location accuracy. The facility can be accessed by clicking ![]() or selecting Menu..Options..NTRIP Configuration Dialog.
or selecting Menu..Options..NTRIP Configuration Dialog.
Pre-Requisites:
- NTRIP-compatible GNSS receiver e.g. u-blox ZED-F9P
- Internet access
- URL of NTRIP caster
- Login credentials for the NTRIP caster (where required)
- Name of local MOUNTPOINT (if not using PyGPSClient's automatic mountpoint locator)
- Data type (normally RTCM but some services output data in SPARTN format)
Instructions:
- Enter the required NTRIP server URL (or IP address), port (defaults to 2101) and HTTPS flag (defaults to 'yes' for ports 443/2102, 'no' for all else). For services which require authorisation, enter your login username and password.
- Select the Data Type (defaults to RTCM, but can be set to SPARTN).
- To retrieve the sourcetable, leave the mountpoint field blank and click connect (response may take a few seconds). The required mountpoint may then be selected from the list, or entered manually. Where possible,
PyGPSClientwill automatically identify the closest mountpoint to the current location. - For NTRIP services which require client position data via NMEA GGA sentences, select the appropriate sentence transmission interval in seconds. The default is 'None' (no GGA sentences sent). A value of 10 or 60 seconds is typical.
- If GGA sentence transmission is enabled, GGA sentences can either be populated from live navigation data (assuming a receiver is connected and outputting valid position data) or from fixed reference settings entered in the NTRIP configuration panel (latitude, longitude, elevation and geoid separation - all four reference settings must be provided).
- To connect to the NTRIP server, click
 . To disconnect, click
. To disconnect, click  .
. - If NTRIP data is being successfully received, the banner 'dgps:' status indicator should change to 'YES' and indicate the age and reference station of the correction data (where available)
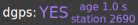 . Note that DGPS status is typically maintained for up to 60 seconds after loss of correction signal.
. Note that DGPS status is typically maintained for up to 60 seconds after loss of correction signal. - Some NTRIP services may output RTCM3 or SPARTN correction messages at a high rate, flooding the GUI console display. To suppress these messages in the console, de-select the 'RTCM' or'SPARTN' options in 'Protocols Shown' - the RTCM3 or SPARTN messages will continue to be processed in the background.
Below is a illustrative NTRIP DGPS data log, showing:
- Outgoing NMEA GPGGA (client position) sentence.
- Incoming RTCM3 correction messages; in this case - 1006 (Ref station ARP (DF003=2690) with antenna height), 1008 (Antenna descriptor), 1033 (Receiver descriptor), 1075 (GPS MSM5), 1085 (GLONASS MSM5), 1095 (Galileo MSM5), 1125 (BeiDou MSM5) and 1230 (GLONASS Code-Phase Biases)
- Corresponding UBX RXM-RTCM acknowledgements generated by the u-blox ZED-F9P receiver, confirming message type, valid checksum (crcFailed=0), successful use (msgUsed=2) and reference station ARP (refStation=2690).

NB: Please respect the terms and conditions of any remote NTRIP service used with this facility. For testing or evaluation purposes, consider deploying a local SNIP LITE server. Inappropriate use of an NTRIP service may result in your account being blocked.
SPARTN Client Facilities
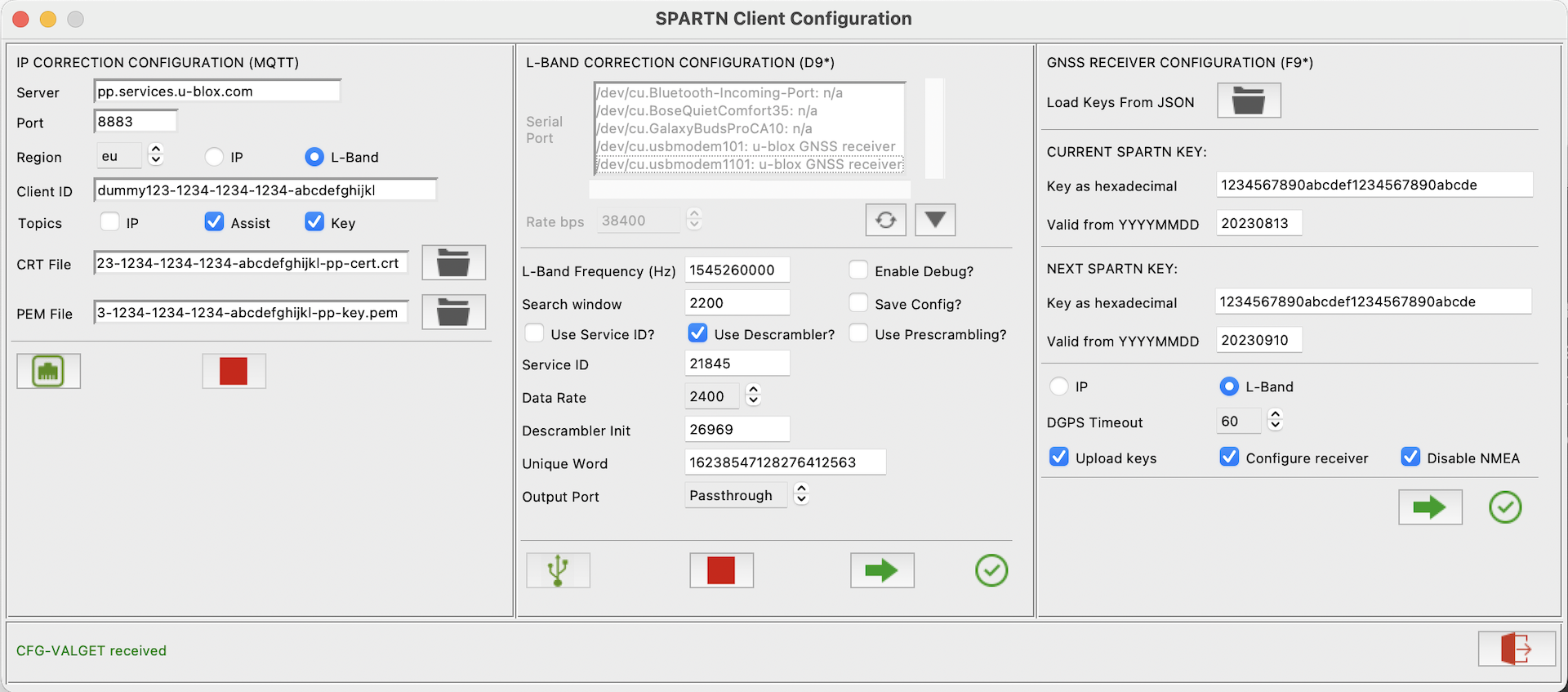
The SPARTN Configuration utility allows users to receive and process SPARTN RTK Correction data from an IP or L-Band source to achieve cm level location accuracy. It provides three independent configuration sections, one for IP Correction (MQTT), one for L-Band Correction (e.g. NEO-D9S) and a third for the GNSS receiver (e.g. ZED-F9P).
The facility can be accessed by clicking ![]() or selecting Menu..Options..SPARTN Configuration Dialog.
or selecting Menu..Options..SPARTN Configuration Dialog.
Pre-Requisites:
NB: SPARTN data from proprietary subscription services like Thingstream PointPerfect (MQTT or L-Band) is encrypted. While it is not necessary for PyGPSClient to decrypt the data prior to sending it to the GNSS receiver (the receiver's own firmware will perform the necessary decryption provided the relevant keys have been uploaded), if you wish to see the decrypted data in the PyGPSClient console it will be necessary to provide current decryption keys via the spartndecode_b and spartnkey_s settings in the json configuration file. Note that these keys are typically only valid for a 4 week period and will require regular updating. See pyspartn Encrypted Payloads for further details.
-
IP Correction (MQTT Client):
- Internet access
- Subscription to a suitable MQTT SPARTN location service e.g. u-blox / Thingstream PointPerfect IP or L-band, which should provide the following details:
- Server URL e.g.
pp.services.u-blox.com - Client ID (which can be stored in the
"mqttclientid_s":json configuration file setting or via environment variableMQTTCLIENTID) - Encryption certificate (
*.crt) and key (*.pem) files required to access the SPARTN service via an encrypted HTTPS connection. If these are placed in the user's HOME directory using the location service's standard naming convention, PyGPSClient will find them automatically. - Region code - select from
us,eu,jp,krorau. - Source - select from either
IPorL-Band(NB: the 'L-Band' MQTT mode provides decryption keys, Assist Now data and L-Band frequency information, but the correction data itself arrives via the L-Band receiver below). - A list of published topics. These typically include:
/pp/ip/region- binary SPARTN correction data (SPARTN-1X-HPAC / OCB / GAD*) for the selected region, for IP sources only./pp/ubx/mga- UBX MGA AssistNow ephemera data for each constellation./pp/ubx/0236/ipor/pp/ubx/0236/Lb- UBX RXM-SPARTNKEY messages containing the IP or L-band decryption keys to be uploaded to the GNSS receiver./pp/frequencies/Lb- json message containing each region's L-band transmission frequency - currentlyusoreu(this is automatically enabled whenL-Bandis selected).
- Server URL e.g.
-
L-BAND Correction (D9* Receiver):
- SPARTN L-Band correction receiver e.g. u-blox NEO-D9S.
- Suitable Inmarsat L-band antenna and good satellite reception on regional frequency (NB: standard GNSS antenna may not be suitable).
- Subscription to L-Band location service e.g. u-blox / Thingstream PointPerfect, which should provide the following details:
- L-Band frequency (also available via
/pp/frequencies/LbMQTT topic) - Search window
- Use Service ID?
- Use Descrambling?
- Use Prescrambling?
- Service ID
- Data Rate
- Descrambler Init
- Unique Word
- L-Band frequency (also available via
-
GNSS Receiver:
- SPARTN-compatible GNSS receiver e.g. u-blox ZED-F9P
- Subscription to either IP and/or L-Band location service(s) e.g. e.g. u-blox / Thingstream PointPerfect, which should provide the following details:
- Current and Next IP or L-band decryption Keys in hexadecimal format. These allow the receiver to decrypt the SPARTN message payloads.
- Valid From dates in YYYYMMDD format (keys normally valid for 4 week period).
Instructions:
IP Correction Configuration (MQTT)
- Enter your MQTT Client ID (or set it up beforehand as *.json configuration setting
"mqttclientid_s":or via environment variableMQTTCLIENTID). - Select the path to the MQTT
*.crtand*.pemfiles provided by the location service (PyGPSClient will use the user's HOME directory by default). - Select the required region and subscription mode (
IPorL-Band). - Select the required topics:
- IP - this is the raw SPARTN correction data as SPARTN-1X-HPAC / OCB / GAD* messages (required for IP; must be unchecked for L-Band).
- Assist - this is Assist Now data as UBX MGA-* messages.
- Key - this is the SPARTN IP or L-band decryption keys as a UBX RXM-SPARTNKEY message.
- To connect to the MQTT server, click
 . To disconnect, click
. To disconnect, click  .
.
L-Band Correction Configuration (D9*)
- To connect to the Correction receiver, select the receiver's port from the SPARTN dialog's Serial Port listbox and click
 . To disconnect, click
. To disconnect, click  .
. - Select the required Output Port - this is the port used to connect the Correction receiver to the GNSS receiver e.g. UART2 or I2C.
- If both Correction and GNSS receivers are connected to the same PyGPSClient workstation (e.g. via separate USB ports), it is possible to run the utility in Output Port = 'Passthough' mode, whereby the output data from the Correction receiver (UBX
RXM-PMPmessages) will be automatically passed through to the GNSS receiver by PyGPSClient, without the need to connect the two externally. - To enable INF-DEBUG messages, which give diagnostic information about current L-Band reception, click 'Enable Debug?'.
- To save the configuration to the device's persistent storage (Battery-backed RAM, Flash or EEPROM), click 'Save Config?'. This only has to be done once for a given region.
- Once connected, click
 to upload the configuration. The utility will send the relevant configuration command(s) to the Correction receiver and poll for an acknowledgement.
to upload the configuration. The utility will send the relevant configuration command(s) to the Correction receiver and poll for an acknowledgement.
GNSS Receiver Configuration (F9*)
- Connect to the GNSS receiver first by clicking
 on the main PyGPSClient settings panel.
on the main PyGPSClient settings panel. - If you are subscribing to the MQTT SPARTNKEY (
/pp/ubx/0236/ipor/pp/ubx/0236/Lb) topic, the decryption key and validity date details will be entered automatically on receipt of a UBX RXM-SPARTNKEY message (which may take a few seconds after connecting). Alternatively, they can be uploaded from the service provider's JSON file, or entered manually as follows: - Enter the current and next decryption keys in hexadecimal format e.g.
0102030405060708090a0b0c0d0e0f10. The keys are normally 16 bytes long, or 32 hexadecimal characters. - Enter the supplied Valid From dates in
YYYYMMDDformat. NB: These are Valid From dates rather than Expiry dates. If the location service provides Expiry dates, subtract 4 weeks from these to get the Valid From dates. - Select 'DGPS Timeout', 'Upload keys', 'Configure receiver' and 'Disable NMEA' options as required.
- Select the SPARTN correction source - either
IPorL-Band. - To reduce traffic volumes, you can choose to disable NMEA messages from the receiver. A minimal set of UBX NAV messages will be enabled in their place.
- Click
 to upload the configuration. The utility will send the relevant configuration command(s) to the receiver and poll for an acknowledgement.
to upload the configuration. The utility will send the relevant configuration command(s) to the receiver and poll for an acknowledgement.
Below is a illustrative SPARTN DGPS data log, showing:
- Incoming SPARTN correction messages (SPARTN-1X-HPAC high-precision atmosphere corrections; SPARTN-OCB orbit / clock / bias corrections; SPARTN-1X-GAD geographic area definitions).
- Outgoing UBX RXM-COR confirmation messages from receiver showing that the SPARTN data has been received and decrypted OK.
Socket Server / NTRIP Caster Facilities
The Socket Server / NTRIP Caster facility is capable of operating in either of two modes;
- SOCKET SERVER - an open, unauthenticated TCP socket server available to any socket client including, for example, another instance of PyGPSClient or the
gnssdumpCLI utility. In this mode it will broadcast the host's currently connected GNSS data stream (NMEA, UBX, RTCM3). The default port is 50012. - NTRIP CASTER - a simple implementation of an authenticated NTRIP caster available to any NTRIP client including, for example, u-blox's legacy u-center NTRIP client, BKG's NTRIP Client (BNC), the PyGPSClient NTRIP Client facility or the
gnssntripclientCLI utility. Login credentials for the NTRIP caster are set via the"ntripcasteruser_s":and"ntripcasterpassword_s":settings in the *.json confirmation file (they can also be set via PyGPSClient command line arguments--ntripcasteruser,--ntripcasterpassword, or by setting environment variablesNTRIPCASTER_USER,NTRIPCASTER_PASSWORD). Default settings are as follows: bind address: 0.0.0.0, port: 2101, mountpoint: pygnssutils, user: anon, password: password.
By default, the server/caster binds to the host address '0.0.0.0' (IPv4) or '::' (IPv6) i.e. all available IP addresses on the host machine. This can be overridden via the settings panel or a host environment variable PYGPSCLIENT_BINDADDRESS. A label on the settings panel indicates the number of connected clients, and the server/caster status is indicated in the topmost banner: running with no clients: ![]() , running with clients:
, running with clients: ![]() .
.
Pre-Requisites:
- Running in NTRIP CASTER mode is predicated on the host being connected to an RTK-compatible GNSS receiver (e.g. u-blox ZED-F9P) operating in Base Station mode (either
FIXEDorSURVEY_IN) and outputting the requisite RTCM3 message types (1005, 1077, 1087, 1097, 1127 and 1230). - It may be necessary to add a firewall rule and/or enable port-forwarding on the host machine or router to allow remote traffic on the specified address:port.
Instructions:
SOCKET SERVER MODE
- Select SOCKET SERVER mode and (if necessary) enter the host IP address and port.
- Check the Socket Server/NTRIP Caster checkbox to activate the server.
- To stop the server, uncheck the checkbox.
NTRIP CASTER MODE
- Select NTRIP CASTER mode and (if necessary) enter the host IP address and port.
- An additional expandable panel is made available to allow the user to configure a connected RTK-compatible u-blox receiver (e.g. ZED-F9P) to operate in either
FIXEDorSURVEY-INBase Station mode (NB: parameters can only be amended while the caster is stopped). If 'Configure Base Station' is checked, the selected configuration will be applied to the connected receiver once the caster is activated. - NMEA messages can be suppressed by checking 'Disable NMEA'. A minimum set of UBX messages will be output in their place.
- NTRIP client login credentials are set via the user and password fields.
- Check the Socket Server/NTRIP Caster checkbox to activate the caster.
- To stop the caster, uncheck the checkbox.
Base Station Configuration
| Configuration Settings | Base Station Mode |
|---|---|
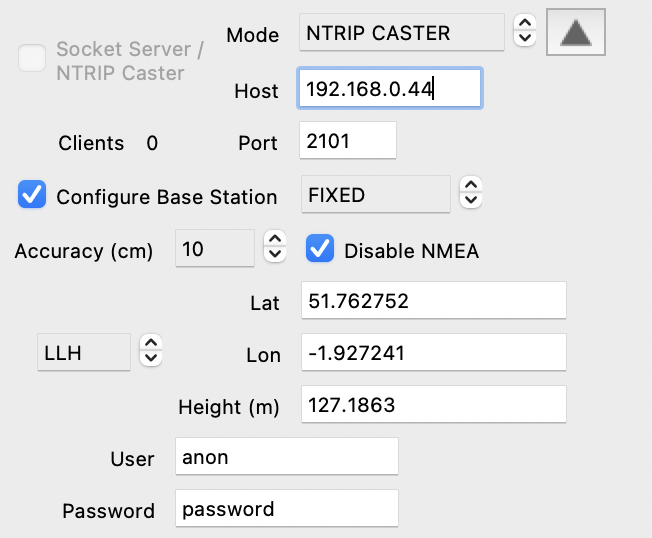 |
FIXED. In this mode, the known base station coordinates (Antenna Reference Point or ARP) are specified in either LLH or ECEF (X,Y,Z) format. The coordinates are pre-populated with the receiver's current navigation solution (if available), but these can (and normally should) be overridden with accurately surveyed values. If the coordinates are accepted, the UBX Fix status will change to TIME ONLY and the receiver will start outputting RTCM 1005 (ARP location) messages. |
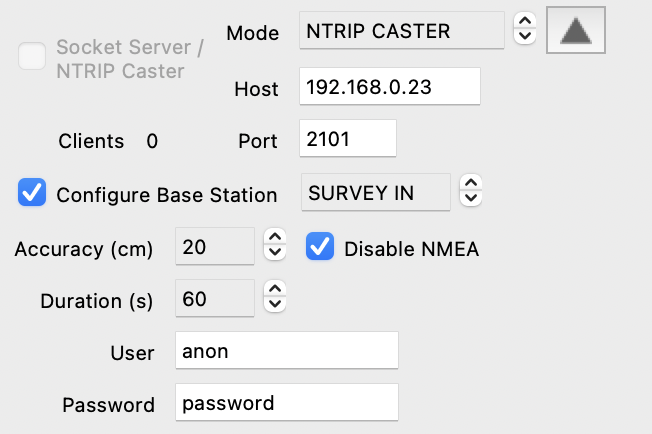 |
SURVEY-IN. In this mode, the base station coordinates are derived from the receiver's current navigation solution, provided the prescribed level of accuracy is met within the specified survey duration. If the survey is successful, the UBX NAV-SVIN monitoring message will indicate valid=1, active=0, the UBX Fix status will change to TIME ONLY and the receiver will start outputting RTCM 1005 (ARP location) messages. |
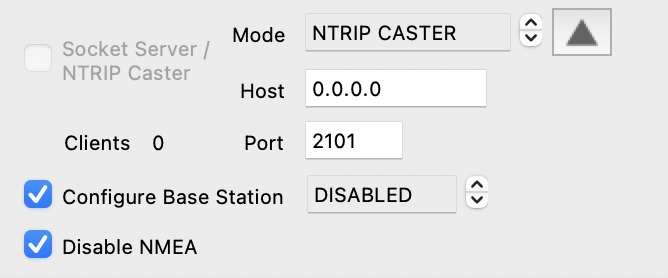 |
DISABLED. Disable base station operation. |
NB: To operate effectively as an RTK Base Station, antenna positioning is of paramount importance. Refer to the following links for advice:
GPX Track Viewer
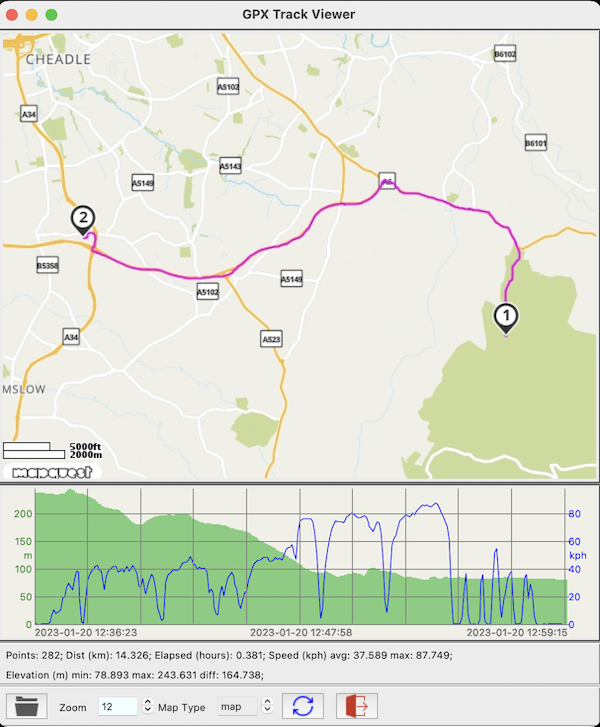
GPX Track Viewer screenshot
The GPX Track Viewer can display any valid GPX file containing trackpoints (<trkpt>..</trkpt> elements) against either an "custom" offline map image, or an online MapQuest "map" or "sat" view. The "map" and "sat" options require a free MapQuest API key. The Y axis scales will reflect the current choice of units (metric or imperial). Click ![]() to refresh the display after any changes (e.g. resizing, zooming or change of units). In "custom" view, zoom is not functional, and mouse right-click will show the position at the mouse cursor.
to refresh the display after any changes (e.g. resizing, zooming or change of units). In "custom" view, zoom is not functional, and mouse right-click will show the position at the mouse cursor.
MapQuest API Key
Pre-Requisites:
To use the optional dynamic web-based mapview or GPX Track Viewer facilities, you need to request and install a MapQuest API key.
Note that, from January 15th 2024, MapQuest require payment card details for the use of this API, but the first 15,000 transactions/month remain free. Usage above 15,000 transactions/month is charged at $.0045 per transaction. See FAQ for further information.
For this reason, the map refresh rate is intentionally limited to 1/minute to avoid exceeding the free transaction limit under normal use. NB: this facility is not* intended to be used for real time navigational purposes.
Instructions:
Once you have received the API key (a 32-character alphanumeric string), you can (in order of precedence):
- Copy it to the
"mqapikey_s":value in your json configuration file (see example provided). - Create an environment variable named
MQAPIKEY(all upper case) and set this to the API key value. It is recommended that this is a User variable rather than a System/Global variable. - Pass it via command line argument
--mqapikey.
*The web map refresh rate can be amended if required by changing the mapupdateinterval_n: value in your json configuration file.
User Defined Presets
The UBX Configuration Dialog includes the facility to send user-defined UBX configuration messages or message sequences to the receiver. These can be set up by adding
appropriate comma-delimited message descriptions and payload definitions to the "ubxpresets_l": list in your json configuration file (see example provided). The message definition comprises a free-format text description (avoid embedded commas)
followed by one or more pyubx2 UBXMessage constructors, i.e.
- message class as a string e.g.
CFG(must be a valid class from pyubx2.UBX_CLASSES) - message id as a string e.g.
CFG-MSG(must be a valid id from pyubx2.UBX_MSGIDS) - payload as a hexadecimal string e.g.
f004010100010100(leave blank for null payloads e.g. most POLL messages) - mode as an integer (
1= SET,2= POLL)
(payload as hex string can be obtained from a UBXMessage created using the pyubx2 library thus: msg.payload.hex())
Multiple commands can be concatenated on a single line. Illustrative examples are shown below:
"ubxpresets_l": [
"Force HOT Reset (!!! Will require reconnection !!!), CFG, CFG-RST, 00000000, 1",
"Force WARM Reset (!!! Will require reconnection !!!), CFG, CFG-RST, 00010000, 1",
"Force COLD Reset (!!! Will require reconnection !!!), CFG, CFG-RST, ffff0000, 1",
"Stop GNSS, CFG, CFG-RST, 00000800, 1",
"Start GNSS, CFG, CFG-RST, 00000900, 1",
"Enable NMEA UBX00 & UBX03 sentences, CFG, CFG-MSG, f100010100010100, 1, CFG, CFG-MSG, f103010100010100, 1",
"Poll NEO-9 UART1/2 baud rates, CFG, CFG-VALGET, 000000000100524001005340, 2",
"Poll NEO-9 Message Rates, CFG, CFG-VALGET, 00000000ffff9120, 2, CFG, CFG-VALGET, 00004000ffff9120, 2, CFG, CFG-VALGET, 00008000ffff9120, 2",
"Set ZED-F9P RTCM3 MSGOUT Basestation, CFG, CFG-VALSET, 00010000c002912001cf02912001d4029120011b03912001d902912001060391200101039120018403912001, 1",
"Set ZED-F9P to Survey-In Timing Mode Basestation, CFG, CFG-VALSET, 0001000001000320011100034070110100100003405a0000008b00912001, 1",
"Poll Receiver Software Version, MON, MON-VER, , 2",
"Poll Datum, CFG, CFG-DAT, , 2",
"Poll GNSS config, CFG, CFG-GNSS, , 2",
"Poll NMEA config, CFG, CFG-NMEA, , 2",
"Poll Satellite-based Augmentation, CFG, CFG-SBAS, , 2",
"Poll Receiver Management, CFG, CFG-RXM, , 2",
"Poll RXM-SPARTN-KEY, RXM, RXM-SPARTN-KEY, , 2",
"Poll RXM-COR, RXM, RXM-COR, , 2",
"Poll Navigation Mode, CFG, CFG-NAV5, , 2",
"Poll Expert Navigation mode, CFG, CFG-NAVX5, , 2",
"Poll Geofencing, CFG, CFG-GEOFENCE, , 2",
"Poll Timepulse, CFG, CFG-TP5, , 2",
"Set NEO-M8T Timepulse to 8 MHz, CFG, CFG-TP5, 000100003200000000127a0000127a003200000032000000000000006f000000, 1",
]Command Line Utilities
The pygnssutils library which underpins many of the functions in PyGPSClient also incorporates command line versions of these functions:
gnssdumpCLI utility. This is essentially a configurable input/output wrapper around thepyubx2.UBXReaderclass with flexible message formatting and filtering options for NMEA, UBX and RTCM3 protocols.gnssserverCLI utility. This implements a TCP Socket Server for GNSS data streams which is also capable of being run as a simple NTRIP Server.gnssntripclientCLI utility. This implements a simple NTRIP Client which receives RTCM3 correction data from an NTRIP Server and (optionally) sends this to a designated output stream.gnssmqttclientCLI utility. This implements a simple SPARTN IP (MQTT) Client which receives SPARTN and UBX correction data from a SPARTN IP location service (e.g. u-blox / Thingstream PointPerfect) and (optionally) sends this to a designated output stream.ubxsaveCLI utility. This saves a complete set of configuration data from any Generation 9+ u-blox device (e.g. NEO-M9N or ZED-F9P) to a file. The file can then be reloaded to any compatible device using theubxloadutility.ubxloadCLI utility. This reads a file containing binary configuration data and loads it into any compatible Generation 9+ u-blox device (e.g. NEO-M9N or ZED-F9P).ubxsetrateCLI utility. A simple utility which sets NMEA or UBX message rates on u-blox GNSS receivers.
For further details, refer to the pygnssutils homepage at https://github.com/semuconsulting/pygnssutils.
--
Known Issues
None
License
BSD 3-Clause License
Copyright © 2020, SEMU Consulting All rights reserved.
Application icons from iconmonstr ©.
Author Information
semuadmin@semuconsulting.com
PyGPSClient is maintained entirely by unpaid volunteers. It receives no funding from advertising or corporate sponsorship. If you find the utility useful, please consider sponsoring the project with the price of a coffee...






